外卖平台及移动端开发–优化篇
一、使用git管理代码
使用Gitee作为远程仓库:https://gitee.com/
1、创建远程仓库
2、IDEA连接远程仓库
1. 在gitee中获取远程仓库的https地址
1. 在IDEA中通过VCS连接git远程仓库
3、配置.gitignore文件
4、提交文件并推送
5、创建新分支v1.0并推送
在IDEA中创建新分支v1.0,便于后面代码优化检测
二、缓存优化
使用Redis缓存数据库内容,减少对数据库的访问
1、环境搭建
1.1 添加maven坐标
pom文件中添加
1
2
3
4
| <dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-redis</artifactId>
</dependency>
|
1.2 yml文件配置
在application.yml文件中添加redis相关配置:
1
2
3
4
5
6
| string:
redis:
host: localhost
port: 6379
password:
database: 0
|
1.3 添加配置类RedisConfig
在config包下添加配置类RedisConfig,以解决key的序列化冗长问题
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
| package com.itreggie.reggie.config;
import org.springframework.cache.annotation.CachingConfigurerSupport;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.data.redis.connection.RedisConnectionFactory;
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.RedisTemplate;
import org.springframework.data.redis.serializer.StringRedisSerializer;
@Configuration
public class RedisConfig extends CachingConfigurerSupport {
@Bean
public RedisTemplate<Object, Object> redisTemplate(RedisConnectionFactory connectionFactory) {
RedisTemplate<Object, Object> redisTemplate = new RedisTemplate<>();
redisTemplate.setKeySerializer(new StringRedisSerializer());
redisTemplate.setHashKeySerializer(new StringRedisSerializer());
redisTemplate.setConnectionFactory(connectionFactory);
return redisTemplate;
}
}
|
1.4 推送到远程仓库
在分支v1.0上进行环境搭建,并上传到远程仓库的v1.0分支上。
2、缓存短信验证码
2.1 实现思路
1. 在服务端UserController中注入RedisTemplate对象,用于操作Redis
1. 在服务端UserController的sendMsg方法中,将随机生成的验证码缓存到Redis中,并设置有效时间为5分钟
1. 在服务端UserController的login方法中,从Redis中获取缓存的验证码,如果登陆成功则删除Redis中的验证码
2.2 代码优化
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
| @Autowired
private RedisTemplate redisTemplate;
@PostMapping("/sendMsg")
public R<String> sendMsg(@RequestBody User user,HttpSession session){
String phone = user.getPhone();
if (StringUtils.isNotEmpty(phone)){
String code = ValidateCodeUtils.generateValidateCode(4).toString();
log.info("code={}",code);
redisTemplate.opsForValue().set(phone,code,5, TimeUnit.MINUTES);
return R.success("手机验证码短信发送成功");
}
return R.error("手机验证码短信发送失败");
}
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
|
@PostMapping("/login")
public R<User> login(@RequestBody Map map, HttpSession session){
log.info(map.toString());
String phone = map.get("phone").toString();
String code = map.get("code").toString();
Object codeInSession = redisTemplate.opsForValue().get(phone);
if (codeInSession != null && codeInSession.equals(code)){
LambdaQueryWrapper<User> queryWrapper = new LambdaQueryWrapper<>();
queryWrapper.eq(User::getPhone,phone);
User user = userService.getOne(queryWrapper);
