欢迎访问本人的算法学习笔记,以下学习路线均借鉴于代码随想录 ,有需要的小伙伴可以去Carl的代码随想录中学习哦
Ω.算法整理 壹.双指针法 双指针法并不隶属于某一种数据结构,在 数组、链表和字符串 中都可以使用双指针法优化,降低时间复杂度。
双指针法(快慢指针法): 通过一个快指针和慢指针在一个for循环下完成两个for循环的工作。
快指针:寻找新数组的元素 ,新数组就是不含有目标元素的数组
慢指针:指向更新 新数组下标的位置
贰.回溯算法 回溯法也可以叫做回溯搜索法,它是一种搜索的方式。回溯是递归的副产品,只要有递归就会有回溯。回溯的本质是穷举,穷举所有可能,然后选出我们想要的答案 ,如果想让回溯法高效一些,可以加一些剪枝的操作,但也改不了回溯法就是穷举的本质。
回溯法解决的问题都可以抽象为树形结构 ,因为回溯法解决的都是在集合中递归查找子集,集合的大小就构成了树的宽度,递归的深度,都构成的树的深度 。递归就要有终止条件,所以必然是一棵高度有限的树(N叉树)。
回溯算法模板框架如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 void backtracking (参数) { if (终止条件) { 存放结果; return ; } for (选择:本层集合中元素(树中节点孩子的数量就是集合的大小)) { 处理节点; backtracking(路径,选择列表); 回溯,撤销处理结果 } }
叁.背包问题 01背包·二维dp数组 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 public static void main (String[] args) { int [] weight = {1 , 3 , 4 }; int [] value = {15 , 20 , 30 }; int bagsize = 4 ; testweightbagproblem(weight, value, bagsize); } public static void testweightbagproblem (int [] weight, int [] value, int bagsize) { int wlen = weight.length, value0 = 0 ; int [][] dp = new int [wlen + 1 ][bagsize + 1 ]; for (int i = 0 ; i <= wlen; i++){ dp[i][0 ] = value0; } for (int i = 1 ; i <= wlen; i++){ for (int j = 1 ; j <= bagsize; j++){ if (j < weight[i - 1 ]){ dp[i][j] = dp[i - 1 ][j]; }else { dp[i][j] = Math.max(dp[i - 1 ][j], dp[i - 1 ][j - weight[i - 1 ]] + value[i - 1 ]); } } } for (int i = 0 ; i <= wlen; i++){ for (int j = 0 ; j <= bagsize; j++){ System.out.print(dp[i][j] + " " ); } System.out.print("\n" ); } }
01背包·一维dp数组(滚动数组) 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 public static void main (String[] args) { int [] weight = {1 , 3 , 4 }; int [] value = {15 , 20 , 30 }; int bagWight = 4 ; testWeightBagProblem(weight, value, bagWight); } public static void testWeightBagProblem (int [] weight, int [] value, int bagWeight) { int wLen = weight.length; int [] dp = new int [bagWeight + 1 ]; for (int i = 0 ; i < wLen; i++){ for (int j = bagWeight; j >= weight[i]; j--){ dp[j] = Math.max(dp[j], dp[j - weight[i]] + value[i]); } } for (int j = 0 ; j <= bagWeight; j++){ System.out.print(dp[j] + " " ); } }
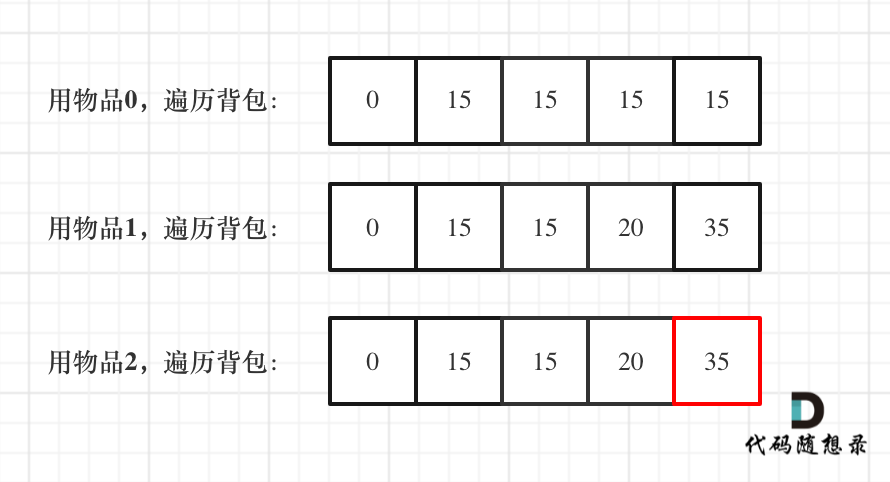
完全背包 完全背包和01背包问题唯一不同 的地方就是,每种物品有无限件 。在完全背包中,两个for循环的先后循序,都不影响计算dp[j]所需要的值
先遍历物品,再遍历背包:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 private static void testCompletePack () { int [] weight = {1 , 3 , 4 }; int [] value = {15 , 20 , 30 }; int bagWeight = 4 ; int [] dp = new int [bagWeight + 1 ]; for (int i = 0 ; i < weight.length; i++){ for (int j = weight[i]; j <= bagWeight; j++){ dp[j] = Math.max(dp[j], dp[j - weight[i]] + value[i]); } } for (int maxValue : dp){ System.out.println(maxValue + " " ); } }
先遍历背包,再遍历物品:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 private static void testCompletePackAnotherWay () { int [] weight = {1 , 3 , 4 }; int [] value = {15 , 20 , 30 }; int bagWeight = 4 ; int [] dp = new int [bagWeight + 1 ]; for (int i = 1 ; i <= bagWeight; i++){ for (int j = 0 ; j < weight.length; j++){ if (i - weight[j] >= 0 ){ dp[i] = Math.max(dp[i], dp[i - weight[j]] + value[j]); } } } for (int maxValue : dp){ System.out.println(maxValue + " " ); } }
多重背包 多重背包是在01背包里面加一个for循环遍历一个每种商品的数量。
版本一:改变物品数量为01背包格式
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 public void testMultiPack1 () { List<Integer> weight = new ArrayList <>(Arrays.asList(1 , 3 , 4 )); List<Integer> value = new ArrayList <>(Arrays.asList(15 , 20 , 30 )); List<Integer> nums = new ArrayList <>(Arrays.asList(2 , 3 , 2 )); int bagWeight = 10 ; for (int i = 0 ; i < nums.size(); i++) { while (nums.get(i) > 1 ) { weight.add(weight.get(i)); value.add(value.get(i)); nums.set(i, nums.get(i) - 1 ); } } int [] dp = new int [bagWeight + 1 ]; for (int i = 0 ; i < weight.size(); i++) { for (int j = bagWeight; j >= weight.get(i); j--) { dp[j] = Math.max(dp[j], dp[j - weight.get(i)] + value.get(i)); } System.out.println(Arrays.toString(dp)); } }
版本二:改变遍历个数
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 public void testMultiPack2 () { int [] weight = new int [] {1 , 3 , 4 }; int [] value = new int [] {15 , 20 , 30 }; int [] nums = new int [] {2 , 3 , 2 }; int bagWeight = 10 ; int [] dp = new int [bagWeight + 1 ]; for (int i = 0 ; i < weight.length; i++) { for (int j = bagWeight; j >= weight[i]; j--) { for (int k = 1 ; k <= nums[i] && (j - k * weight[i]) >= 0 ; k++) { dp[j] = Math.max(dp[j], dp[j - k * weight[i]] + k * value[i]); } System.out.println(Arrays.toString(dp)); } } }
背包递推公式 问背包装满最大价值:
1 2 3 4 5 for (int i = 0 ; i < weight.length; i++){ for (int j = weight[i]; j <= bagWeight; j++){ dp[j] = Math.max(dp[j], dp[j - weight[i]] + value[i]); } }
问能否能装满背包(或者最多装多少):
1 dp[j] = Math.max(dp[j], dp[j - nums[i]] + nums[i]);
问装满背包所有物品的最小个数:
1 dp[j] = Math.min(dp[j - coins[i]] + 1 , dp[j]);
问装满背包方法数量:
1 dp[j] += dp[j - nums[i]];
遍历顺序 01背包
二维 dp数组01背包先遍历物品还是先遍历背包都是可以的,且第二层for循环是从小到大 遍历。一维 dp数组01背包只能先遍历物品再遍历背包容量 ,且第二层for循环是从大到小 遍历。
完全背包 target(背包),nums(物品)
如果求组合数 就是外层for循环遍历物品,内层for遍历背包
如果求排列数 就是外层for遍历背包,内层for循环遍历物品
如果求最小数 ,那么两层for循环的先后顺序就无所谓
总结 一、数组 二分查找 704.二分查找 给定一个 n 个元素有序的(升序)整型数组 nums 和一个目标值 target ,写一个函数搜索 nums 中的 target,如果目标值存在返回下标,否则返回 -1。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 class Solution { public int search (int [] nums, int target) { int left = 0 ; int right = nums.length - 1 ; while (left <= right){ int mid = left + (right - left) / 2 ; if (nums[mid] == target){ return mid; }else if (nums[mid] > target){ right = mid - 1 ; }else { left = mid + 1 ; } } return -1 ; } }
34.在排序数组中查找元素的第一个和最后一个位置 给你一个按照非递减顺序排列的整数数组 nums,和一个目标值 target。请你找出给定目标值在数组中的开始位置和结束位置。如果数组中不存在目标值 target,返回 [-1, -1]。
你必须设计并实现时间复杂度为 O(log n) 的算法解决此问题。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 class Solution { public int [] searchRange(int [] nums, int target) { return new int []{getBegin(nums,target), getEnd(nums,target)}; } public int getBegin (int [] nums, int target) { for (int i = 0 ; i < nums.length; i++){ if (nums[i] == target){ return i; } } return -1 ; } public int getEnd (int [] nums, int target) { for (int i = nums.length - 1 ; i >= 0 ; i--){ if (nums[i] == target){ return i; } } return -1 ; } }
35.搜索插入位置 给定一个排序数组和一个目标值,在数组中找到目标值,并返回其索引。如果目标值不存在于数组中,返回它将会被按顺序插入的位置。请必须使用时间复杂度为 O(log n) 的算法。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 class Solution { public int searchInsert (int [] nums, int target) { int left = 0 , right = nums.length - 1 ; while (left <= right){ int mid = left + ((right - left) >> 1 ); if (nums[mid] == target){ return mid; }else if (nums[mid] > target){ right = mid - 1 ; }else { left = mid + 1 ; } } return left; } }
69.x 的平方根 给你一个非负整数 x ,计算并返回 x 的 算术平方根 。由于返回类型是整数,结果只保留整数部分 ,小数部分将被舍去 。
注意:不允许使用任何内置指数函数和算符,例如 pow(x, 0.5) 或者 x ** 0.5 。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 class Solution { public int mySqrt (int x) { long num = x; while (num * num > x){ num = (num + x / num) >> 1 ; } return (int ) num; } }
367.有效的完全平方数 给定一个 正整数 num ,编写一个函数,如果 num 是一个完全平方数,则返回 true ,否则返回 false 。
进阶:不要 使用任何内置的库函数,如 sqrt 。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 class Solution { public boolean isPerfectSquare (int num) { int i = 1 ; while (num > 0 ){ num -= i; i += 2 ; } return num == 0 ; } }
移除元素 27.移除元素 给你一个数组 nums 和一个值 val,你需要原地移除所有数值等于 val 的元素,并返回移除后数组的新长度。不要使用额外的数组空间,你必须仅使用 O(1) 额外空间并原地修改输入数组 。
元素的顺序可以改变。你不需要考虑数组中超出新长度后面的元素。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 class Solution { public int removeElement (int [] nums, int val) { int res = 0 ; for (int num : nums){ if (num != val){ nums[res] = num; res++; } } return res; } }
26.删除有序数组中的重复项 给你一个 升序排列 的数组 nums ,请你原地删除重复出现的元素,使每个元素 只出现一次 ,返回删除后数组的新长度。元素的 相对顺序 应该保持 一致 。
由于在某些语言中不能改变数组的长度,所以必须将结果放在数组nums的第一部分。更规范地说,如果在删除重复项之后有 k 个元素,那么 nums 的前 k 个元素应该保存最终结果。
将最终结果插入 nums 的前 k 个位置后返回 k 。
不要使用额外的空间,你必须在 原地修改输入数组 并在使用 O(1) 额外空间的条件下完成。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 class Solution { public int removeDuplicates (int [] nums) { int i = 0 ; for (int j = 1 ; j < nums.length; j++){ if (nums[i] != nums[j]){ nums[++i] = nums[j]; } } return i + 1 ; } }
283.移动零 给定一个数组 nums,编写一个函数将所有 0 移动到数组的末尾,同时保持非零元素的相对顺序。
请注意 ,必须在不复制数组的情况下原地对数组进行操作。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 class Solution { public void moveZeroes (int [] nums) { int cur = 0 , pre = 1 ; while (pre < nums.length){ if (nums[cur] == 0 ){ if (nums[pre] != 0 ){ int tmp = nums[pre]; nums[pre] = nums[cur]; nums[cur] = tmp; }else { pre++; } }else { cur++; pre++; } } } }
844.比较含退格的字符串 给定 s 和 t 两个字符串,当它们分别被输入到空白的文本编辑器后,如果两者相等,返回 true 。# 代表退格字符。
注意:如果对空文本输入退格字符,文本继续为空。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 class Solution { public boolean backspaceCompare (String s, String t) { int skipS = 0 ; int skipT = 0 ; int i = s.length() - 1 ; int j = t.length() - 1 ; while (i >= 0 || j >= 0 ){ while (i >= 0 ){ if (s.charAt(i) == '#' ){ skipS++; i--; }else if (s.charAt(i) != '#' ){ if (skipS > 0 ){ skipS--; i--; }else { break ; } } } while (j >= 0 ){ if (t.charAt(j) == '#' ){ skipT++; j--; }else if (t.charAt(j) != '#' ){ if (skipT > 0 ){ skipT--; j--; }else { break ; } } } if (i >= 0 && j >= 0 ){ if (s.charAt(i) != t.charAt(j)){ return false ; }else { i--; j--; } }else if ((i >= 0 && j < 0 ) || (i < 0 && j >= 0 )){ return false ; } } return true ; } }
有序数组的平方 977.有序数组的平方 给你一个按 非递减顺序 排序的整数数组 nums,返回 每个数字的平方 组成的新数组,要求也按 非递减顺序 排序。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 class Solution { public int [] sortedSquares(int [] nums) { int [] res = new int [nums.length]; int left = 0 , right = nums.length - 1 ; for (int i = nums.length-1 ; i >= 0 ; i--){ if (nums[left] * nums[left] > nums[right] * nums[right]){ res[i] = nums[left] * nums[left]; left++; }else { res[i] = nums[right] * nums[right]; right--; } } return res; } }
长度最小的子数组 209.长度最小的子数组 给定一个含有 n 个正整数的数组和一个正整数 target 。找出该数组中满足其和 ≥ target 的长度最小的 连续子数组 [numsl, numsl+1, …, numsr-1, numsr] ,并返回其长度。如果不存在符合条件的子数组,返回 0 。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 class Solution { public int minSubArrayLen (int target, int [] nums) { int left = 0 , right = 0 , len = nums.length; int sum = 0 ; int min = len + 1 ; while (right < len){ sum += nums[right]; while (sum >= target){ min = Math.min(min, right - left + 1 ); sum -= nums[left++]; } right++; } return min == len + 1 ? 0 : min; } }
904.水果成篮 农场从左到右种植了一排果树。这些树用一个整数数组 fruits 表示,其中 fruits[i] 是第 i 棵树上的水果 种类编号 。你想要尽可能多地收集水果。然而,农场的主人设定了一些严格的规矩,你必须按照要求采摘水果:
你只有 两个 篮子,并且每个篮子只能装 单一类型 的水果。每个篮子能够装的水果总量没有限制。
你可以选择任意一棵树开始采摘,你必须从 每棵 树(包括开始采摘的树)上 恰好摘一个水果 。采摘的水果应当符合篮子中的水果类型。每采摘一次,你将会向右移动到下一棵树,并继续采摘。
一旦你走到某棵树前,但水果不符合篮子的水果类型,那么就必须停止采摘。
给你一个整数数组 fruits ,返回你可以收集的水果的 最大 数目。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 class Solution { public int totalFruit (int [] fruits) { int len = fruits.length; Map<Integer,Integer> map = new HashMap <>(); int left = 0 ; int res = 0 ; for (int right = 0 ; right < len; right++){ map.put(fruits[right], map.getOrDefault(fruits[right], 0 ) + 1 ); while (map.size() > 2 ){ map.put(fruits[left], map.get(fruits[left]) - 1 ); if (map.get(fruits[left]) == 0 ){ map.remove(fruits[left]); } ++left; } res = Math.max(res, right - left + 1 ); } return res; } }
76.最小覆盖子串 给你一个字符串 s 、一个字符串 t 。返回 s 中涵盖 t 所有字符的最小子串。如果 s 中不存在涵盖 t 所有字符的子串,则返回空字符串 “” 。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 class Solution { public String minWindow (String s, String t) { if (s.length() < t.length() || s == null || t == null ) { return "" ; } char [] cs = s.toCharArray(); char [] ct = t.toCharArray(); Map<Character, Integer> need = new HashMap <>(); for (int i = 0 ; i < ct.length; i++) { need.put(ct[i], need.getOrDefault(ct[i], 0 ) + 1 ); } Map<Character, Integer> str = new HashMap <>(); int left = 0 , right = 0 ; int finishCount = 0 ; String res = "" ; int minLen = cs.length; while (right < s.length()){ if (need.containsKey(cs[right])){ str.put(cs[right], str.getOrDefault(cs[right], 0 ) + 1 ); if (str.get(cs[right]).equals(need.get(cs[right]))){ finishCount++; } } right++; while (finishCount == need.size()){ if (str.containsKey(cs[left]) && str.get(cs[left]) >= need.get(cs[left])){ String tmp = s.substring(left, right); if (tmp.length() <= minLen){ res = tmp; minLen = tmp.length(); } str.put(cs[left], str.get(cs[left]) - 1 ); if (str.get(cs[left]) < need.get(cs[left])){ finishCount--; } } left++; } } return res; } }