if (user == null){
user = new User();
user.setPhone(phone);
user.setStatus(1);
userService.save(user);
}
session.setAttribute("user",user.getId());
redisTemplate.delete(phone);
return R.success(user);
}
return R.error("登录失败");
}
|
2.3 功能测试
- 打开本地的Redis,运行项目,在移动端页面点击"获取验证码",查看Redis客户端中是否产生key
- 登陆成功后,查看Redis客户端中key是否删除
3、缓存菜品数据
移动端菜品查看功能是通过调用DishController中的list方法实现,list方法会根据前端提供的查询条件对数据库进行查询操作。在高并发的情况下,频繁查询数据库会导致系统性能下降,服务端响应时间增长。因此需要对数据进行缓存优化,提供系统性能。
3.1 实现思路
1. 改造DishController的list方法,先从Redis中获取菜品数据,如果有则直接返回,无需查询数据库;如果没有则查询数据库,并将查询到的菜品数据放入Redis中
1. 改造DishController的save和update方法,加入清理缓存的逻辑
注意:在使用缓存过程中,要保证数据库中的数据和缓存中的数据一致,如果数据库中的数据发生变化,要及时清理缓存数据并更新。
3.2 代码优化
3.2.1 list方法优化
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
| @Autowired
private RedisTemplate redisTemplate;
@GetMapping("/list")
public R<List<DishDto>> list(Dish dish){
List<DishDto> dishDtoList = null;
String key = "dish_" + dish.getCategoryId() + "_" + dish.getStatus();
dishDtoList = (List<DishDto>) redisTemplate.opsForValue().get(key);
if (dishDtoList != null){
return R.success(dishDtoList);
}
LambdaQueryWrapper<Dish> queryWrapper = new LambdaQueryWrapper();
queryWrapper.eq(dish.getCategoryId() != null,Dish::getCategoryId,dish.getCategoryId());
queryWrapper.eq(Dish::getStatus,1);
queryWrapper.orderByAsc(Dish::getSort).orderByDesc(Dish::getUpdateTime);
List<Dish> list = dishService.list(queryWrapper);
dishDtoList = list.stream().map((item)->{
DishDto dishDto = new DishDto();
BeanUtils.copyProperties(item,dishDto);
Long categoryId = item.getCategoryId();
Category category = categoryService.getById(categoryId);
if (category != null){
String categoryName = category.getName();
dishDto.setCategoryName(categoryName);
}
Long dishId = item.getId();
LambdaQueryWrapper<DishFlavor> wrapper = new LambdaQueryWrapper<>();
wrapper.eq(DishFlavor::getDishId,dishId);
List<DishFlavor> dishFlavorList = dishFlavorService.list(wrapper);
dishDto.setFlavors(dishFlavorList);
return dishDto;
}).collect(Collectors.toList());
redisTemplate.opsForValue().set(key,dishDtoList,1, TimeUnit.HOURS);
return R.success(dishDtoList);
}
|
3.2.2 save和update方法优化
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
| @PostMapping
public R<String> save(@RequestBody DishDto dishDto){
log.info(dishDto.toString());
dishService.saveWithFlavor(dishDto);
String key = "dish_" + dishDto.getCategoryId() + "_1";
redisTemplate.delete(key);
return R.success("新增菜品成功");
}
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
|
@PutMapping
public R<String> update(@RequestBody DishDto dishDto){
log.info(dishDto.toString());
dishService.updateWithFlavor(dishDto);
String key = "dish_" + dishDto.getCategoryId() + "_1";
redisTemplate.delete(key);
return R.success("新增菜品成功");
}
|
3.2.3 菜品启售/停售方法修改
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
|
@PostMapping("/status/{status}")
public R<String> status(@PathVariable("status") Integer status,@RequestParam List<Long> ids){
LambdaQueryWrapper<Dish> queryWrapper = new LambdaQueryWrapper();
queryWrapper.in(ids !=null,Dish::getId,ids);
List<Dish> list = dishService.list(queryWrapper);
for (Dish dish : list) {
if (dish != null){
dish.setStatus(status);
dishService.updateById(dish);
Long categoryId = dish.getCategoryId();
String key = "dish_" + categoryId + "_1";
redisTemplate.delete(key);
}
}
return R.success("售卖状态修改成功");
}
|
3.3 功能测试
- 首次点击菜品分类按钮(粤菜...),查看redis是否存入key,IDEA控制台是否查询了数据库
- 再次点击菜品分类按钮,查看IDEA控制台是否没有数据库
- 打开系统后台管理页面,增加/修改菜品,点击保存后查看redis是否删除key
- 再次点击移动端菜品分类按钮,查看新增菜品是否更新
3.4 推送到远程仓库
功能测试没问题后,推送至v1.0分支上,再合并到master分支上。
4、缓存套餐数据
4.1 实现思路
1. 导入Spring Cache和Redis相关的maven坐标(Part3已完成↓)
1. 在application.yml中配置缓存数据的过期时间(Part3已完成↓)
1. 在启动类上加入@EnableCaching注解,开启缓存注解功能(Part3已完成↓)
1. 在SetmealController的list方法加上@Cacheable注解
1. 在SetmealController的save和update方法加上@CacheEvict注解
4.2 代码实现
4.2.1 list方法修改
添加@Cacheable注释
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
|
@Cacheable(value = "setmealCache",key = "#setmeal.categoryId + '_' + #setmeal.status")
@GetMapping("/list")
public R<List<Setmeal>> list(Setmeal setmeal){
}
|
进行功能测试时会报错,原因是返回结果类R未实现序列化,因此需对R.class添加序列化接口:
1
| public class R<T> implements Serializable {
|
4.2.2 save&delete方法修改
添加@CacheEvict注释
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
|
@PostMapping
@CacheEvict(value = "setmealCache",allEntries = true)
public R<String> save(@RequestBody SetmealDto setmealDto){
}
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
|
@DeleteMapping
@CacheEvict(value = "setmealCache",allEntries = true)
public R<String> delete(@RequestParam List<Long> ids){
}
|
注意:完善了套餐修改和停/启售功能也需要添加@CacheEvict注释,以保证缓存数据和数据库数据保持一致
4.2.3 移动端套餐菜品显示缓存
添加@Cacheable注释
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
|
@GetMapping("/dish/{id}")
@Cacheable(value = "setmealCache",key = "#SetmealId")
public R<List<DishDto>> dish(@PathVariable("id") Long SetmealId){
}
|
三、Spring Cache
Spring Cache是一个框架,实现基于注解的缓存功能。Spring Cache提供了一层抽象,底层可以切换不同的cache实现:通过CacheManager接口统一不同的缓存技术。
1、CacheManager 接口
CacheManager是Spring提供的各种缓存技术抽象接口,针对不同的缓存技术需要不同的CacheManager:
| CacheManager |
描述 |
| EhCacheCacheManager |
使用EhCache作为缓存技术 |
| GuavaCacheManager |
使用Google的GuavaCache作为缓存技术 |
| RedisCacheManager |
使用Redis作为缓存技术 |
2、Spring Cache常用注解
| 注解 |
说明 |
| @EnableCaching |
开启缓存注解功能 |
| @Cacheable |
在方法执行前spring先查看缓存中是否有数据,如果有数据,则直接返回缓存数据;如果无数据,调用方法并将方法返回值放入缓存中 |
| @CachePut |
将方法的返回值放到缓存中 |
| @CacheEvict |
将一条或多条数据从缓存中删除 |