螺旋矩阵 59.螺旋矩阵II 给定一个正整数 n,生成一个包含 1 到 n^2 所有元素,且元素按顺时针顺序螺旋排列的正方形矩阵。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 class Solution { public int [][] generateMatrix(int n) { int [][] res = new int [n][n]; int up = 0 ; int down = n-1 ; int left = 0 ; int right = n-1 ; int index = 1 ; while (index <= n*n){ for (int i=left;i<=right;++i){ res[up][i] = index++; } up++; for (int i=up;i<=down;++i){ res[i][right] = index++; } right--; for (int i=right;i>=left;--i){ res[down][i] = index++; } down--; for (int i=down;i>=up;--i){ res[i][left] = index++; } left++; } return res; } }
54.螺旋矩阵 给你一个 m 行 n 列的矩阵 matrix ,请按照 顺时针螺旋顺序 ,返回矩阵中的所有元素。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 class Solution { public List<Integer> spiralOrder (int [][] matrix) { int m = matrix.length, n = matrix[0 ].length; List<Integer> res = new ArrayList <>(); int left = 0 , right = n - 1 , top = 0 , down = m - 1 ; while (true ) { for (int i = left; i <= right; ++i) { res.add(matrix[top][i]); } if (++top > down){ break ; } for (int i = top; i <= down; ++i) { res.add(matrix[i][right]); } if (--right < left){ break ; } for (int i = right; i >= left; --i) { res.add(matrix[down][i]); } if (--down < top){ break ; } for (int i = down; i >= top; --i) { res.add(matrix[i][left]); } if (++left > right){ break ; } } return res; } }
[剑指Offer 29] 顺时针打印矩阵 输入一个矩阵,按照从外向里以顺时针的顺序依次打印出每一个数字。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 class Solution { public int [] spiralOrder(int [][] matrix) { if (matrix == null || matrix.length == 0 ){ return new int [0 ]; } int left = 0 , top = 0 ,right = matrix[0 ].length - 1 ,down = matrix.length - 1 ; int [] res = new int [matrix[0 ].length * matrix.length]; int key = 0 ; while (top <= down && left <= right){ for (int i=left;i <= right;i++){ res[key++] = matrix[top][i]; } top++; for (int i=top;i<=down;i++){ res[key++] = matrix[i][right]; } right--; for (int i=right;i>=left && top <= down;i--){ res[key++] = matrix[down][i]; } down--; for (int i=down;i>=top && left <= right;i--){ res[key++] = matrix[i][left]; } left++; } return res; } }
二、链表 2.两数相加 给定两个非空链表来表示两个非负整数。位数按照逆序方式存储,它们的每个节点只存储单个数字。将两数相加返回一个新的链表。你可以假设除了数字 0 之外,这两个数字都不会以零开头。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 class Solution { public ListNode addTwoNumbers (ListNode l1, ListNode l2) { ListNode head = new ListNode (0 ); ListNode tail = head; int carry = 0 ; while (l1 != null || l2 != null ){ int v1 = l1 != null ? l1.val :0 ; int v2 = l2 != null ? l2.val :0 ; int sum = v1 + v2 +carry; tail.next = new ListNode (sum%10 ); tail = tail.next; carry = sum/10 ; if (l1 != null ){ l1=l1.next; } if (l2 != null ){ l2 = l2.next; } } if (carry==1 ){ tail.next = new ListNode (carry); } return head.next; } }
203.移除链表元素 删除链表中等于给定值 val 的所有节点
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 class Solution { public ListNode removeElements (ListNode head, int val) { if (head == null ){ return null ; } ListNode dummy = new ListNode (0 ); dummy.next = head; ListNode pre = dummy; while (pre.next != null ){ if (pre.next.val == val){ pre.next = pre.next.next; }else { pre = pre.next; } } return dummy.next; } }
707.设计链表 在链表类中实现这些功能:
get(index):获取链表中第 index 个节点的值。如果索引无效,则返回-1。
addAtHead(val):在链表的第一个元素之前添加一个值为 val 的节点。插入后,新节点将成为链表的第一个节点。
addAtTail(val):将值为 val 的节点追加到链表的最后一个元素。
addAtIndex(index,val):在链表中的第 index 个节点之前添加值为 val 的节点。如果 index 等于链表的长度,则该节点将附加到链表的末尾。如果 index 大于链表长度,则不会插入节点。如果index小于0,则在头部插入节点。
deleteAtIndex(index):如果索引 index 有效,则删除链表中的第 index 个节点。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 class ListNode { int val; ListNode next; public ListNode (int val) { this .val = val; } } class MyLinkedList { int size; ListNode head; public MyLinkedList () { size = 0 ; head = new ListNode (0 ); } public int get (int index) { if (index < 0 || index >= size){ return -1 ; } ListNode cur = head; for (int i=0 ;i<=index;i++){ cur = cur.next; } return cur.val; } public void addAtHead (int val) { addAtIndex(0 ,val); } public void addAtTail (int val) { addAtIndex(size,val); } public void addAtIndex (int index, int val) { if (index < 0 || index >size){ return ; } index = Math.max(0 ,index); size++; ListNode pre = head; for (int i=0 ;i<index;i++){ pre = pre.next; } ListNode add = new ListNode (val); add.next = pre.next; pre.next = add; } public void deleteAtIndex (int index) { if (index <0 || index >=size){ return ; } size--; ListNode pre = head; for (int i=0 ;i<index;i++){ pre = pre.next; } pre.next = pre.next.next; } }
206.反转链表 反转一个单链表。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 class Solution { public ListNode reverseList (ListNode head) { ListNode pre = null ; ListNode next = null ; while (head != null ){ next = head.next; head.next = pre; pre = head; head = next; } return pre; } }
24.两两交换链表中的节点 给定一个链表,两两交换其中相邻的节点,并返回交换后的链表。你不能只是单纯的改变节点内部的值,而是需要实际的进行节点交换。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 class Solution { public ListNode swapPairs (ListNode head) { if (head == null || head.next == null ){ return head; } ListNode dummy = new ListNode (0 ); dummy.next = head; ListNode temp = dummy; while (temp.next != null && temp.next.next != null ) { ListNode left = temp.next; ListNode right = temp.next.next; temp.next = right; left.next = right.next; right.next = left; temp = left; } return dummy.next; } }
19.删除链表的倒数第N个节点 给你一个链表,删除链表的倒数第 n 个结点,并且返回链表的头结点。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 class Solution { public ListNode removeNthFromEnd (ListNode head, int n) { ListNode dum = new ListNode (0 ); dum.next = head; ListNode slow = dum; ListNode fast = dum; while (n-- > 0 ){ fast = fast.next; } ListNode pre = null ; while (fast != null ){ pre = slow; slow = slow.next; fast = fast.next; } pre.next = slow.next; return dum.next; } }
[面试题02.07] 链表相交 给你两个单链表的头节点 headA 和 headB ,请你找出并返回两个单链表相交的起始节点。如果两个链表没有交点,返回 null 。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 public class Solution { public ListNode getIntersectionNode (ListNode headA, ListNode headB) { if (headA == null || headB == null ){ return null ; } ListNode a = headA; ListNode b = headB; while (a != b){ a = a == null ? headB : a.next; b = b == null ? headA : b.next; } return a; } }
142.环形链表II 给定一个链表,返回链表开始入环的第一个节点。 如果链表无环,则返回 null。为了表示给定链表中的环,使用整数 pos 来表示链表尾连接到链表中的位置(索引从 0 开始)。 如果 pos 是 -1,则在该链表中没有环。
说明:不允许修改给定的链表。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 public class Solution { public ListNode detectCycle (ListNode head) { if (head == null || head.next == null ){ return null ; } ListNode fast = head; ListNode slow = head; while (fast.next != null && fast.next.next != null ){ fast = fast.next.next; slow = slow.next; if (fast == slow){ fast = head; while (fast != slow){ fast = fast.next; slow = slow.next; } return fast; } } return null ; } }
三、哈希表 242.有效的字母异位词 给定两个字符串 s 和 t ,编写一个函数来判断 t 是否是 s 的字母异位词。
示例 1: 输入: s = “anagram”, t = “nagaram” 输出: true
示例 2: 输入: s = “rat”, t = “car” 输出: false
说明: 你可以假设字符串只包含小写字母。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 class Solution { public boolean isAnagram (String s, String t) { int [] record = new int [26 ]; for (char c : s.toCharArray()) { record[c - 'a' ]++; } for (char c : t.toCharArray()){ record[c - 'a' ]--; } for (int count : record){ if (count != 0 ){ return false ; } } return true ; } }
383.赎金信 给定一个赎金信 (ransom) 字符串和一个杂志(magazine)字符串,判断第一个字符串 ransom 能不能由第二个字符串 magazines 里面的字符构成。如果可以构成,返回 true ;否则返回 false。
(题目说明:为了不暴露赎金信字迹,要从杂志上搜索各个需要的字母,组成单词来表达意思。杂志字符串中的每个字符只能在赎金信字符串中使用一次。)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 class Solution { public boolean canConstruct (String ransomNote, String magazine) { int [] record = new int [26 ]; for (char c : magazine.toCharArray()){ record[c - 'a' ] ++; } for (char c : ransomNote.toCharArray()){ record[c - 'a' ] --; } for (int count : record){ if (count < 0 ){ return false ; } } return true ; } }
49.字母异位词分组 给你一个字符串数组,请你将 字母异位词 组合在一起。可以按任意顺序返回结果列表。
字母异位词 是由重新排列源单词的字母得到的一个新单词,所有源单词中的字母通常恰好只用一次。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 class Solution { public List<List<String>> groupAnagrams (String[] strs) { Map<String, List<String>> map = new HashMap <>(); for (String str : strs){ char [] arr = str.toCharArray(); Arrays.sort(arr); String key = new String (arr); List<String> list = map.getOrDefault(key, new ArrayList <String>()); list.add(str); map.put(key,list); } return new ArrayList <List<String>>(map.values()); } }
438.找到字符串中所有字母异位词 给定两个字符串 s 和 p,找到 s 中所有 p 的 异位词 的子串,返回这些子串的起始索引。不考虑答案输出的顺序。
异位词 指由相同字母重排列形成的字符串(包括相同的字符串)。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 class Solution { public List<Integer> findAnagrams (String s, String p) { List<Integer> lists = new ArrayList <>(); int lens = s.length(), lenp = p.length(); if (lens < lenp){ return lists; } int [] record = new int [26 ]; for (int i = 0 ; i < lenp; i++){ record[s.charAt(i) - 'a' ]--; record[p.charAt(i) - 'a' ]++; } if (isDiffer(record)){ lists.add(0 ); } for (int i = lenp; i < lens; i++){ record[s.charAt(i - lenp) - 'a' ]++; record[s.charAt(i) - 'a' ]--; if (isDiffer(record)){ lists.add(i - lenp + 1 ); } } return lists; } public boolean isDiffer (int [] record) { for (int i = 0 ; i < 26 ; i++){ if (record[i] != 0 ){ return false ; } } return true ; } }
349.两个数组的交集 题意:给定两个数组,编写一个函数来计算它们的交集。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 class Solution { public int [] intersection(int [] nums1, int [] nums2) { if (nums1 == null || nums1.length == 0 || nums2 == null || nums2.length == 0 ){ return new int [0 ]; } Set<Integer> set = new HashSet <>(); Set<Integer> res = new HashSet <>(); for (int num : nums1){ set.add(num); } for (int i : nums2){ if (set.contains(i)){ res.add(i); } } return res.stream().mapToInt(x -> x).toArray(); } }
350.两个数组的交集II 给你两个整数数组 nums1 和 nums2 ,请你以数组形式返回两数组的交集。返回结果中每个元素出现的次数,应与元素在两个数组中都出现的次数一致(如果出现次数不一致,则考虑取较小值)。可以不考虑输出结果的顺序。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 class Solution { public int [] intersect(int [] nums1, int [] nums2) { Arrays.sort(nums1); Arrays.sort(nums2); int len1 = nums1.length, len2 = nums2.length; int [] intersection = new int [Math.min(len1,len2)]; int index1 = 0 , index2 = 0 , index = 0 ; while (index1 < len1 && index2 < len2){ if (nums1[index1] < nums2[index2]){ index1++; }else if (nums1[index1] > nums2[index2]){ index2++; }else { intersection[index] = nums1[index1]; index++; index1++; index2++; } } return Arrays.copyOfRange(intersection, 0 , index); } }
202.快乐数 编写一个算法来判断一个数 n 是不是快乐数。
「快乐数」 定义为:
对于一个正整数,每一次将该数替换为它每个位置上的数字的平方和。
然后重复这个过程直到这个数变为 1,也可能是 无限循环 但始终变不到 1。
如果这个过程 结果为 1,那么这个数就是快乐数。
如果 n 是 快乐数 就返回 true ;不是,则返回 false 。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 class Solution { public boolean isHappy (int n) { Set<Integer> set = new HashSet <>(); while (n != 1 && !set.contains(n)){ set.add(n); n = getNext(n); } return n == 1 ; } public int getNext (int n) { int total = 0 ; while (n > 0 ){ int digit = n % 10 ; n = n / 10 ; total += digit * digit; } return total; } }
1.两数之和 给定一个整数数组 nums 和一个整数目标值 target,请你在该数组中找出 和为目标值 target两个 整数,并返回它们的数组下标。你可以假设每种输入只会对应一个答案。但是,数组中同一个元素在答案里不能重复出现。
你可以按任意顺序返回答案。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 class Solution { public int [] twoSum(int [] nums, int target) { Map<Integer,Integer> map = new HashMap <>(); for (int i = 0 ; i < nums.length; i++){ int tmp = target - nums[i]; if (map.containsKey(tmp)){ res[1 ] = i; res[0 ] = map.get(tmp); } map.put(nums[i], i); } return res; } }
454.四数相加II 给定四个包含整数的数组列表 A , B , C , D ,计算有多少个元组 (i, j, k, l) ,使得 A[i] + B[j] + C[k] + D[l] = 0。为了使问题简单化,所有的 A, B, C, D 具有相同的长度 N,且 0 ≤ N ≤ 500 。所有整数的范围在 -2^28 到 2^28 - 1 之间,最终结果不会超过 2^31 - 1 。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 class Solution { public int fourSumCount (int [] nums1, int [] nums2, int [] nums3, int [] nums4) { Map<Integer,Integer> map = new HashMap <>(); for (int a : nums1){ for (int b : nums2){ map.put(a + b, map.getOrDefault(a + b, 0 ) + 1 ); } } int ans = 0 ; for (int c : nums3){ for (int d : nums4){ if (map.containsKey(- (c + d))){ ans += map.get(-(c + d)); } } } return ans; } }
15.三数相加 给你一个包含 n 个整数的数组 nums,判断 nums 中是否存在三个元素 a,b,c ,使得 a + b + c = 0 ?请你找出所有满足条件且不重复的三元组。
注意: 答案中不可以包含重复的三元组。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 class Solution { public List<List<Integer>> threeSum (int [] nums) { List<List<Integer>> lists = new ArrayList <>(); if (nums == null || nums.length < 3 ) { return lists; } int len = nums.length; Arrays.sort(nums); for (int i = 0 ; i < len; i++){ if (nums[i] > 0 ){ return lists; } if (i > 0 && nums[i] == nums[i - 1 ]){ continue ; } int cur = nums[i]; int left = i + 1 , right = len - 1 ; while (left < right){ int tmp = cur + nums[left] + nums[right]; if (tmp == 0 ){ List<Integer> list = new ArrayList <>(); list.add(cur); list.add(nums[left]); list.add(nums[right]); lists.add(list); while (left < right && nums[left + 1 ] == nums[left]){ ++left; } while (left < right && nums[right - 1 ] == nums[right]){ --right; } ++left; --right; }else if (tmp > 0 ){ --right; }else { ++left; } } } return lists; } }
18.四数之和 题意:给定一个包含 n 个整数的数组 nums 和一个目标值 target,判断 nums 中是否存在四个元素 a,b,c 和 d ,使得 a + b + c + d 的值与 target 相等?找出所有满足条件且不重复的四元组。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 class Solution { public List<List<Integer>> fourSum (int [] nums, int target) { List<List<Integer>> lists = new ArrayList <>(); Arrays.sort(nums); int len = nums.length; for (int i = 0 ; i < len; i++){ if (nums[i] > target && nums[i] > 0 ){ return lists; } if (i > 0 && nums[i - 1 ] == nums[i]){ continue ; } for (int j = i + 1 ; j < len; j++){ if (j > i + 1 && nums[j - 1 ] == nums[j]){ continue ; } int left = j + 1 ; int right = len - 1 ; while (left < right){ long sum = nums[i] + nums[j] + nums[left] + nums[right]; if (sum == target){ lists.add(Arrays.asList(nums[i],nums[j],nums[left],nums[right])); while (left < right && nums[left + 1 ] == nums[left]){ ++left; } while (left < right && nums[right - 1 ] == nums[right]){ --right; } ++left; --right; }else if (sum > target){ --right; }else { ++left; } } } } return lists; } }
四、字符串 344.反转字符串 编写一个函数,其作用是将输入的字符串反转过来。输入字符串以字符数组 s 的形式给出。
不要给另外的数组分配额外的空间,你必须原地修改输入数组 、使用 O(1) 的额外空间解决这一问题。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 class Solution { public void reverseString (char [] s) { int left = 0 ; int right = s.length - 1 ; while (left < right){ s[left] ^= s[right]; s[right] ^= s[left]; s[left] ^= s[right]; left++; right--; } } }
541.反转字符串II 给定一个字符串 s 和一个整数 k,从字符串开头算起,每计数至 2k 个字符,就反转这 2k 字符中的前 k 个字符。
如果剩余字符少于 k 个,则将剩余字符全部反转。
如果剩余字符小于 2k 但大于或等于 k 个,则反转前 k 个字符,其余字符保持原样。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 class Solution { public String reverseStr (String s, int k) { char [] cs = s.toCharArray(); int len = s.length(); for (int left = 0 ; left < len; left = left + 2 * k){ int right = left + k - 1 ; swap(cs, left, Math.min(right, len - 1 )); } return String.valueOf(cs); } public void swap (char [] cs, int left, int right) { while (left < right){ cs[left] ^= cs[right]; cs[right] ^= cs[left]; cs[left] ^= cs[right]; left++; right--; } } }
[剑指offer 05] 替换空格 请实现一个函数,把字符串 s 中的每个空格替换成”%20”。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 class Solution { public String replaceSpace (String s) { int len = s.length(); char [] arr = new char [len * 3 ]; int index = 0 ; for (int i = 0 ; i < len; i++){ char x = s.charAt(i); if (x == ' ' ){ arr[index++] = '%' ; arr[index++] = '2' ; arr[index++] = '0' ; }else { arr[index++] = x; } } return new String (arr, 0 , index); } }
151.反转字符串中的单词 给你一个字符串 s ,请你反转字符串中 单词 的顺序。单词 是由非空格字符组成的字符串。s 中使用至少一个空格将字符串中的 单词 分隔开。返回 单词 顺序颠倒且 单词 之间用单个空格连接的结果字符串。
注意: 输入字符串 s中可能会存在前导空格、尾随空格或者单词间的多个空格。返回的结果字符串中,单词间应当仅用单个空格分隔,且不包含任何额外的空格。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 class Solution { public String reverseWords (String s) { if (s == null || s.length() == 0 ){ return "" ; } String[] arr = s.trim().split(" " ); StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder (); int len = arr.length; for (int i = len - 1 ; i >= 0 ; i--){ if (arr[i].equals("" )){ continue ; } if (i == 0 ){ sb.append(arr[i]); }else { sb.append(arr[i]).append(" " ); } } return sb.toString(); } }
[剑指offer 58 - II] 左旋转字符串 字符串的左旋转操作是把字符串前面的若干个字符转移到字符串的尾部。请定义一个函数实现字符串左旋转操作的功能。
比如,输入字符串”abcdefg”和数字2,该函数将返回左旋转两位得到的结果”cdefgab”。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 class Solution { public String reverseLeftWords (String s, int n) { return s.substring(n,s.length()) + s.substring(0 ,n); } }
28.找出字符串中第一个匹配项的下标 给你两个字符串 haystack 和 needle ,请你在 haystack 字符串中找出 needle 字符串的第一个匹配项的下标(下标从 0 开始)。如果 needle 不是 haystack 的一部分,则返回 -1 。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 class Solution { public int strStr (String haystack, String needle) { if (needle == null || needle.length() == 0 ){ return 0 ; } int hlen = haystack.length(); int nlen = needle.length(); if (hlen < nlen){ return -1 ; } char [] ch = haystack.toCharArray(); char [] cn = needle.toCharArray(); for (int i = 0 ; i <= hlen - nlen; i++){ int h = i, n = 0 ; while (n < nlen && ch[h] == cn[n]){ h++; n++; } if (n == nlen){ return i; } } return -1 ; } }
459.重复的子字符串 给定一个非空的字符串 s ,检查是否可以通过由它的一个子串重复多次构成。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 class Solution { public boolean repeatedSubstringPattern (String s) { int len = s.length(); if (len == 0 ){ return false ; } int [] next = getNext(s); int maxLen = next[len - 1 ] + 1 ; if (maxLen == 0 || s.charAt(len - 1 ) != s.charAt(len - 1 - maxLen)){ return false ; } return len % (len - maxLen) == 0 ; } public int [] getNext(String s){ int i = 0 ; int j = -1 ; int len = s.length(); int [] next = new int [len]; next[0 ] = -1 ; while (i < len - 1 ){ if (j == -1 || s.charAt(i) == s.charAt(j)){ i += 1 ; j += 1 ; next[i] = j; }else { j = next[j]; } } return next; } }
五、栈和队列 232.用栈实现队列 请你仅使用两个栈实现先入先出队列。队列应当支持一般队列支持的所有操作(push、pop、peek、empty):
实现 MyQueue 类:
void push(int x) 将元素 x 推到队列的末尾int pop() 从队列的开头移除并返回元素int peek() 返回队列开头的元素boolean empty() 如果队列为空,返回 true ;否则,返回 false
说明:
你 只能 使用标准的栈操作 —— 也就是只有 push to top, peek/pop from top, size, 和 is empty 操作是合法的。
你所使用的语言也许不支持栈。你可以使用 list 或者 deque(双端队列)来模拟一个栈,只要是标准的栈操作即可。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 import java.util.Stack;class MyQueue { private Stack<Integer> stackPush; private Stack<Integer> stackPop; public MyQueue () { stackPush = new Stack <>(); stackPop = new Stack <>(); } public void push (int x) { stackPush.push(x); } public int pop () { dumpStack(); return stackPop.pop(); } public int peek () { dumpStack(); return stackPop.peek(); } public boolean empty () { return stackPush.isEmpty() && stackPop.isEmpty(); } private void dumpStack () { if (stackPop.isEmpty()){ while (!stackPush.isEmpty()){ stackPop.push(stackPush.pop()); } } } }
225.用队列实现栈 请你仅使用两个队列实现一个后入先出(LIFO)的栈,并支持普通栈的全部四种操作(push、top、pop 和 empty)。
实现 MyStack 类:
void push(int x) 将元素 x 压入栈顶。int pop() 移除并返回栈顶元素。int top() 返回栈顶元素。boolean empty() 如果栈是空的,返回 true ;否则,返回 false 。
注意:
你只能使用队列的基本操作 —— 也就是 push to back、peek/pop from front、size 和 is empty 这些操作。
你所使用的语言也许不支持队列。 你可以使用 list (列表)或者 deque(双端队列)来模拟一个队列 , 只要是标准的队列操作即可。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 class MyStack { Deque<Integer> que; public MyStack () { que = new ArrayDeque <>(); } public void push (int x) { que.addLast(x); } public int pop () { return que.pollLast(); } public int top () { return que.peekLast(); } public boolean empty () { return que.isEmpty(); } }
20.有效的括号 给定一个只包括 '(',')','{','}','[',']' 的字符串 s ,判断字符串是否有效。
有效字符串需满足:
左括号必须用相同类型的右括号闭合。
左括号必须以正确的顺序闭合。
每个右括号都有一个对应的相同类型的左括号。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 class Solution { public boolean isValid (String s) { Deque<Character> deque = new ArrayDeque <>(); char cs; for (int i = 0 ; i < s.length(); i++){ cs = s.charAt(i); if (cs == '(' ){ deque.push(')' ); }else if (cs == '{' ){ deque.push('}' ); }else if (cs == '[' ){ deque.push(']' ); }else if (deque.isEmpty() || deque.peek() != cs){ return false ; }else { deque.pop(); } } return deque.isEmpty(); } }
1047.删除字符串中所以相邻重复项 给出由小写字母组成的字符串 S,重复项删除操作 会选择两个相邻且相同的字母,并删除它们。在 S 上反复执行重复项删除操作,直到无法继续删除。
在完成所有重复项删除操作后返回最终的字符串。答案保证唯一。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 class Solution { public String removeDuplicates (String s) { char [] cs = s.toCharArray(); int fast = 0 ; int slow = 0 ; while (fast < s.length()) { cs[slow] = cs[fast]; if (slow > 0 && cs[slow] == cs[slow - 1 ]){ slow--; }else { slow++; } fast++; } return new String (cs, 0 , slow); } }
150.逆波兰表达式 根据 逆波兰表示法 ,求表达式的值。有效的算符包括 +、-、*、/ 。每个运算对象可以是整数,也可以是另一个逆波兰表达式。
注意 两个整数之间的除法只保留整数部分。
可以保证给定的逆波兰表达式总是有效的。换句话说,表达式总会得出有效数值且不存在除数为 0 的情况。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 class Solution { public int evalRPN (String[] tokens) { Stack<Integer> stack = new Stack <>(); for (String str : tokens){ if ("+" .equals(str)){ stack.push(stack.pop() + stack.pop()); }else if ("-" .equals(str)){ stack.push(- stack.pop() + stack.pop()); }else if ("*" .equals(str)){ stack.push(stack.pop() * stack.pop()); }else if ("/" .equals(str)){ int num2 = stack.pop(); int num1 = stack.pop(); stack.push(num1 / num2); }else { stack.push(Integer.valueOf(str)); } } return stack.pop(); } }
239.滑动窗口最大值 给你一个整数数组 nums,有一个大小为 k 的滑动窗口从数组的最左侧移动到数组的最右侧。你只可以看到在滑动窗口内的 k 个数字。滑动窗口每次只向右移动一位。返回 滑动窗口中的最大值 。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 import java.util.LinkedList;class Solution { public int [] maxSlidingWindow(int [] nums, int k) { int len = nums.length; Deque<Integer> deque = new ArrayDeque <>(); int [] res = new int [len - k + 1 ]; int index = 0 ; for (int i = 0 ; i < len; i++){ while (!deque.isEmpty() && deque.peek() < i - k + 1 ){ deque.poll(); } while (!deque.isEmpty() && nums[deque.peekLast()] < nums[i]){ deque.pollLast(); } deque.offer(i); if (i - k + 1 >= 0 ){ res[index++] = nums[deque.peek()]; } } return res; } }
347.前k个高频元素 给你一个整数数组 nums 和一个整数 k ,请你返回其中出现频率前 k 高的元素。你可以按 任意顺序 返回答案。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 class Solution { public int [] topKFrequent(int [] nums, int k) { Map<Integer,Integer> map = new HashMap <>(); for (int num : nums){ map.put(num,map.getOrDefault(num,0 ) + 1 ); } PriorityQueue<int []> queue = new PriorityQueue <>((pair1,pair2) -> pair1[1 ] - pair2[1 ]); for (Map.Entry<Integer,Integer> entry : map.entrySet()){ if (queue.size() < k) { queue.add(new int []{entry.getKey(), entry.getValue()}); }else { if (entry.getValue() > queue.peek()[1 ]){ queue.poll(); queue.add(new int []{entry.getKey(), entry.getValue()}); } } } int [] ans = new int [k]; for (int i = k - 1 ; i >= 0 ; i--){ ans[i] = queue.poll()[0 ]; } return ans; } }
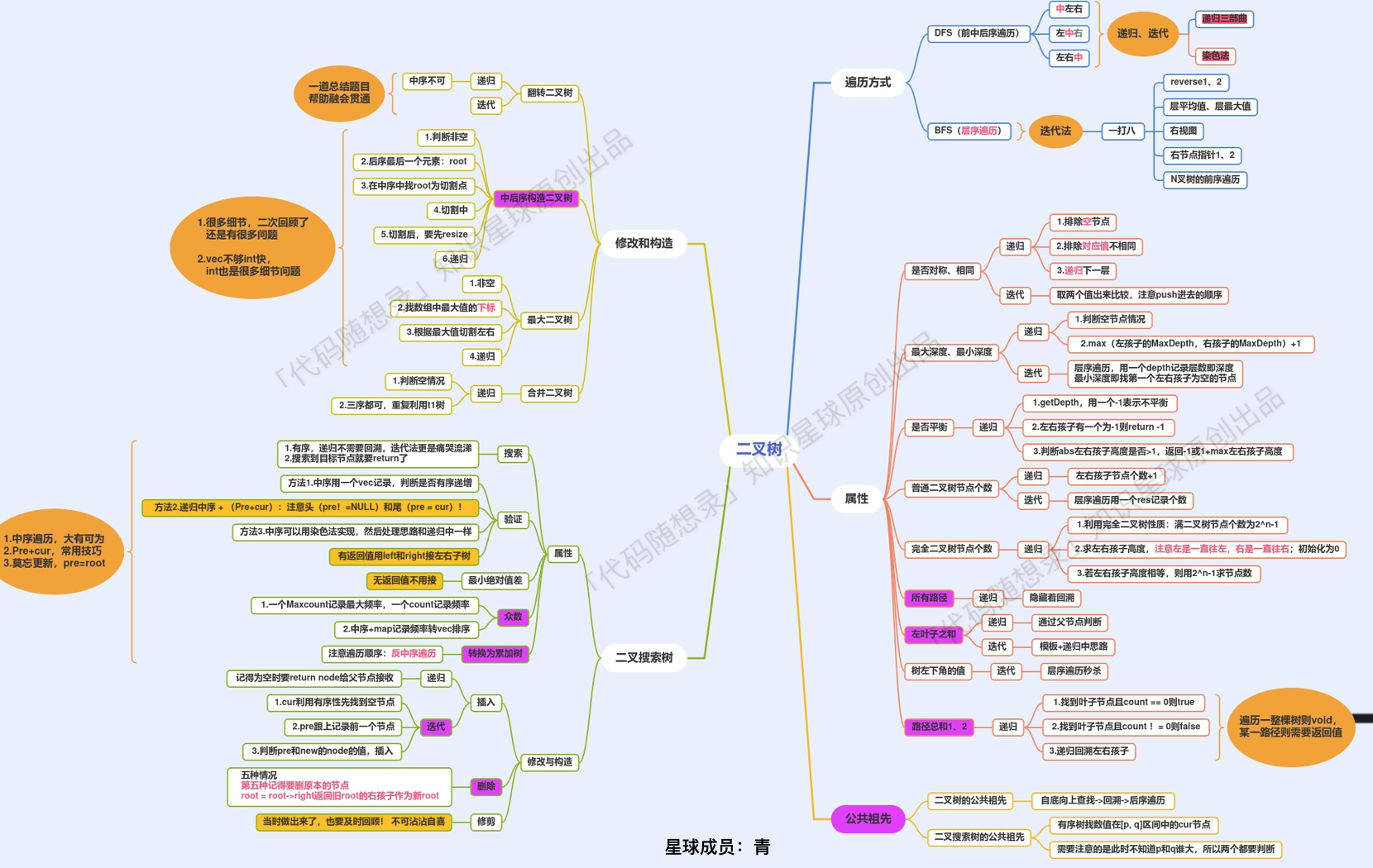
六、二叉树
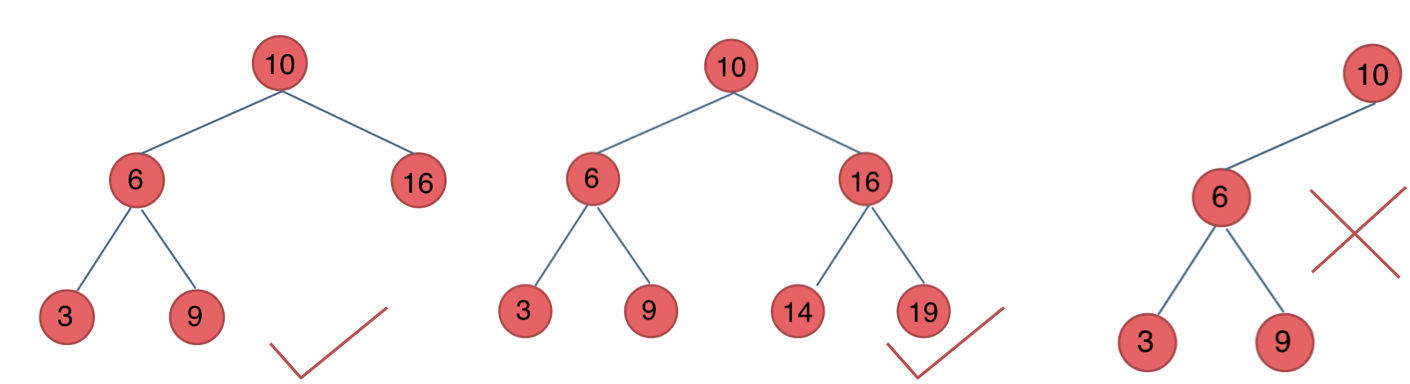
二叉树理论基础 1.二叉树的种类 满二叉树 如果一棵二叉树只有度为0的结点和度为2的结点,并且度为0的结点在同一层上,则这棵二叉树为满二叉树。
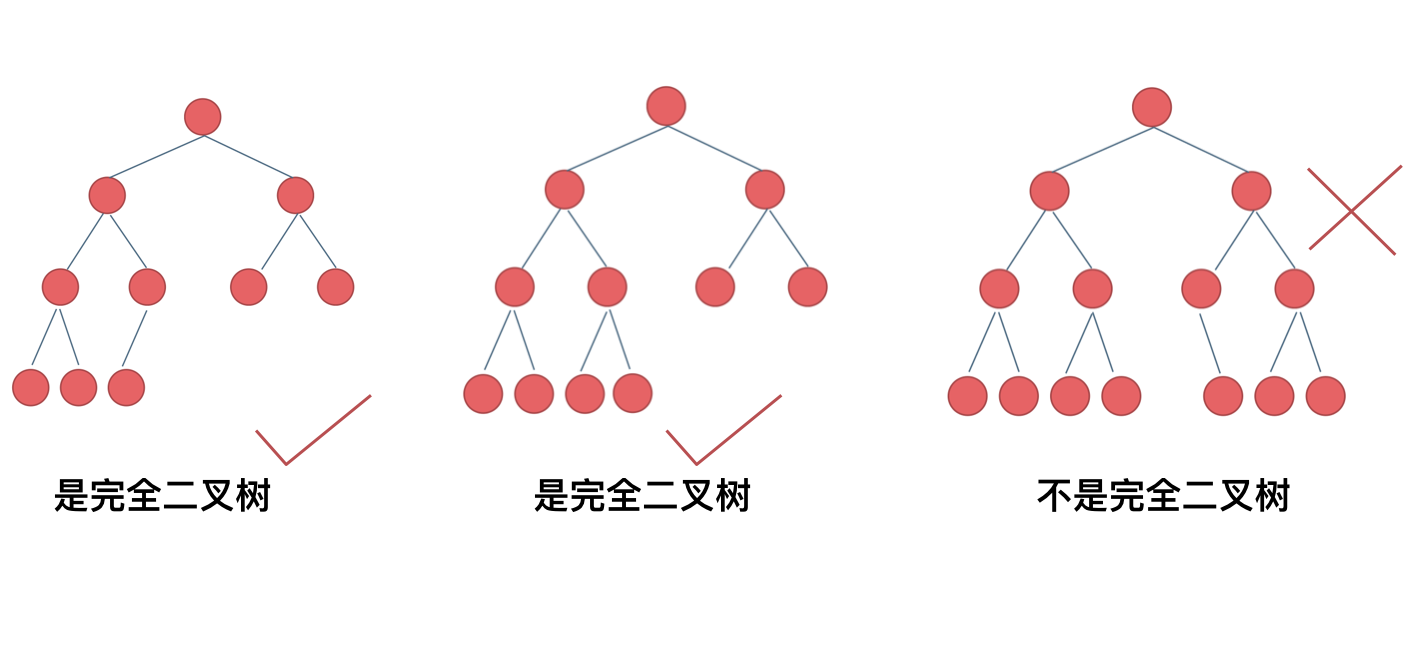
完全二叉树 在完全二叉树中,除了最底层节点可能没填满外,其余每层节点数都达到最大值,并且最下面一层的节点都集中在该层最左边的若干位置。若最底层为第 h 层,则该层包含 1~ 2^(h-1) 个节点。
二叉搜索树 前面介绍的树,都没有数值的,而二叉搜索树是有数值的了,二叉搜索树是一个有序树。
若它的左子树不空,则左子树上所有结点的值均小于它的根结点的值;
若它的右子树不空,则右子树上所有结点的值均大于它的根结点的值;
它的左、右子树也分别为二叉排序树
平衡二叉搜索树 空树或它的左右两个子树的高度差的绝对值不超过1,并且左右两个子树都是一棵平衡二叉树。
2.二叉树的存储方式 二叉树可以链式 存储,也可以顺序 存储。链式存储方式就用指针 , 顺序存储的方式就是用数组 。
如果使用数组 存储二叉树,有 如果父节点的数组下标是 i,那么它的左孩子就是 i * 2 + 1,右孩子就是 i * 2 + 2。
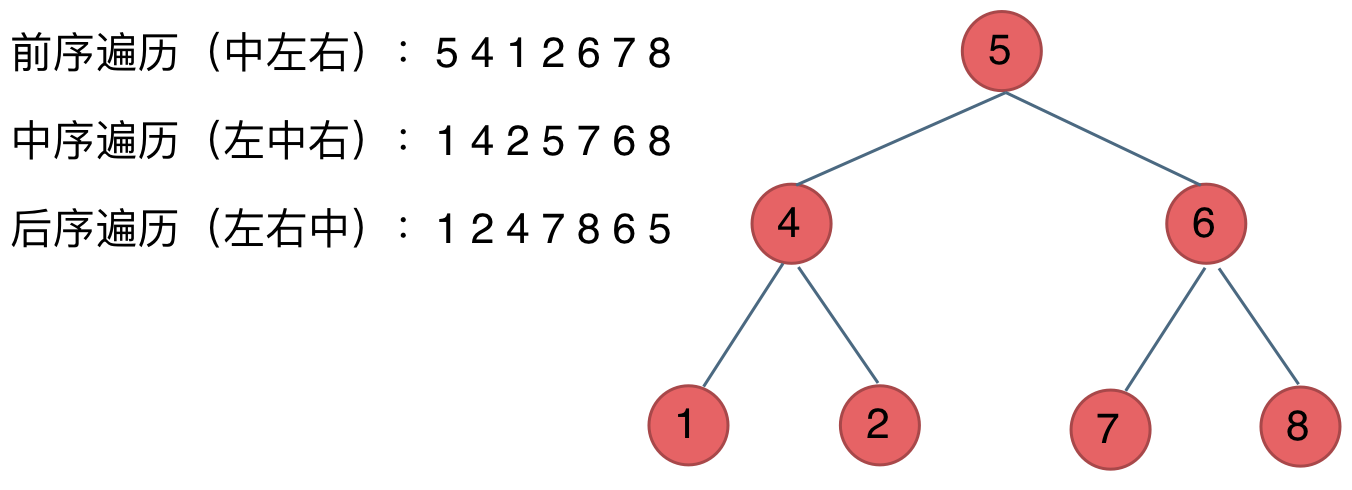
3.二叉树的遍历方式 二叉树主要有两种遍历方式:
深度优先遍历(dfs):先往深走,遇到叶子节点再往回走
前序遍历(递归,迭代)–> 中左右
中序遍历(递归,迭代)–> 左中右
后序遍历(递归,迭代)–> 左右中
广度优先遍历(bfs):一层一层的遍历
4.二叉树的代码实现 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 public class TreeNode { int val; TreeNode left; TreeNode right; TreeNode() {} TreeNode(int val) { this .val = val; } TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) { this .val = val; this .left = left; this .right = right; } }
二叉树的递归遍历 144.二叉树的前序遍历(递归) 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 class Solution { public List<Integer> preorderTraversal (TreeNode root) { List<Integer> result = new ArrayList <Integer>(); preorder(root, result); return result; } public void preorder (TreeNode root, List<Integer> result) { if (root == null ) { return ; } result.add(root.val); preorder(root.left, result); preorder(root.right, result); } }
589.N叉树的前序遍历(递归) 给定一个 n 叉树的根节点 root ,返回 其节点值的 前序遍历 。
n 叉树 在输入中按层序遍历进行序列化表示,每组子节点由空值 null 分隔(请参见示例)。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 class Solution { public List<Integer> preorder (Node root) { List<Integer> res = new ArrayList <>(); preorder(root,res); return res; } public void preorder (Node root, List<Integer> res) { if (root != null ){ res.add(root.val); List<Node> child = root.children; for (int i = 0 ; i < child.size(); i++){ preorder(child.get(i),res); } } } }
94.二叉树的中序遍历(递归) 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 class Solution { public List<Integer> inorderTraversal (TreeNode root) { List<Integer> res = new ArrayList <>(); inorder(root, res); return res; } void inorder (TreeNode root, List<Integer> list) { if (root == null ) { return ; } inorder(root.left, list); list.add(root.val); inorder(root.right, list); } }