在springboot项目中,使用缓存技术只需在项目中导入相关缓存技术的依赖包吗,并在启动类上使用@EnableCaching开启缓存支持即可。例如使用Redis作为缓存技术,只需要导入Spring data Redis 的maven坐标即可。
3、Spring Cache使用方式
在springboot项目中使用spring cache的操作步骤:
3.1 导入maven坐标
1
2
3
4
| <dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-cache</artifactId>
</dependency>
|
3.2 配置application.yml文件
1
2
3
4
| string:
cache:
redis:
time-to-live: 180000
|
3.3 在启动类上加入@EnableCaching注解,开启缓存注解功能
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
| package com.itreggie.reggie;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.web.servlet.ServletComponentScan;
import org.springframework.cache.annotation.EnableCaching;
import org.springframework.transaction.annotation.EnableTransactionManagement;
@Slf4j
@SpringBootApplication
@ServletComponentScan
@EnableTransactionManagement
@EnableCaching
public class ReggieApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(ReggieApplication.class,args);
log.info("项目启动成功。。。");
}
}
|
3.4 在Controller的方法上加入@Cacheable、@CacheEvict等注解,进行缓存操作
四、读写分离
1、MySQL主从复制
MySQL主从复制是一个异步的复制过程,底层是基于MySQL数据库自带的二进制日志功能。
原理是一台或多台MySQL数据库(slave从库)从MySQL数据库(master主库)进行日志复制再解析应用日志到自身,最终实现从库数据和主库数据保持一致。
MySQL复制过程分为三步:
- master将改变记录到二进制日志(binary log)
- slave将master的binary log拷贝到自身的中继日志(relay log)
- slave重做中继日志中的事件,将改变应用到自己的数据库中
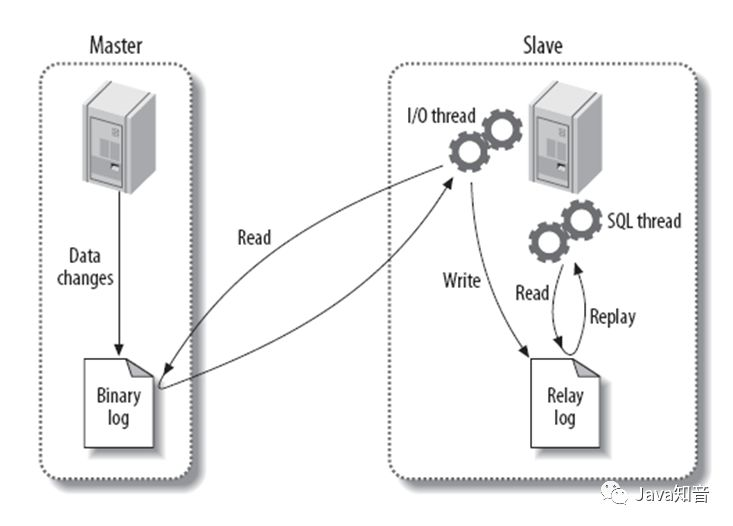
1.1 配置主库master
1.1.1 修改mysql数据库配置文件
在/etc/my.cnf中添加
1
2
3
4
| [mysqld]
log-bin=mysql-bin #[必须]启用二进制日志
server-id=100 #[必须]服务器唯一ID(可自定义)
|
1.1.2 重启mysql数据库
1
| systemctl restart mysqld
|
1.1.3 创建用户
登陆mysql数据库,执行下面sql:
1
| grant replication slave on *.* to 'xiaoming'@'%' identified by 'Root@123q321q';
|
sql语句的作用是创建一个用户xiaoming,密码为Root@123q321q,并且给予xiaoming用户replication slave权限。常用于建立复制时所需要用到的用户权限,换言之,只有被master授权该权限的用户,slave才能通过该用户进行复制。
1.1.4 查看主库状态
获取结果中File和Position的值。
注意:上面sql语句作用是查看master状态,执行后不要再进行其他操作,以免状态发生改变。
1.2 配置从库slave
1.2.1 修改mysql数据库配置文件
在/etc/my.cnf中添加
1
2
| [mysqld]
server-id=101 #[必须]服务器唯一ID
|
1.2.2 重启mysql数据库
1
| systemctl restart mysqld
|
1.2.3 从库连接主库
登陆mysql数据库,在sql中实现(根据实际情况填写):
1
2
3
4
5
6
| change master to
-> master_host='虚拟机ip',
-> master_user='',
-> master_password='',
-> master_log_file='',
-> master_log_pos=441;
|
如遇到已有slave线程进行,可使用以下代码取消当前线程:
sql语句运行成功后,启动slave:
1.2.4 查看slave连接情况


能得到以上结果,说明slave连接master成功
2、使用Sharding-JDBC实现读写分离
2.1 导入maven坐标
1
2
3
4
5
| <dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.shardingsphere</groupId>
<artifactId>sharding-jdbc-spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>4.0.0-RC1</version>
</dependency>
|
2.2 配置application.yml文件
2.2.1 配置读写分离规则
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
| server:
port: 8090
mybatis-plus:
configuration:
#在映射实体或者属性时,将数据库中表名和字段名中的下划线去掉,按照驼峰命名法映射