145.二叉树的后序遍历(递归) 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 class Solution { public List<Integer> postorderTraversal (TreeNode root) { List<Integer> res = new ArrayList <>(); postorder(root, res); return res; } void postorder (TreeNode root, List<Integer> list) { if (root == null ) { return ; } postorder(root.left, list); postorder(root.right, list); list.add(root.val); } }
590.N叉树的后序遍历(递归) 给定一个 n 叉树的根节点 root ,返回 其节点值的 后序遍历 。n 叉树 在输入中按层序遍历进行序列化表示,每组子节点由空值 null 分隔
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 class Solution { List<Integer> res = new ArrayList <>(); public List<Integer> postorder (Node root) { postOrder(root); return res; } public void postOrder (Node root) { if (root == null ){ return ; } for (Node child : root.children){ postorder(child); } res.add(root.val); return ; } }
二叉树的迭代遍历 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 class Solution { public List<Integer> preorderTraversal (TreeNode root) { List<Integer> result = new ArrayList <>(); if (root == null ){ return result; } Stack<TreeNode> stack = new Stack <>(); stack.push(root); while (!stack.isEmpty()){ TreeNode node = stack.pop(); result.add(node.val); if (node.right != null ){ stack.push(node.right); } if (node.left != null ){ stack.push(node.left); } } return result; } }
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 class Solution { public List<Integer> inorderTraversal (TreeNode root) { List<Integer> result = new ArrayList <>(); if (root == null ){ return result; } Stack<TreeNode> stack = new Stack <>(); TreeNode cur = root; while (cur != null || !stack.isEmpty()){ if (cur != null ){ stack.push(cur); cur = cur.left; }else { cur = stack.pop(); result.add(cur.val); cur = cur.right; } } return result; } }
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 class Solution { public List<Integer> postorderTraversal (TreeNode root) { List<Integer> result = new ArrayList <>(); if (root == null ){ return result; } Stack<TreeNode> stack = new Stack <>(); stack.push(root); while (!stack.isEmpty()){ TreeNode node = stack.pop(); result.add(node.val); if (node.left != null ){ stack.push(node.left); } if (node.right != null ){ stack.push(node.right); } } Collections.reverse(result); return result; } }
二叉树的统一迭代法 144.二叉树的前序遍历(迭代) 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 class Solution { public List<Integer> preorderTraversal (TreeNode root) { List<Integer> result = new LinkedList <>(); Stack<TreeNode> st = new Stack <>(); if (root != null ) st.push(root); while (!st.empty()) { TreeNode node = st.peek(); if (node != null ) { st.pop(); if (node.right!=null ) st.push(node.right); if (node.left!=null ) st.push(node.left); st.push(node); st.push(null ); } else { st.pop(); node = st.peek(); st.pop(); result.add(node.val); } } return result; } }
590.N叉树的后序遍历(迭代) 通过迭代前序遍历逆序进行
给定一个 n 叉树的根节点 root ,返回 其节点值的 后序遍历 。n 叉树 在输入中按层序遍历进行序列化表示,每组子节点由空值 null 分隔
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 public List<Integer> postorder (Node root) { List<Integer> res = new ArrayList <>(); if (root == null ){ return res; } Deque<Node> queue = new LinkedList <>(); queue.offer(root); while (!queue.isEmpty()){ int size = queue.size(); Node cur = queue.pollLast(); res.add(cur.val); for (Node child : cur.children){ queue.offer(child); } } Collections.reverse(res); return res; }
94.二叉树的中序遍历(迭代) 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 class Solution { public List<Integer> inorderTraversal (TreeNode root) { List<Integer> result = new LinkedList <>(); Stack<TreeNode> st = new Stack <>(); if (root != null ) st.push(root); while (!st.empty()) { TreeNode node = st.peek(); if (node != null ) { st.pop(); if (node.right!=null ) st.push(node.right); st.push(node); st.push(null ); if (node.left!=null ) st.push(node.left); } else { st.pop(); node = st.peek(); st.pop(); result.add(node.val); } } return result; } }
145.二叉树的后序遍历(迭代) 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 class Solution { public List<Integer> postorderTraversal (TreeNode root) { List<Integer> result = new LinkedList <>(); Stack<TreeNode> st = new Stack <>(); if (root != null ) st.push(root); while (!st.empty()) { TreeNode node = st.peek(); if (node != null ) { st.pop(); st.push(node); st.push(null ); if (node.right!=null ) st.push(node.right); if (node.left!=null ) st.push(node.left); } else { st.pop(); node = st.peek(); st.pop(); result.add(node.val); } } return result; } }
二叉树的层序遍历 102.二叉树的层序遍历 给你一个二叉树,请你返回其按 层序遍历 得到的节点值。 (即逐层地,从左到右访问所有节点)。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 class Solution { public List<List<Integer>> resList = new ArrayList <List<Integer>>(); public List<List<Integer>> levelOrder (TreeNode root) { checkFun01(root,0 ); return resList; } public void checkFun01 (TreeNode node, Integer deep) { if (node == null ) return ; deep++; if (resList.size() < deep) { List<Integer> item = new ArrayList <Integer>(); resList.add(item); } resList.get(deep - 1 ).add(node.val); checkFun01(node.left, deep); checkFun01(node.right, deep); } public void checkFun02 (TreeNode node) { if (node == null ) return ; Queue<TreeNode> que = new LinkedList <TreeNode>(); que.offer(node); while (!que.isEmpty()) { List<Integer> itemList = new ArrayList <Integer>(); int len = que.size(); while (len > 0 ) { TreeNode tmpNode = que.poll(); itemList.add(tmpNode.val); if (tmpNode.left != null ) que.offer(tmpNode.left); if (tmpNode.right != null ) que.offer(tmpNode.right); len--; } resList.add(itemList); } } }
107.二叉树的层次遍历II 给你二叉树的根节点 root ,返回其节点值 自底向上的层序遍历 。 (即按从叶子节点所在层到根节点所在的层,逐层从左向右遍历)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 class Solution { List<List<Integer>> resList = new ArrayList <>(); public List<List<Integer>> levelOrderBottom (TreeNode root) { if (root == null ){ return resList; } Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList <>(); queue.offer(root); TreeNode cur; while (!queue.isEmpty()){ int len = queue.size(); List<Integer> list = new ArrayList <>(); for (int i = 0 ; i < len; i++){ cur = queue.poll(); list.add(cur.val); if (cur.left != null ){ queue.offer(cur.left); } if (cur.right != null ){ queue.offer(cur.right); } } resList.add(list); } List<List<Integer>> res = new ArrayList <>(); for (int i = resList.size() - 1 ; i >= 0 ; i--){ res.add(resList.get(i)); } return res; } }
199.二叉树的右视图 给定一个二叉树的 根节点 root,想象自己站在它的右侧,按照从顶部到底部的顺序,返回从右侧所能看到的节点值
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 class Solution { public List<Integer> rightSideView (TreeNode root) { List<Integer> res = new ArrayList <>(); if (root == null ){ return res; } Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList <>(); queue.offer(root); while (!queue.isEmpty()){ int size = queue.size(); for (int i = 0 ; i < size; i++){ TreeNode cur = queue.poll(); if (i == size - 1 ){ res.add(cur.val); } if (cur.left != null ){ queue.offer(cur.left); } if (cur.right != null ){ queue.offer(cur.right); } } } return res; } }
637.二叉树的层平均值 给定一个非空二叉树的根节点 root , 以数组的形式返回每一层节点的平均值。与实际答案相差 10-5 以内的答案可以被接受。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 class Solution { public List<Double> averageOfLevels (TreeNode root) { List<Double> list = new ArrayList <>(); if (root == null ){ return list; } Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList <>(); queue.offer(root); while (!queue.isEmpty()){ int size = queue.size(); double sum = 0.0 ; for (int i = 0 ; i < size; i++){ TreeNode cur = queue.poll(); sum += cur.val; if (i == size - 1 ) { sum /= size; } if (cur.left != null ){ queue.offer(cur.left); } if (cur.right != null ){ queue.offer(cur.right); } } list.add(sum); } return list; } }
429.N叉树的层序遍历 给定一个 N 叉树,返回其节点值的层序遍历 。(即从左到右,逐层遍历)。树的序列化输入是用层序遍历,每组子节点都由 null 值分隔。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 class Solution { public List<List<Integer>> levelOrder (Node root) { List<List<Integer>> resList = new ArrayList <>(); if (root == null ){ return resList; } Deque<Node> deque = new LinkedList <>(); deque.offer(root); while (!deque.isEmpty()){ int size = deque.size(); List<Integer> list = new ArrayList <>(); for (int i = 0 ; i < size; i++) { Node cur = deque.pollFirst(); list.add(cur.val); List<Node> children = cur.children; if (children == null || children.size() == 0 ){ continue ; } for (Node child : children){ if (child != null ){ deque.offer(child); } } } resList.add(list); } return resList; } }
515.在每个树行中找最大值 给定一棵二叉树的根节点 root ,请找出该二叉树中每一层的最大值。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 class Solution { public List<Integer> largestValues (TreeNode root) { List<Integer> resList = new ArrayList <>(); if (root == null ){ return resList; } Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList <>(); queue.offer(root); while (!queue.isEmpty()){ int size = queue.size(); int num = Integer.MIN_VALUE; for (int i = 0 ; i < size; i++){ TreeNode cur = queue.poll(); num = Math.max(num, cur.val); if (cur.left != null ){ queue.offer(cur.left); } if (cur.right != null ){ queue.offer(cur.right); } } resList.add(num); } return resList; } }
116.填充每个节点的下一个右侧节点指针 给定一个 完美二叉树 ,其所有叶子节点都在同一层,每个父节点都有两个子节点。二叉树定义如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 struct Node { int val; Node *left; Node *right; Node *next; }
填充它的每个 next 指针,让这个指针指向其下一个右侧节点。如果找不到下一个右侧节点,则将 next 指针设置为 NULL。
初始状态下,所有 next 指针都被设置为 NULL。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 class Solution { public Node connect (Node root) { Queue<Node> queue = new LinkedList <>(); if (root != null ) { queue.offer(root); } while (queue.size() != 0 ) { int size = queue.size(); Node cur = queue.poll(); if (cur.left != null ) { queue.offer(cur.left); } if (cur.right != null ) { queue.offer(cur.right); } for (int j = 1 ; j < size; j++) { Node next = queue.poll(); if (next.left != null ) { queue.offer(next.left); } if (next.right != null ) { queue.offer(next.right); } cur.next = next; cur = next; } } return root; } }
117.填充每个节点的下一个右侧节点指针II 给定一个二叉树(和116相比,非完全二叉树)
1 2 3 4 5 6 struct Node { int val; Node *left; Node *right; Node *next; }
填充它的每个 next 指针,让这个指针指向其下一个右侧节点。如果找不到下一个右侧节点,则将 next 指针设置为 NULL。
初始状态下,所有 next 指针都被设置为 NULL。
代码可以直接沿用116 :
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 class Solution { public Node connect (Node root) { Queue<Node> queue = new LinkedList <>(); if (root != null ) { queue.offer(root); } while (queue.size() != 0 ) { int size = queue.size(); Node cur = queue.poll(); if (cur.left != null ) { queue.offer(cur.left); } if (cur.right != null ) { queue.offer(cur.right); } for (int j = 1 ; j < size; j++) { Node next = queue.poll(); if (next.left != null ) { queue.offer(next.left); } if (next.right != null ) { queue.offer(next.right); } cur.next = next; cur = next; } } return root; } }
104.二叉树的最大深度 给定一个二叉树,找出其最大深度。二叉树的深度为根节点到最远叶子节点的最长路径上的节点数。
说明: 叶子节点是指没有子节点的节点。
递归方法:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 class Solution { public int maxDepth (TreeNode root) { if (root == null ){ return 0 ; } return deepLen(root,1 ); } public int deepLen (TreeNode root,int len) { if (root == null ){ return len-1 ; } return Math.max(deepLen(root.left,len+1 ),deepLen(root.right,len+1 )); } }
递归方法(DFS版):
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 int maxDep = 0 ;public int maxDepth (TreeNode root) { countDep(root,0 ); return maxDep; } public void countDep (TreeNode root, int dep) { if (root == null ){ return ; } dep++; maxDep = Math.max(maxDep, dep); countDep(root.left, dep); countDep(root.right, dep); dep--; }
迭代方法:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 class Solution { public int maxDepth (TreeNode root) { if (root == null ){ return 0 ; } Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList <>(); queue.offer(root); int depth = 0 ; while (!queue.isEmpty()){ int size = queue.size(); while (size > 0 ){ TreeNode node = queue.poll(); if (node.left != null ){ queue.offer(node.left); } if (node.right != null ){ queue.offer(node.right); } size--; } depth++; } return depth; } }
111.二叉树的最小深度 给定一个二叉树,找出其最小深度。最小深度是从根节点到最近叶子节点的最短路径上的节点数量。
说明: 叶子节点是指没有子节点的节点。
递归法:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 public int minDepth (TreeNode root) { if (root == null ){ return 0 ; } int leftDep = minDepth(root.left); int rightDep = minDepth(root.right); if (root.left == null ){ return rightDep + 1 ; } if (root.right == null ){ return leftDep + 1 ; } return Math.min(leftDep, rightDep) + 1 ; }
迭代法:层序遍历法
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 class Solution { public int minDepth (TreeNode root) { if (root == null ){ return 0 ; } Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList <>(); queue.offer(root); int depth = 0 ; while (!queue.isEmpty()){ int size = queue.size(); depth++; TreeNode cur = null ; for (int i = 0 ; i < size; i++){ cur = queue.poll(); if (cur.left != null ){ queue.offer(cur.left); } if (cur.right != null ){ queue.offer(cur.right); } if (cur.left == null && cur.right == null ){ return depth; } } } return depth; } }
226.翻转二叉树 给你一棵二叉树的根节点 root ,翻转这棵二叉树,并返回其根节点。
递归方法:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 class Solution { public TreeNode invertTree (TreeNode root) { if (root == null ){ return null ; } TreeNode tmp = root.right; root.right = invertTree(root.left); root.left = invertTree(tmp); return root; } }
迭代方法:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 public TreeNode invertTree (TreeNode root) { if (root == null ){ return null ; } ArrayDeque<TreeNode> deque = new ArrayDeque <>(); deque.offer(root); while (!deque.isEmpty()){ int size = deque.size(); while (size-- > 0 ){ TreeNode cur = deque.poll(); swap(cur); if (cur.left != null ){ deque.offer(cur.left); } if (cur.right != null ){ deque.offer(cur.right); } } } return root; } public void swap (TreeNode root) { TreeNode tmp = root.left; root.left = root.right; root.right = tmp; }
101.对称二叉树 给定一个二叉树,检查它是否是镜像对称的。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 class Solution { public boolean isSymmetric (TreeNode root) { if (root == null ){ return true ; } return isEquals(root.left, root.right); } public boolean isEquals (TreeNode root1, TreeNode root2) { if (root1 == null && root2 == null ){ return true ; } if (root1 == null || root2 == null ){ return false ; } return root1.val == root2.val && isEquals(root1.left, root2.right) && isEquals(root1.right, root2.left); } }
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 class Solution { public boolean isSymmetric (TreeNode root) { if (root == null ){ return true ; } return DFS(root.left, root.right); } public boolean DFS (TreeNode left, TreeNode right) { if (left == null && right == null ){ return true ; } if (left == null || right == null ){ return false ; } if (left.val != right.val){ return false ; } return DFS(left.left, right.right) && DFS(left.right, right.left); } }
222.完全二叉树的节点个数 给你一棵 完全二叉树 的根节点 root ,求出该树的节点个数。
完全二叉树 的定义如下:在完全二叉树中,除了最底层节点可能没填满外,其余每层节点数都达到最大值,并且最下面一层的节点都集中在该层最左边的若干位置。若最底层为第 h 层,则该层包含 1~ 2h 个节点。
递归法:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 class Solution { public int countNodes (TreeNode root) { if (root == null ){ return 0 ; } return countNodes(root.left) + countNodes(root.right) + 1 ; } }
迭代法:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 class Solution { public int countNodes (TreeNode root) { if (root == null ){ return 0 ; } Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList <>(); queue.offer(root); int res = 0 ; while (!queue.isEmpty()){ int size = queue.size(); while (size-- > 0 ){ TreeNode cur = queue.poll(); res++; if (cur.left != null ){ queue.offer(cur.left); } if (cur.right != null ){ queue.offer(cur.right); } } } return res; } }
针对完全二叉树(2^depth - 1) 这一特性的解法:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 class Solution { public int countNodes (TreeNode root) { if (root == null ){ return 0 ; } int leftDepth = getDepth(root.left); int rightDepth = getDepth(root.right); if (leftDepth == rightDepth){ return (1 << leftDepth) + countNodes(root.right); }else { return (1 << rightDepth) + countNodes(root.left); } } public int getDepth (TreeNode root) { int depth = 0 ; while (root != null ){ root = root.left; depth++; } return depth; } }
110.平衡二叉树 给定一个二叉树,判断它是否是高度平衡的二叉树。本题中,高度平衡二叉树定义为:一个二叉树每个节点 的左右两个子树的高度差的绝对值不超过 1 。
递归算法:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 public boolean isBalanced (TreeNode root) { return getHeight(root) != -1 ; } public int getHeight (TreeNode root) { if (root == null ){ return 0 ; } int leftHeight = getHeight(root.left); if (leftHeight == -1 ){ return -1 ; } int rightHeight = getHeight(root.right); if (rightHeight == -1 ){ return -1 ; } if (Math.abs(leftHeight - rightHeight) > 1 ){ return -1 ; } return Math.max(leftHeight, rightHeight) + 1 ; }
迭代算法:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 public boolean isBalanced (TreeNode root) { if (root == null ){ return true ; } Stack<TreeNode> stack = new Stack <>(); TreeNode pre = null ; while (root != null || !stack.isEmpty()){ while (root != null ){ stack.push(root); root = root.left; } TreeNode inNode = stack.peek(); if (inNode.right == null || inNode.right == pre){ if (Math.abs(getHeight(inNode.left) - getHeight(inNode.right)) > 1 ){ return false ; } stack.pop(); pre = inNode; root = null ; }else { root = inNode.right; } } return true ; } public int getHeight (TreeNode root) { if (root == null ){ return 0 ; } int leftHeight = root.left != null ? root.left.val : 0 ; int rightHeight = root.right != null ? root.right.val : 0 ; int height = Math.max(leftHeight, rightHeight) + 1 ; root.val = height; return height; }
257.二叉树的所有路径 递归算法:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 class Solution { public List<String> binaryTreePaths (TreeNode root) { List<String> list = new ArrayList <>(); if (root == null ){ return list; } List<Integer> paths = new ArrayList <>(); traversal(root, paths, list); return list; } public void traversal (TreeNode root, List<Integer> paths, List<String> list) { paths.add(root.val); if (root.left == null && root.right == null ){ StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder (); for (int i = 0 ; i < paths.size() - 1 ; i++){ sb.append(paths.get(i)).append("->" ); } sb.append(paths.get(paths.size() - 1 )); list.add(sb.toString()); return ; } if (root.left != null ){ traversal(root.left,paths,list); paths.remove(paths.size() - 1 ); } if (root.right != null ){ traversal(root.right,paths,list); paths.remove(paths.size() - 1 ); } } }
迭代算法:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 class Solution { public List<String> binaryTreePaths (TreeNode root) { List<String> result = new ArrayList <>(); if (root == null ) return result; Stack<Object> stack = new Stack <>(); stack.push(root); stack.push(root.val + "" ); while (!stack.isEmpty()) { String path = (String) stack.pop(); TreeNode node = (TreeNode) stack.pop(); if (node.left == null && node.right == null ) { result.add(path); } if (node.right != null ) { stack.push(node.right); stack.push(path + "->" + node.right.val); } if (node.left != null ) { stack.push(node.left); stack.push(path + "->" + node.left.val); } } return result; } }
100.相同的树 给你两棵二叉树的根节点 p 和 q ,编写一个函数来检验这两棵树是否相同。如果两个树在结构上相同,并且节点具有相同的值,则认为它们是相同的。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 class Solution { public boolean isSameTree (TreeNode p, TreeNode q) { return dfs(p, q); } public boolean dfs (TreeNode p, TreeNode q) { if (p == null && q == null ) { return true ; } if (p == null && q != null ) { return false ; } if (p != null && q == null ) { return false ; } if (p.val != q.val) { return false ; } boolean leftSame = dfs(p.left, q.left); boolean rightSame = dfs(p.right, q.right); return leftSame && rightSame; } }
572.另外一个树的子树 给你两棵二叉树 root 和 subRoot 。检验 root 中是否包含和 subRoot 具有相同结构和节点值的子树。如果存在,返回 true ;否则,返回 false 。
二叉树 tree 的一棵子树包括 tree 的某个节点和这个节点的所有后代节点。tree 也可以看做它自身的一棵子树。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 class Solution { public boolean isSubtree (TreeNode root, TreeNode subRoot) { if (root == null ){ return false ; } if (subRoot == null ){ return true ; } return dfs(root, subRoot) || isSubtree(root.left, subRoot) || isSubtree(root.right, subRoot); } public boolean dfs (TreeNode p, TreeNode q) { if (p == null && q == null ) { return true ; } if (p == null || q == null ) { return false ; } if (p.val != q.val) { return false ; } boolean leftSame = dfs(p.left, q.left); boolean rightSame = dfs(p.right, q.right); return leftSame && rightSame; } }
404.左子叶之和 给定二叉树的根节点 root ,返回所有左叶子之和。
递归算法:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 class Solution { public int sumOfLeftLeaves (TreeNode root) { if (root == null ){ return 0 ; } int leftValue = sumOfLeftLeaves(root.left); int rightValue = sumOfLeftLeaves(root.right); int mid = 0 ; if (root.left != null && root.left.left == null && root.left.right == null ){ mid = root.left.val; } int sum = mid + leftValue + rightValue; return sum; } }
迭代算法:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 class Solution { public int sumOfLeftLeaves (TreeNode root) { Stack<TreeNode> stack = new Stack <>(); if (root == null ){ return 0 ; } stack.add(root); int sum = 0 ; while (!stack.isEmpty()){ TreeNode node = stack.pop(); if (node.left != null && node.left.left == null && node.left.right == null ){ sum += node.left.val; } if (node.left != null ){ stack.add(node.left); } if (node.right != null ){ stack.add(node.right); } } return sum; } }
层序遍历算法:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 class Solution { public int sumOfLeftLeaves (TreeNode root) { if (root == null ){ return 0 ; } Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList <>(); queue.offer(root); int sum = 0 ; while (!queue.isEmpty()){ TreeNode node = queue.poll(); if (node.left != null && node.left.left == null && node.left.right == null ){ sum += node.left.val; } if (node.left != null ){ queue.offer(node.left); } if (node.right != null ){ queue.offer(node.right); } } return sum; } }
513.找树左下角的值 给定一个二叉树的 根节点 root,请找出该二叉树的 最底层 最左边 节点的值。
假设二叉树中至少有一个节点。
递归算法:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 class Solution { private int Deep = -1 ; private int value = 0 ; public int findBottomLeftValue (TreeNode root) { value = root.val; findLeftValue(root, 0 ); return value; } public void findLeftValue (TreeNode root, int deep) { if (root == null ){ return ; } if (root.left == null && root.right == null ){ if (deep > Deep){ value = root.val; Deep = deep; } } if (root.left != null ){ findLeftValue(root.left, deep + 1 ); } if (root.right != null ){ findLeftValue(root.right, deep + 1 ); } } }
迭代算法:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 class Solution { public int findBottomLeftValue (TreeNode root) { Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList <>(); queue.offer(root); int res = 0 ; while (!queue.isEmpty()){ int size = queue.size(); for (int i = 0 ; i < size; i++){ TreeNode node = queue.poll(); if (i == 0 ){ res = node.val; } if (node.left != null ){ queue.offer(node.left); } if (node.right != null ){ queue.offer(node.right); } } } return res; } }
112.路径总和 给你二叉树的根节点 root 和一个表示目标和的整数 targetSum 。判断该树中是否存在 根节点到叶子节点 的路径,这条路径上所有节点值相加等于目标和 targetSum 。如果存在,返回 true ;否则,返回 false 。
叶子节点 是指没有子节点的节点。
递归算法:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 class Solution { public boolean hasPathSum (TreeNode root, int targetSum) { if (root == null ){ return false ; } if (root.left == null && root.right == null ){ return root.val == targetSum; } return hasPathSum(root.left, targetSum - root.val) || hasPathSum(root.right, targetSum - root.val); } }
迭代算法:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 class Solution { public boolean hasPathSum (TreeNode root, int targetSum) { if (root == null ){ return false ; } Stack<TreeNode> stack1 = new Stack <>(); Stack<Integer> stack2 = new Stack <>(); stack1.push(root); stack2.push(root.val); while (!stack1.isEmpty()){ int size = stack1.size(); for (int i = 0 ; i < size; i++){ TreeNode node = stack1.pop(); int sum = stack2.pop(); if (node.left == null && node.right == null && sum == targetSum){ return true ; } if (node.right != null ){ stack1.push(node.right); stack2.push(sum + node.right.val); } if (node.left != null ){ stack1.push(node.left); stack2.push(sum + node.left.val); } } } return false ; } }
113.路径总和 - II 给你二叉树的根节点 root 和一个整数目标和 targetSum ,找出所有 从根节点到叶子节点 路径总和等于给定目标和的路径。
叶子节点 是指没有子节点的节点。
解法一:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 class Solution { List<List<Integer>> res = new ArrayList <>(); public List<List<Integer>> pathSum (TreeNode root, int targetSum) { if (root == null ){ return res; } List<Integer> path = new ArrayList <>(); preorderDfs(root, targetSum, res, path); return res; } public void preorderDfs (TreeNode root, int targetSum, List<List<Integer>> res, List<Integer> path) { path.add(root.val); if (root.left == null && root.right == null ){ if (targetSum - root.val == 0 ){ res.add(new ArrayList <>(path)); } return ; } if (root.left != null ){ preorderDfs(root.left, targetSum - root.val, res, path); path.remove(path.size() - 1 ); } if (root.right != null ){ preorderDfs(root.right, targetSum - root.val, res, path); path.remove(path.size() - 1 ); } } }