map-underscore-to-camel-case: true
log-impl: org.apache.ibatis.logging.stdout.StdOutImpl
global-config:
db-config:
id-type: ASSIGN_ID
spring:
shardingsphere:
datasource:
names:
master,slave
# 主数据源
master:
type: com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource
driver-class-name: com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
url: jdbc:mysql:
username: root
password: root
# 从数据源
slave:
type: com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource
driver-class-name: com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
url: jdbc:mysql:
username: root
password: root
masterslave:
# 读写分离配置
load-balance-algorithm-type: round_robin #轮询
# 最终的数据源名称
name: dataSource
# 主库数据源名称
master-data-source-name: master
# 从库数据源名称列表,多个逗号分隔
slave-data-source-names: slave
props:
sql:
show: true #开启SQL显示,默认false
|
2.2.2 配置允许bean定义覆盖的配置项
1
2
3
| spring:
main:
allow-bean-definition-overriding: true
|
3、项目实现读写分离
3.1 数据库环境准备(主从分离)
直接使用已经搭建好的虚拟机主从复制的数据库环境,在master中导入数据库即可。
3.2 配置application.yml文件
3.2.1 配置读写分离规则
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
| server:
port: 8090
mybatis-plus:
configuration:
#在映射实体或者属性时,将数据库中表名和字段名中的下划线去掉,按照驼峰命名法映射
map-underscore-to-camel-case: true
log-impl: org.apache.ibatis.logging.stdout.StdOutImpl
global-config:
db-config:
id-type: ASSIGN_ID
spring:
shardingsphere:
datasource:
names:
master,slave
# 主数据源
master:
type: com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource
driver-class-name: com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
url: jdbc:mysql:
username: root
password: root
# 从数据源
slave:
type: com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource
driver-class-name: com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
url: jdbc:mysql:
username: root
password: root
masterslave:
# 读写分离配置
load-balance-algorithm-type: round_robin #轮询
# 最终的数据源名称
name: dataSource
# 主库数据源名称
master-data-source-name: master
# 从库数据源名称列表,多个逗号分隔
slave-data-source-names: slave
props:
sql:
show: true #开启SQL显示,默认false
|
3.2.2 配置允许bean定义覆盖的配置项
1
2
3
| spring:
main:
allow-bean-definition-overriding: true
|
3.3 功能测试
切换数据库后重新登录后台管理页面,查看IDEA控制台的输出情况,出现增删改在master,查在slave则说明读写分离成功。
五、Nginx
官网:https://nginx.org/
Nginx是一款轻量级的Web服务器/反向代理服务器及电子邮件(IMAP/POP3)代理服务器。特点是占有内存少,并发能力强。
1、Nginx下载与安装
- 安装依赖包 yum -y install gcc pcre-devel zlib-devel openssl openssl-devel
- 下载Nginx安装包 wget https://nginx.org/download/nginx-1.16.1.tar.gz
- 解压 tar -zxvf nginx-1.16.1.tar.gz
- 访问 **cd nginx-1.16.1 **
- 检查安装目录环境 ./configure –prefix=/usr/local/nginx
- 编译并安装 make && make install
2、Nginx常用命令
| 命令 |
意义 |
备注 |
| ./nginx -v |
查看版本号 |
在sbin目录下 |
| ./nginx -t |
检查nginx.conf文件配置 |
在sbin目录下 |
| ./nginx |
启动Nginx |
在sbin目录下 |