解法二:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 class Solution { List<List<Integer>> result; LinkedList<Integer> path; public List<List<Integer>> pathSum (TreeNode root, int targetSum) { result = new ArrayList <>(); path = new LinkedList <>(); traversal(root, targetSum); return result; } public void traversal (TreeNode root, int count) { if (root == null ){ return ; } path.offer(root.val); count -= root.val; if (root.left == null && root.right == null && count == 0 ){ result.add(new LinkedList <>(path)); } traversal(root.left, count); traversal(root.right, count); path.removeLast(); } }
106.从中序与后序遍历序列构造二叉树 给定两个整数数组 inorder 和 postorder ,其中 inorder 是二叉树的中序遍历, postorder 是同一棵树的后序遍历,请你构造并返回这颗 二叉树 。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 class Solution { Map<Integer, Integer> map; public TreeNode buildTree (int [] inorder, int [] postorder) { map = new HashMap <>(); for (int i = 0 ; i < inorder.length; i++){ map.put(inorder[i], i); } return findNode(inorder, 0 , inorder.length, postorder, 0 , postorder.length); } public TreeNode findNode (int [] inorder, int inStart, int inEnd, int [] postorder, int postStart, int postEnd) { if (inStart >= inEnd || postStart >= postEnd){ return null ; } int rootIndex = map.get(postorder[postEnd - 1 ]); TreeNode root = new TreeNode (inorder[rootIndex]); int lenOfLeft = rootIndex - inStart; root.left = findNode(inorder, inStart, rootIndex, postorder, postStart, postStart + lenOfLeft); root.right = findNode(inorder, rootIndex + 1 , inEnd, postorder, postStart + lenOfLeft, postEnd - 1 ); return root; } }
105.从前序与中序遍历序列构造二叉树 给定两个整数数组 preorder 和 inorder ,其中 preorder 是二叉树的先序遍历 , inorder 是同一棵树的中序遍历 ,请构造二叉树并返回其根节点。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 class Solution { Map<Integer, Integer> map; public TreeNode buildTree (int [] preorder, int [] inorder) { map = new HashMap <>(); for (int i = 0 ; i < inorder.length; i++){ map.put(inorder[i], i); } return findNode(preorder, 0 , preorder.length, inorder, 0 , inorder.length); } public TreeNode findNode (int [] preorder, int preStart, int preEnd, int [] inorder, int inStart, int inEnd) { if (preStart >= preEnd || inStart >= inEnd){ return null ; } int rootIndex = map.get(preorder[preStart]); TreeNode root = new TreeNode (inorder[rootIndex]); int lenOfLeft = rootIndex - inStart; root.left = findNode(preorder, preStart + 1 , preStart + lenOfLeft + 1 , inorder, inStart, rootIndex); root.right = findNode(preorder, preStart + lenOfLeft + 1 , preEnd, inorder, rootIndex + 1 , inEnd); return root; } }
654.最大二叉树 给定一个不重复的整数数组 nums 。 最大二叉树 可以用下面的算法从 nums 递归地构建:
创建一个根节点,其值为 nums 中的最大值。
递归地在最大值 左边 的 子数组前缀上 构建左子树。
递归地在最大值 右边 的 子数组后缀上 构建右子树。
返回 nums 构建的最大二叉树*
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 class Solution { public TreeNode constructMaximumBinaryTree (int [] nums) { return MaxBinaryTree(nums, 0 , nums.length); } public TreeNode MaxBinaryTree (int [] nums, int left, int right) { if (right - left < 1 ){ return null ; } if (right - left == 1 ){ return new TreeNode (nums[left]); } int maxIndex = left; int maxVal = nums[maxIndex]; for (int i = left + 1 ; i < right; i++){ if (nums[i] > maxVal){ maxVal = nums[i]; maxIndex = i; } } TreeNode root = new TreeNode (maxVal); root.left = MaxBinaryTree(nums, left, maxIndex); root.right = MaxBinaryTree(nums, maxIndex + 1 , right); return root; } }
617.合并二叉树 给你两棵二叉树: root1 和 root2 。想象一下,当你将其中一棵覆盖到另一棵之上时,两棵树上的一些节点将会重叠(而另一些不会)。你需要将这两棵树合并成一棵新二叉树。合并的规则是:如果两个节点重叠,那么将这两个节点的值相加作为合并后节点的新值;否则,不为 null 的节点将直接作为新二叉树的节点。返回合并后的二叉树。
注意: 合并过程必须从两个树的根节点开始。
递归方法:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 class Solution { public TreeNode mergeTrees (TreeNode root1, TreeNode root2) { if (root1 == null ){ return root2; } if (root2 == null ){ return root1; } root1.val += root2.val; root1.left = mergeTrees(root1.left, root2.left); root1.right = mergeTrees(root1.right, root2.right); return root1; } }
迭代方法:使用栈/队列迭代(原理一样)
使用栈迭代:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 class Solution { public TreeNode mergeTrees (TreeNode root1, TreeNode root2) { if (root1 == null ){ return root2; } if (root2 == null ){ return root1; } Stack<TreeNode> stack = new Stack <>(); stack.push(root2); stack.push(root1); while (!stack.isEmpty()){ TreeNode node1 = stack.pop(); TreeNode node2 = stack.pop(); node1.val += node2.val; if (node2.right != null && node1.right != null ){ stack.push(node2.right); stack.push(node1.right); }else { if (node1.right == null ){ node1.right = node2.right; } } if (node2.left != null && node1.left != null ){ stack.push(node2.left); stack.push(node1.left); }else { if (node1.left == null ){ node1.left = node2.left; } } } return root1; } }
使用队列迭代:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 class Solution { public TreeNode mergeTrees (TreeNode root1, TreeNode root2) { if (root1 == null ){ return root2; } if (root2 == null ){ return root1; } Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList <>(); queue.offer(root1); queue.offer(root2); while (!queue.isEmpty()){ TreeNode node1 = queue.poll(); TreeNode node2 = queue.poll(); node1.val = node1.val + node2.val; if (node1.left != null && node2.left != null ){ queue.offer(node1.left); queue.offer(node2.left); } if (node1.right != null && node2.right != null ){ queue.offer(node1.right); queue.offer(node2.right); } if (node1.left == null && node2.left != null ){ node1.left = node2.left; } if (node1.right == null && node2.right != null ){ node1.right = node2.right; } } return root1; } }
700.二叉搜索树的搜索 给定二叉搜索树(BST)的根节点 root 和一个整数值 val。你需要在 BST 中找到节点值等于 val 的节点。 返回以该节点为根的子树。 如果节点不存在,则返回 null 。
递归方法:
针对普通二叉树:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 class Solution { public TreeNode searchBST (TreeNode root, int val) { if (root == null || root.val == val){ return root; } TreeNode left = searchBST(root.left, val); if (left != null ){ return left; } return searchBST(root.right, val); } }
针对二叉搜索树:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 class Solution { public TreeNode searchBST (TreeNode root, int val) { if (root == null || root.val == val){ return root; } if (root.val < val){ return searchBST(root.right, val); }else { return searchBST(root.left, val); } } }
迭代方法:
针对普通二叉树:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 class Solution { public TreeNode searchBST (TreeNode root, int val) { if (root == null || root.val == val){ return root; } Stack<TreeNode> stack = new Stack <>(); stack.push(root); while (!stack.isEmpty()){ TreeNode node = stack.pop(); if (node.val == val){ return node; } if (node.right != null ){ stack.push(node.right); } if (node.left != null ){ stack.push(node.left); } } return null ; } }
针对二叉搜索树:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 class Solution { public TreeNode searchBST (TreeNode root, int val) { while (root != null ){ if (val < root.val){ root = root.left; }else if (val > root.val){ root = root.right; }else { return root; } } return null ; } }
98.验证二叉搜索树 给定一个二叉树,判断其是否是一个有效的二叉搜索树。假设一个二叉搜索树具有如下特征:
节点的左子树只包含小于当前节点的数。
节点的右子树只包含大于当前节点的数。
所有左子树和右子树自身必须也是二叉搜索树。
递归方法:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 class Solution { TreeNode max; public boolean isValidBST (TreeNode root) { if (root == null ){ return true ; } boolean left = isValidBST(root.left); if (!left){ return false ; } if (max != null && root.val <= max.val){ return false ; } max = root; boolean right = isValidBST(root.right); return right; } }
简洁优化递归:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 class Solution { public boolean isValidBST (TreeNode root) { return vaildBST(Long.MIN_VALUE, Long.MAX_VALUE, root); } public boolean vaildBST (long lower, long upper, TreeNode root) { if (root == null ){ return true ; } if (root.val <= lower || root.val >= upper){ return false ; } return vaildBST(lower, root.val, root.left) && vaildBST(root.val, upper, root.right); } }
迭代方法:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 class Solution { public boolean isValidBST (TreeNode root) { if (root == null ){ return true ; } Stack<TreeNode> stack = new Stack <>(); TreeNode pre = null ; while (root != null || !stack.isEmpty()){ while (root != null ){ stack.push(root); root = root.left; } TreeNode node = stack.pop(); if (pre != null && node.val <= pre.val){ return false ; } pre = node; root = node.right; } return true ; } }
简洁实现中序遍历:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 class Solution { long pre = Long.MIN_VALUE; public boolean isValidBST (TreeNode root) { if (root == null ){ return true ; } if (!isValidBST(root.left)){ return false ; } if (root.val <= pre){ return false ; } pre = root.val; return isValidBST(root.right); } }
530.二叉搜索树的最小绝对值 给你一个二叉搜索树的根节点 root ,返回 树中任意两不同节点值之间的最小差值 。差值是一个正数,其数值等于两值之差的绝对值。
递归方法:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 class Solution { TreeNode pre; int res = Integer.MAX_VALUE; public int getMinimumDifference (TreeNode root) { if (root == null ){ return 0 ; } traversal(root); return res; } public void traversal (TreeNode root) { if (root == null ){ return ; } traversal(root.left); if (pre != null ){ res = Math.min(res, root.val - pre.val); } pre = root; traversal(root.right); } }
迭代方法:中序遍历
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 class Solution { TreeNode pre; Stack<TreeNode> stack; public int getMinimumDifference (TreeNode root) { if (root == null ){ return 0 ; } stack = new Stack <>(); TreeNode cur = root; int result = Integer.MAX_VALUE; while (cur != null || !stack.isEmpty()){ if (cur != null ){ stack.push(cur); cur = cur.left; }else { cur = stack.pop(); if (pre != null ){ result = Math.min(result, cur.val - pre.val); } pre = cur; cur = cur.right; } } return result; } }
501.二叉搜索树中的众数 给你一个含重复值的二叉搜索树(BST)的根节点 root ,找出并返回 BST 中的所有 众数 (即,出现频率最高的元素)。如果树中有不止一个众数,可以按 任意顺序 返回。
假定 BST 满足如下定义:
结点左子树中所含节点的值 小于等于 当前节点的值
结点右子树中所含节点的值 大于等于 当前节点的值
左子树和右子树都是二叉搜索树
中序遍历:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 class Solution { ArrayList<Integer> resList; int maxCount; int count; TreeNode pre; public int [] findMode(TreeNode root) { resList = new ArrayList <>(); maxCount = 0 ; count = 0 ; pre = null ; findModel(root); int [] res = new int [resList.size()]; for (int i = 0 ; i < resList.size(); i++){ res[i] = resList.get(i); } return res; } public void findModel (TreeNode root) { if (root == null ){ return ; } findModel(root.left); int rootValue = root.val; if (pre == null || rootValue != pre.val){ count = 1 ; }else { count++; } if (count > maxCount){ resList.clear(); resList.add(rootValue); maxCount = count; }else if (count == maxCount){ resList.add(rootValue); } pre = root; findModel(root.right); } }
迭代方法:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 class Solution { public int [] findMode(TreeNode root) { TreeNode pre = null ; Stack<TreeNode> stack = new Stack <>(); List<Integer> result = new ArrayList <>(); int maxCount = 0 ; int count = 0 ; TreeNode cur = root; while (cur != null || !stack.isEmpty()){ if (cur != null ){ stack.push(cur); cur = cur.left; }else { cur = stack.pop(); if (pre == null || cur.val != pre.val){ count = 1 ; }else { count++; } if (count > maxCount){ maxCount = count; result.clear(); result.add(cur.val); }else if (count == maxCount){ result.add(cur.val); } pre = cur; cur = cur.right; } } return result.stream().mapToInt(Integer::intValue).toArray(); } }
236.二叉树的最近公共祖先 给定一个二叉树 , 找到该树中两个指定节点的最近公共祖先。最近公共祖先的定义为:“对于有根树 T 的两个节点 p、q,最近公共祖先表示为一个节点 x,满足 x 是 p、q 的祖先且 x 的深度尽可能大(一个节点也可以是它自己的祖先 )。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 class Solution { public TreeNode lowestCommonAncestor (TreeNode root, TreeNode p, TreeNode q) { if (root == null || root == p || root == q){ return root; } TreeNode left = lowestCommonAncestor(root.left,p,q); TreeNode right = lowestCommonAncestor(root.right,p,q); if (left != null && right != null ){ return root; } return left != null ? left : right; } }
235.二叉搜索树的最近公共祖先 给定一个二叉搜索树 , 找到该树中两个指定节点的最近公共祖先。最近公共祖先的定义为:“对于有根树 T 的两个节点 p、q,最近公共祖先表示为一个节点 x,满足 x 是 p、q 的祖先且 x 的深度尽可能大(一个节点也可以是它自己的祖先 )。
递归方法:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 class Solution { public TreeNode lowestCommonAncestor (TreeNode root, TreeNode p, TreeNode q) { if (root.val > p.val && root.val > q.val){ return lowestCommonAncestor(root.left, p, q); } if (root.val < p.val && root.val < q.val){ return lowestCommonAncestor(root.right, p, q); } return root; } }
迭代方法:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 class Solution { public TreeNode lowestCommonAncestor (TreeNode root, TreeNode p, TreeNode q) { while (true ){ if (root.val > p.val && root.val > q.val){ root = root.left; }else if (root.val < p.val && root.val < q.val){ root = root.right; }else { break ; } } return root; } }
701.二叉搜索树中的插入操作 给定二叉搜索树(BST)的根节点 root 和要插入树中的值 value ,将值插入二叉搜索树。 返回插入后二叉搜索树的根节点。 输入数据 保证 ,新值和原始二叉搜索树中的任意节点值都不同。
注意 ,可能存在多种有效的插入方式,只要树在插入后仍保持为二叉搜索树即可。 你可以返回 任意有效的结果 。
递归方法:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 class Solution { public TreeNode insertIntoBST (TreeNode root, int val) { if (root == null ){ return new TreeNode (val); } if (root.val < val){ root.right = insertIntoBST(root.right, val); }else if (root.val > val){ root.left = insertIntoBST(root.left, val); } return root; } }
迭代方法:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 class Solution { public TreeNode insertIntoBST (TreeNode root, int val) { if (root == null ){ return new TreeNode (val); } TreeNode newRoot = root; TreeNode pre = root; while (root != null ){ pre = root; if (root.val > val){ root = root.left; }else if (root.val < val){ root = root.right; } } if (pre.val > val){ pre.left = new TreeNode (val); }else { pre.right = new TreeNode (val); } return newRoot; } }
450.删除二叉搜索树中的节点 给定一个二叉搜索树的根节点 root 和一个值 key ,删除二叉搜索树中的 key 对应的节点,并保证二叉搜索树的性质不变。返回二叉搜索树(有可能被更新)的根节点的引用。
一般来说,删除节点可分为两个步骤:
首先找到需要删除的节点;
如果找到了,删除它。
递归方法一:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 class Solution { public TreeNode deleteNode (TreeNode root, int key) { root = delete(root, key); return root; } public TreeNode delete (TreeNode root, int key) { if (root == null ){ return null ; } if (root.val > key){ root.left = delete(root.left, key); }else if (root.val < key){ root.right = delete(root.right, key); }else { if (root.left == null ){ return root.right; } if (root.right == null ){ return root.left; } TreeNode tmp = root.right; while (tmp.left != null ){ tmp = tmp.left; } root.val = tmp.val; root.right = delete(root.right, tmp.val); } return root; } }
递归方法二:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 class Solution { public TreeNode deleteNode (TreeNode root, int key) { if (root == null ){ return root; } if (root.val == key){ if (root.left == null ){ return root.right; }else if (root.right == null ){ return root.left; }else { TreeNode cur = root.right; while (cur.left != null ){ cur = cur.left; } cur.left = root.left; root = root.right; return root; } } if (root.val > key){ root.left = deleteNode(root.left, key); } if (root.val < key){ root.right = deleteNode(root.right, key); } return root; } }
669.修剪二叉搜索树 给你二叉搜索树的根节点 root ,同时给定最小边界low 和最大边界 high。通过修剪二叉搜索树,使得所有节点的值在[low, high]中。修剪树 不应该 改变保留在树中的元素的相对结构 (即,如果没有被移除,原有的父代子代关系都应当保留)。 可以证明,存在 唯一的答案 。
所以结果应当返回修剪好的二叉搜索树的新的根节点。注意,根节点可能会根据给定的边界发生改变。
递归方法:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 class Solution { public TreeNode trimBST (TreeNode root, int low, int high) { if (root == null ){ return null ; } if (root.val < low){ return trimBST(root.right, low, high); } if (root.val > high){ return trimBST(root.left, low, high); } root.left = trimBST(root.left, low, high); root.right = trimBST(root.right, low, high); return root; } }
108.将有序数组转换为二叉搜索树 给你一个整数数组 nums ,其中元素已经按 升序 排列,请你将其转换为一棵 高度平衡 二叉搜索树。高度平衡 二叉树是一棵满足「每个节点的左右两个子树的高度差的绝对值不超过 1 的二叉树。
递归方法:左闭右开
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 class Solution { public TreeNode sortedArrayToBST (int [] nums) { return sortedArray(nums, 0 , nums.length); } public TreeNode sortedArray (int [] nums, int left, int right) { if (left >= right){ return null ; } if (right - left == 1 ){ return new TreeNode (nums[left]); } int mid = left + (right - left) / 2 ; TreeNode root = new TreeNode (nums[mid]); root.left = sortedArray(nums, left, mid); root.right = sortedArray(nums, mid + 1 , right); return root; } }
538.把二叉搜索树转换为累加树 给出二叉 搜索 树的根节点,该树的节点值各不相同,请你将其转换为累加树(Greater Sum Tree),使每个节点 node 的新值等于原树中大于或等于 node.val 的值之和。
提醒一下,二叉搜索树满足下列约束条件:
节点的左子树仅包含键 小于 节点键的节点。
节点的右子树仅包含键 大于 节点键的节点。
左右子树也必须是二叉搜索树。
递归方法:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 class Solution { int sum = 0 ; public TreeNode convertBST (TreeNode root) { if (root == null ){ return null ; } convertBST(root.right); sum += root.val; root.val = sum; convertBST(root.left); return root; } }
七、回溯算法 77.组合 给定两个整数 n 和 k,返回范围 [1, n] 中所有可能的 k 个数的组合。你可以按 任何顺序 返回答案。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 class Solution { List<List<Integer>> result = new ArrayList <>(); LinkedList<Integer> path = new LinkedList <>(); public List<List<Integer>> combine (int n, int k) { combineHelper(n, k, 1 ); return result; } public void combineHelper (int n, int k, int startIndex) { if (path.size() == k){ result.add(new ArrayList <>(path)); return ; } for (int i = startIndex; i <= n - (k - path.size()) + 1 ; i++){ path.add(i); combineHelper(n, k, i + 1 ); path.removeLast(); } } }
216.组合总和-III 找出所有相加之和为 n 的 k 个数的组合,且满足下列条件:
返回 所有可能的有效组合的列表 。该列表不能包含相同的组合两次,组合可以以任何顺序返回。
方法一:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 class Solution { List<List<Integer>> result = new ArrayList <>(); LinkedList<Integer> path = new LinkedList <>(); public List<List<Integer>> combinationSum3 (int k, int n) { backTracking(n, k, 1 , 0 ); return result; } public void backTracking (int targetSum, int k, int startIndex, int sum) { if (sum > targetSum){ return ; } if (path.size() == k){ if (sum == targetSum){ result.add(new ArrayList <>(path)); return ; } } for (int i = startIndex; i <= 9 - (k - path.size()) + 1 ; i++){ path.add(i); sum += i; backTracking(targetSum, k, i + 1 , sum); path.removeLast(); sum -= i; } } }
方法二:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 class Solution { List<List<Integer>> result = new ArrayList <>(); List<Integer> list = new ArrayList <>(); public List<List<Integer>> combinationSum3 (int k, int n) { result.clear(); list.clear(); backTracking(k, n, 9 ); return result; } public void backTracking (int k, int n, int maxNum) { if (k == 0 && n == 0 ){ result.add(new ArrayList <>(list)); return ; } if (maxNum == 0 || n > k * maxNum - k * (k - 1 ) / 2 || n < (1 + k) * k / 2 ){ return ; } list.add(maxNum); backTracking(k - 1 , n - maxNum, maxNum - 1 ); list.remove(list.size() - 1 ); backTracking(k, n, maxNum - 1 ); } }
17.电话号码的字符组合 给定一个仅包含数字 2-9 的字符串,返回所有它能表示的字母组合。答案可以按 任意顺序 返回。给出数字到字母的映射如下(与电话按键相同)。
注意 :1 不对应任何字母。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 class Solution { List<String> list = new ArrayList <>(); StringBuilder tmp = new StringBuilder (); public List<String> letterCombinations (String digits) { if (digits == null || digits.length() == 0 ){ return list; } String[] numString = {"" , "" , "abc" , "def" , "ghi" , "jkl" , "mno" , "pqrs" , "tuv" , "wxyz" }; backTracking(digits, numString, 0 ); return list; } public void backTracking (String digits, String[] numString, int num) { if (num == digits.length()){ list.add(tmp.toString()); return ; } String str = numString[digits.charAt(num) - '0' ]; for (int i = 0 ; i < str.length(); i++){ tmp.append(str.charAt(i)); backTracking(digits, numString, num + 1 ); tmp.deleteCharAt(tmp.length() - 1 ); } } }
39.组合总和 给你一个 无重复元素 的整数数组 candidates 和一个目标整数 target ,找出 candidates 中可以使数字和为目标数 target 的 所有 不同组合 ,并以列表形式返回。你可以按 任意顺序 返回这些组合。
candidates 中的 同一个 数字可以 无限制重复被选取 。如果至少一个数字的被选数量不同,则两种组合是不同的。对于给定的输入,保证和为 target 的不同组合数少于 150 个。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 class Solution { public List<List<Integer>> combinationSum (int [] candidates, int target) { List<List<Integer>> res = new ArrayList <>(); Arrays.sort(candidates); backTracking(res, new ArrayList <>(), candidates, target, 0 , 0 ); return res; } public void backTracking (List<List<Integer>> res, List<Integer> path, int [] candidates, int target, int sum, int index) { if (sum == target){ res.add(new ArrayList <>(path)); return ; } for (int i = index; i < candidates.length; i++){ if (sum + candidates[i] > target){ break ; } path.add(candidates[i]); backTracking(res, path, candidates, target, sum + candidates[i], i); path.remove(path.size() - 1 ); } } }
40.组合总和-II 给定一个候选人编号的集合 candidates 和一个目标数 target ,找出 candidates 中所有可以使数字和为 target 的组合。candidates 中的每个数字在每个组合中只能使用 一次 。
注意: 解集不能包含重复的组合。
使用标记数组:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 class Solution { LinkedList<Integer> path = new LinkedList <>(); List<List<Integer>> res = new ArrayList <>(); boolean [] used; int sum = 0 ; public List<List<Integer>> combinationSum2 (int [] candidates, int target) { used = new boolean [candidates.length]; Arrays.fill(used, false ); Arrays.sort(candidates); backTracking(candidates, target, 0 ); return res; } public void backTracking (int [] candidates, int target, int startIndex) { if (sum == target){ res.add(new ArrayList <>(path)); } for (int i = startIndex; i < candidates.length; i++){ if (sum + candidates[i] > target){ break ; } if (i > 0 && candidates[i] == candidates[i - 1 ] && !used[i - 1 ]){ continue ; } used[i] = true ; sum += candidates[i]; path.add(candidates[i]); backTracking(candidates, target, i + 1 ); used[i] = false ; sum -= candidates[i]; path.removeLast(); } } }
不使用标记数组:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 class Solution { LinkedList<Integer> path = new LinkedList <>(); List<List<Integer>> res = new ArrayList <>(); int sum = 0 ; public List<List<Integer>> combinationSum2 (int [] candidates, int target) { Arrays.sort(candidates); backTracking(candidates, target, 0 ); return res; } public void backTracking (int [] candidates, int target, int start) { if (sum == target){ res.add(new ArrayList <>(path)); return ; } for (int i = start; i < candidates.length && sum + candidates[i] <= target; i++){ if (i > start && candidates[i] == candidates[i - 1 ]){ continue ; } sum += candidates[i]; path.add(candidates[i]); backTracking(candidates, target, i + 1 ); int tmp = path.getLast(); sum -= tmp; path.removeLast(); } } }
131.分割回文串 给你一个字符串 s,请你将 s 分割成一些子串,使每个子串都是 回文串 。返回 s 所有可能的分割方案。回文串 是正着读和反着读都一样的字符串。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 class Solution { List<List<String>> res = new ArrayList <>(); Deque<String> deque = new LinkedList <>(); public List<List<String>> partition (String s) { backTracking(s, 0 ); return res; } public boolean isPalindrome (String s, int startIndex, int end) { for (int i = startIndex, j = end; i < j; i++, j--){ if (s.charAt(i) != s.charAt(j)){ return false ; } } return true ; } public void backTracking (String s, int startIndex) { if (startIndex >= s.length()){ res.add(new ArrayList <>(deque)); return ; } for (int i = startIndex; i < s.length(); i++){ if (isPalindrome(s, startIndex, i)){ String str = s.substring(startIndex, i + 1 ); deque.addLast(str); }else { continue ; } backTracking(s, i + 1 ); deque.removeLast(); } } }
93.复原IP地址 给定一个只包含数字的字符串,复原它并返回所有可能的 IP 地址格式。有效的 IP 地址 正好由四个整数(每个整数位于 0 到 255 之间组成,且不能含有前导 0),整数之间用 ‘.’ 分隔。
例如:”0.1.2.201” 和 “192.168.1.1” 是 有效的 IP 地址,但是 “0.011.255.245”、”192.168.1.312” 和 “192.168@1.1 “ 是 无效的 IP 地址。
方法一:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 class Solution { List<String> result = new ArrayList <>(); StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder (); public List<String> restoreIpAddresses (String s) { restoreIpAddressesHandler(s, 0 , 0 ); return result; } public void restoreIpAddressesHandler (String s, int start, int number) { if (start == s.length() && number == 4 ){ result.add(sb.toString()); return ; } if (start == s.length() || number == 4 ){ return ; } for (int i = start; i < s.length() && i - start < 3 && Integer.parseInt(s.substring(start, i + 1 )) >= 0 && Integer.parseInt(s.substring(start, i + 1 )) <= 255 ; i++){ if (i + 1 - start > 1 && s.charAt(start) - '0' == 0 ){ continue ; } sb.append(s.substring(start, i + 1 )); if (number < 3 ){ sb.append("." ); } number++; restoreIpAddressesHandler(s, i + 1 , number); number--; sb.delete(start + number, i + number + 2 ); } } }