| ./nginx -s stop |
停止Nginx服务 |
在sbin目录下 |
| ps -ef | grep nginx |
查看Nginx进程 |
|
| ./nginx -s reload |
重新加载配置文件 |
在sbin目录下 |
配置环境变量,使Nginx命令能直接运行,在/etc/profile的PATH中修改:
1
| PATH=/usr/local/nginx/sbin:$JAVA_HOME/bin:$PATH
|
3、Nginx配置文件结构
- 全局块:和Nginx运行相关的全局配置
- events块:和网络连接相关的配置
- http块:代理、缓存、日志记录、虚拟主机配置
注意:http块可以配置多个server块,每个server块可以配置多个location块
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
| #全局块
worker_processes 2;
#events块
events {
worker_connections 1024;
}
#http块
http {
#http全局块
include mime.types;
default_type application/octet-stream;
sendfile on;
keepalive_timeout 65;
#Server块
server {
#Server全局块
listen 80;
server_name localhost;
#location块
location / {
root html;
index index.html index.htm;
}
error_page 500 502 503 504 /50x.html;
location = /50x.html {
root html;
}
}
}
|
4、Nginx具体应用
4.1 部署静态资源
Nginx可以作为静态web服务器来部署静态资源。静态资源指在服务端真实存在且能够直接展示的一些文件,如http页面、css文件、js文件、图片、视频等。
相比于Tomcat,Nginx处理静态资源的能力更加高效,在生产环境中,一般将静态资源部署在Nginx中。将静态资源部署在Nginx中只需要将文件复制到Nginx安装目录下的html目录即可。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
| #Server块
server {
#Server全局块
listen 80; #监听端口
server_name localhost; #服务器名称
#location块
location / { #匹配客户端请求url
root html; #指定静态资源根目录
index index.html index.htm; #指定默认首页
}
}
|
4.2 反向代理
4.2.1 正向代理概念补充
正向代理是位于客户端和原始服务器(origin server)之间的服务器。为了从原始服务器获取内容,客户端向代理发送请求并指定目标为原始服务器,然后代理向原始服务器转交请求并将获取到的内容返回给客户端。
正向代理主要是 帮助在防火墙内的局域网客户端提供访问Internet的途径。
正向代理一般在客户端设置代理服务器,通过代理服务器发送请求,最终访问到目标服务器。
4.2.2 反向代理
反向代理服务器位于客户和目标服务器之间,但对于客户而言,反向代理服务器相当于目标服务器,即用户直接访问反向代理服务器就可以获得目标服务器的资源,反向服务器负责将请求转发给目标服务器。
用户不需要知道目标服务器的地址,也不需要用户端作任何设置。
4.2.3 反向代理配置
#Server块
server {
#Server全局块
listen 82;
server_name localhost;
#location块
location / {
proxy_pass http://虚拟机ip:8090; #反向代理配置,将请求转发到指定服务器
}
}
4.3 负载均衡
- 应用集群:将同一应用部署到多台机器上组成应用集群,接收负载均衡器分发的请求,进行业务处理并返回响应数据
- 负载均衡器:将用户请求根据对应的负载均衡算法分发到应用集群中的一台服务器进行处理
4.3.1 配置负载均衡
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
| upstream targetserver{ # upstream指令可以定义一组服务器
server 虚拟机ip:8090 weight=10; #部署负载均衡策略
server 虚拟机ip:8090 weight=5; #部署不同的服务器(也可以使用同一台服务器,调用不同的端口作为学习)
}
#Server块
server {
#Server全局块
listen 8090;
server_name localhost;
#location块
location / {
proxy_pass http://targetserver; #反向代理配置,将请求转发到指定服务器
}
}
|
4.2.2 负载均衡策略
| 名称 |
说明 |
| 轮询 |
默认方式 |
| weight |
权重方式 |
| ip_hash |
依据ip分配方式 |
| least_conn |
依据最少连接方式 |
| url_hash |
依据url分配方式 |
| fair |
依据响应时间方式 |
六、前后端分离开发
1、开发流程

接口(API接口) 就是一个http的请求地址,主要就是去定义:请求路径、请求方式、请求参数、响应参数等内容。

2、前端技术栈
- 开发工具
- visual studio code
- hbuilder
- 技术框架
- node.js(基石)
- VUE
- ElementUI
- mock(用于测试)
- webpack(用于打包)
3、YApi
YApi是高效、易用、功能强大的api管理平台,旨在为用户提供更优雅的接口管理服务。可以帮助开发者轻松创建、发布、维护API,YApi还为用户提供了优秀的交互体验,开发人员只需要利用平台提供的接口数据写入工具以及简单的点击操作就可以实现接口的管理。
YApi让接口开发更简单高效,让接口的管理更具有可读性、可维护性,让团队协作更合理。
源码地址:https://github.com/YMFE/yapi
3.1 YApi使用方式
- 添加项目
- 添加分类
- 添加接口
- 编辑接口
- 查看接口
七、Swagger
官网:https://swagger.io/
1、介绍
只需要按照Swagger的规范去定义接口及接口相关的信息,再通过Swagger衍生出来的一系列项目和工具,就可以做成各种格式的接口文档,以及在线接口调试页面等。
knife4j是为Java MVC框架集成Swagger生成Api文档的增强解决方法。
1
2
3
4
5
| <dependency>
<groupId>com.github.xiaoymin</groupId>
<artifactId>knife4j-spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>3.0.3</version>
</dependency>
|
2、使用方式
2.1 导入knife4j的maven坐标
2.2 导入knife4j的相关配置类WebMvcConfig
对原有的WebMvcConfig进行修改:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
| @Slf4j
@Configuration
@EnableSwagger2
@EnableKnife4j
public class WebMvcConfig extends WebMvcConfigurationSupport {
@Bean
public Docket createRestApi() {
return new Docket(DocumentationType.SWAGGER_2)
.apiInfo(apiInfo())
.select()
.apis(RequestHandlerSelectors.basePackage("com.itheima.reggie.controller"))
.paths(PathSelectors.any())
.build();
}
private ApiInfo apiInfo() {
return new ApiInfoBuilder()
.title("外卖")
.version("1.0")
.description("外卖接口文档")
.build();
}
}
|
2.3 设置静态资源
将代码添加到WebMvcConfig类中的addResourceHandlers方法中,解决接口文档页面访问问题。
1
2
| registry.addResourceHandler("doc.html").addResourceLocations("classpath:/META-INF/resources/");
registry.addResourceHandler("/webjars/**").addResourceLocations("classpath:/META-INF/resources/webjars/");
|
2.4 添加请求路径
在LoginCheckFilter中设置不需要处理的请求路径:
1
2
3
4
| "/doc.html",
"/webjars/**",
"/swagger-resources",
"/v2/api-docs"
|
3、常用注解
| 注解 |
说明 |
| @Api |
用在请求的类(eg:controller)上,表示对类的说明 |
| @ApiModel |
用在类上,通常是实体类,表示一个返回响应数据的信息 |
| @ApiModelProperty |
用在属性上,描述响应类的属性 |
| @ApiOperation |
用在请求的方法上,说明方法的用途、作用 |
| @ApiImplicitParams |
用在请求的方法上,表示一组参数说明 |
| @ApiImplicitParam |
用在@ApiImplicitParams注解中,指定一个请求参数的各个方面 |
八、项目部署
1、部署架构

2、部署环境说明
- 192.168.197.100(服务器A)
- Nginx:部署前端项目、配置反向代理
- MySQL:主从复制结构中的主库
- 192.168.197.101(服务器B)
- jdk:运行java项目
- git:版本控制工具
- maven:项目构建工具
- jar:spring boot项目打包成jar包基于内置Tomcat运行
- MySQL:主从复制结构中的从库
- localhost(服务器C)
3、部署前端项目(存在问题–未解决)
3.1 部署Nginx
导入项目前端文件dist到Nginx的html目录下。
3.2 修改Nginx配置文件
修改Nginx的配置文件nginx.conf
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
| server {
listen 80;
server_name localhost;
location / {
root html/dist;
index index.html;
}
#反向代理配置
location ^~ /api/ {
rewrite ^/api/(.*)$ /$1 break; #对url进行重写
proxy_pass http://192.168.138.101:8090;
}
}
|
4、部署后端项目
4.1 工具部署
安装好jdk、git、maven、MySQL等工具,使用git clone命令将git远程仓库代码克隆下来
4.2 上传reggieStart.sh文件并重新设置权限
1
| chmod 777 reggieStart.sh
|
注意:reggieStart.sh内的名称需要修改为自己项目的名称,否则会打包失败
运行.sh文件后,查看java进程确定程序是否启动。
4.3 修改图片路径
将本地的菜品图片传到linux目录下,在application.yml文件中修改文件路径:
1
2
| reggie:
path: /usr/local/img/
|
4.4 功能测试
将Nginx和reggieStart.sh同时运行,在网页进行登陆测试,能成功登陆即项目前后端分离成功。