方法二:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 class Solution { int setSize = 4 ; List<String> res; int [] segments; public List<String> restoreIpAddresses (String s) { res = new ArrayList <>(); segments = new int [setSize]; dfs(s,0 ,0 ); return res; } public void dfs (String s, int id, int start) { if (id == setSize){ if (start == s.length()){ StringBuffer sf = new StringBuffer (); for (int i = 0 ; i < setSize; ++i){ sf.append(segments[i]); if (i != setSize - 1 ){ sf.append('.' ); } } res.add(sf.toString()); } return ; } if (start == s.length()){ return ; } if (s.charAt(start) == '0' ){ segments[id] = 0 ; dfs(s,id + 1 , start + 1 ); } int address = 0 ; for (int end = start; end < s.length(); ++end){ address = address * 10 + (s.charAt(end) - '0' ); if (address > 0 && address <= 0xFF ){ segments[id] = address; dfs(s,id + 1 , end + 1 ); }else { break ; } } } }
78.子集 给你一个整数数组 nums ,数组中的元素 互不相同 。返回该数组所有可能的子集(幂集)。解集 不能 包含重复的子集。你可以按 任意顺序 返回解集。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 class Solution { List<List<Integer>> result = new ArrayList <>(); LinkedList<Integer> path = new LinkedList <>(); public List<List<Integer>> subsets (int [] nums) { subsetsHelper(nums, 0 ); return result; } public void subsetsHelper (int [] nums, int startIndex) { result.add(new ArrayList <>(path)); if (startIndex >= nums.length){ return ; } for (int i = startIndex; i < nums.length; i++){ path.add(nums[i]); subsetsHelper(nums, i + 1 ); path.removeLast(); } } }
90.子集-II 给你一个整数数组 nums ,其中可能包含重复元素,请你返回该数组所有可能的子集(幂集)。解集 不能 包含重复的子集。返回的解集中,子集可以按 任意顺序 排列。
使用标记数组:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 class Solution { List<List<Integer>> result = new ArrayList <>(); LinkedList<Integer> path = new LinkedList <>(); boolean [] used; public List<List<Integer>> subsetsWithDup (int [] nums) { if (nums.length == 0 ){ result.add(path); return result; } Arrays.sort(nums); used = new boolean [nums.length]; subsetsWithDupHelper(nums, 0 ); return result; } public void subsetsWithDupHelper (int [] nums, int startIndex) { result.add(new ArrayList <>(path)); if (startIndex >= nums.length){ return ; } for (int i = startIndex; i < nums.length; i++){ if (i > 0 && nums[i] == nums[i - 1 ] && !used[i - 1 ]){ continue ; } path.add(nums[i]); used[i] = true ; subsetsWithDupHelper(nums, i + 1 ); path.removeLast(); used[i] = false ; } } }
不使用标记数组:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 class Solution { List<List<Integer>> result = new ArrayList <>(); LinkedList<Integer> path = new LinkedList <>(); public List<List<Integer>> subsetsWithDup (int [] nums) { Arrays.sort(nums); subsetsWithDupHelper(nums, 0 ); return result; } public void subsetsWithDupHelper (int [] nums, int startIndex) { result.add(new ArrayList <>(path)); for (int i = startIndex; i < nums.length; i++){ if (i > startIndex && nums[i - 1 ] == nums[i]){ continue ; } path.add(nums[i]); subsetsWithDupHelper(nums, i + 1 ); path.removeLast(); } } }
491.递增子序列 给你一个整数数组 nums ,找出并返回所有该数组中不同的递增子序列,递增子序列中 至少有两个元素 。你可以按 任意顺序 返回答案。数组中可能含有重复元素,如出现两个整数相等,也可以视作递增序列的一种特殊情况。
方法一: 回溯
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 class Solution { private List<Integer> path = new ArrayList <>(); private List<List<Integer>> res = new ArrayList <>(); public List<List<Integer>> findSubsequences (int [] nums) { backtracking(nums,0 ); return res; } private void backtracking (int [] nums, int start) { if (path.size() > 1 ) { res.add(new ArrayList <>(path)); } int [] used = new int [201 ]; for (int i = start; i < nums.length; i++) { if (!path.isEmpty() && nums[i] < path.get(path.size() - 1 ) || (used[nums[i] + 100 ] == 1 )) continue ; used[nums[i] + 100 ] = 1 ; path.add(nums[i]); backtracking(nums, i + 1 ); path.remove(path.size() - 1 ); } } }
方法二:使用map(推荐)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 class Solution { List<List<Integer>> result = new ArrayList <>(); LinkedList<Integer> path = new LinkedList <>(); public List<List<Integer>> findSubsequences (int [] nums) { getSubsequences(nums, 0 ); return result; } public void getSubsequences (int [] nums, int start) { if (path.size() > 1 ){ result.add(new ArrayList <>(path)); } HashMap<Integer, Integer> map = new HashMap <>(); for (int i = start; i < nums.length; i++){ if (!path.isEmpty() && nums[i] < path.getLast()){ continue ; } if (map.getOrDefault(nums[i], 0 ) >= 1 ){ continue ; } map.put(nums[i], map.getOrDefault(nums[i] , 0 ) + 1 ); path.add(nums[i]); getSubsequences(nums, i + 1 ); path.removeLast(); } } }
46.全排列 给定一个不含重复数字的数组 nums ,返回其 所有可能的全排列 。你可以 按任意顺序 返回答案。
方法一: 通过判断path中是否存在数字,排除已经选择的数字
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 class Solution { List<List<Integer>> result = new ArrayList <>(); LinkedList<Integer> path = new LinkedList <>(); public List<List<Integer>> permute (int [] nums) { if (nums == null || nums.length == 0 ){ return result; } backTracking(nums, path); return result; } public void backTracking (int [] nums, LinkedList<Integer> path) { if (path.size() == nums.length){ result.add(new ArrayList <>(path)); } for (int i = 0 ; i < nums.length; i++){ if (path.contains(nums[i])){ continue ; } path.add(nums[i]); backTracking(nums, path); path.removeLast(); } } }
方法二:添加used参数判断排除重复
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 class Solution { List<List<Integer>> result = new ArrayList <>(); LinkedList<Integer> path = new LinkedList <>(); boolean [] used; public List<List<Integer>> permute (int [] nums) { if (nums == null || nums.length == 0 ){ return result; } used = new boolean [nums.length]; backTracking(nums); return result; } public void backTracking (int [] nums) { if (path.size() == nums.length){ result.add(new ArrayList <>(path)); return ; } for (int i = 0 ; i < nums.length; i++){ if (used[i]){ continue ; } used[i] = true ; path.add(nums[i]); backTracking(nums); path.removeLast(); used[i] = false ; } } }
47.全排列-II 给定一个可包含重复数字的序列 nums ,按任意顺序
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 class Solution { List<List<Integer>> result = new ArrayList <>(); List<Integer> path = new ArrayList <>(); boolean [] used; public List<List<Integer>> permuteUnique (int [] nums) { used = new boolean [nums.length]; Arrays.sort(nums); Arrays.fill(used, false ); backTracking(nums, used); return result; } public void backTracking (int [] nums, boolean [] used) { if (path.size() == nums.length){ result.add(new ArrayList <>(path)); return ; } for (int i = 0 ; i < nums.length; i++){ if (i > 0 && nums[i] == nums[i - 1 ] && used[i - 1 ] == false ){ continue ; } if (used[i] == false ){ used[i] = true ; path.add(nums[i]); backTracking(nums, used); path.remove(path.size() - 1 ); used[i] = false ; } } } }
332.重新安排行程 给你一份航线列表 tickets ,其中 tickets[i] = [fromi, toi] 表示飞机出发和降落的机场地点。请你对该行程进行重新规划排序。
所有这些机票都属于一个从 JFK(肯尼迪国际机场)出发的先生,所以该行程必须从 JFK 开始。如果存在多种有效的行程,请你按字典排序返回最小的行程组合。
例如,行程 ["JFK", "LGA"] 与 ["JFK", "LGB"] 相比就更小,排序更靠前。
假定所有机票至少存在一种合理的行程。且所有的机票 必须都用一次 且 只能用一次。
方法一:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 class Solution { private LinkedList<String> res; private LinkedList<String> path = new LinkedList <>(); public List<String> findItinerary (List<List<String>> tickets) { Collections.sort(tickets, (a, b) -> a.get(1 ).compareTo(b.get(1 ))); path.add("JFK" ); boolean [] used = new boolean [tickets.size()]; backTracking((ArrayList) tickets, used); return res; } public boolean backTracking (ArrayList<List<String>> tickets, boolean [] used) { if (path.size() == tickets.size() + 1 ) { res = new LinkedList (path); return true ; } for (int i = 0 ; i < tickets.size(); i++) { if (!used[i] && tickets.get(i).get(0 ).equals(path.getLast())) { path.add(tickets.get(i).get(1 )); used[i] = true ; if (backTracking(tickets, used)) { return true ; } used[i] = false ; path.removeLast(); } } return false ; } }
方法二:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 class Solution { Deque<String> result; Map<String, Map<String, Integer>> map; public List<String> findItinerary (List<List<String>> tickets) { map = new HashMap <String, Map<String, Integer>>(); result = new LinkedList <>(); for (List<String> t : tickets){ Map<String, Integer> tmp; if (map.containsKey(t.get(0 ))){ tmp = map.get(t.get(0 )); tmp.put(t.get(1 ), tmp.getOrDefault(t.get(1 ), 0 ) + 1 ); }else { tmp = new TreeMap <>(); tmp.put(t.get(1 ), 1 ); } map.put(t.get(0 ), tmp); } result.add("JFK" ); backTracking(tickets.size()); return new ArrayList <>(result); } public boolean backTracking (int ticketNum) { if (result.size() == ticketNum + 1 ){ return true ; } String last = result.getLast(); if (map.containsKey(last)){ for (Map.Entry<String, Integer> target : map.get(last).entrySet()){ int count = target.getValue(); if (count > 0 ){ result.add(target.getKey()); target.setValue(count - 1 ); if (backTracking(ticketNum)){ return true ; } result.removeLast(); target.setValue(count); } } } return false ; } }
51.N皇后问题 按照国际象棋的规则,皇后可以攻击与之处在同一行或同一列或同一斜线上的棋子。n 皇后问题 研究的是如何将 n 个皇后放置在 n×n 的棋盘上,并且使皇后彼此之间不能相互攻击。
给你一个整数 n ,返回所有不同的 n 皇后问题 的解决方案。每一种解法包含一个不同的 n 皇后问题 的棋子放置方案,该方案中 'Q' 和 '.' 分别代表了皇后和空位。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 class Solution { List<List<String>> res = new ArrayList <>(); public List<List<String>> solveNQueens (int n) { char [][] chessboard = new char [n][n]; for (char [] c : chessboard) { Arrays.fill(c, '.' ); } backTrack(n, 0 , chessboard); return res; } public void backTrack (int n, int row, char [][] chessboard) { if (row == n) { res.add(Array2List(chessboard)); return ; } for (int col = 0 ;col < n; ++col) { if (isValid (row, col, n, chessboard)) { chessboard[row][col] = 'Q' ; backTrack(n, row+1 , chessboard); chessboard[row][col] = '.' ; } } } public List Array2List (char [][] chessboard) { List<String> list = new ArrayList <>(); for (char [] c : chessboard) { list.add(String.copyValueOf(c)); } return list; } public boolean isValid (int row, int col, int n, char [][] chessboard) { for (int i=0 ; i<row; ++i) { if (chessboard[i][col] == 'Q' ) { return false ; } } for (int i=row-1 , j=col-1 ; i>=0 && j>=0 ; i--, j--) { if (chessboard[i][j] == 'Q' ) { return false ; } } for (int i=row-1 , j=col+1 ; i>=0 && j<=n-1 ; i--, j++) { if (chessboard[i][j] == 'Q' ) { return false ; } } return true ; } }
37.解数独 编写一个程序,通过填充空格来解决数独问题。数独的解法需 遵循如下规则 :
数字 1-9 在每一行只能出现一次。
数字 1-9 在每一列只能出现一次。
数字 1-9 在每一个以粗实线分隔的 3x3 宫内只能出现一次。(请参考示例图)
数独部分空格内已填入了数字,空白格用 '.' 表示。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 class Solution { public void solveSudoku (char [][] board) { solveSudokuHelper(board); } public boolean solveSudokuHelper (char [][] board) { for (int i = 0 ; i < 9 ; i++){ for (int j = 0 ; j < 9 ; j++){ if (board[i][j] != '.' ){ continue ; } for (char k = '1' ; k <= '9' ; k++){ if (isVaildSudoku(i, j, k, board)){ board[i][j] = k; if (solveSudokuHelper(board)){ return true ; } board[i][j] = '.' ; } } return false ; } } return true ; } public boolean isVaildSudoku (int row, int col, char val, char [][] board) { for (int i = 0 ; i < 9 ; i++){ if (board[row][i] == val){ return false ; } } for (int j = 0 ; j < 9 ; j++){ if (board[j][col] == val){ return false ; } } int startRow = (row / 3 ) * 3 ; int startCol = (col / 3 ) * 3 ; for (int i = startRow; i < startRow + 3 ; i++){ for (int j = startCol; j < startCol + 3 ; j++){ if (board[i][j] == val){ return false ; } } } return true ; } }
698.划分为k个相等的子集 给定一个整数数组 nums 和一个正整数 k,找出是否有可能把这个数组分成 k 个非空子集,其总和都相等。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 class Solution { public boolean canPartitionKSubsets (int [] nums, int k) { int sum = 0 ; for (int num : nums){ sum += num; } if (sum % k != 0 ){ return false ; } int target = sum / k; int len = nums.length; nums = Arrays.stream(nums) .boxed() .sorted((a, b) -> b - a) .mapToInt(int1 -> int1) .toArray(); int [] bucket = new int [k]; return backTracking(nums, 0 , bucket, k, target); } public boolean backTracking (int [] nums, int index, int [] bucket, int k, int target) { if (index == nums.length){ return true ; } for (int i = 0 ; i < k; i++){ if (i > 0 && index == 0 ){ break ; } if (bucket[i] + nums[index] > target){ continue ; } if (i > 0 && bucket[i] == bucket[i - 1 ]){ continue ; } bucket[i] += nums[index]; if (backTracking(nums, index + 1 , bucket, k, target)){ return true ; } bucket[i] -= nums[index]; } return false ; } }
473.火柴拼正方形 你将得到一个整数数组 matchsticks ,其中 matchsticks[i] 是第 i 个火柴棒的长度。你要用 所有的火柴棍 拼成一个正方形。你 不能折断 任何一根火柴棒,但你可以把它们连在一起,而且每根火柴棒必须 使用一次 。
如果可以组成正方形,则返回 true ,否则返回 false 。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 class Solution { public boolean makesquare (int [] matchsticks) { int sum = 0 ; for (int num : matchsticks){ sum += num; } if (sum % 4 != 0 ){ return false ; } int target = sum / 4 ; int len = matchsticks.length; matchsticks = Arrays.stream(matchsticks) .boxed() .sorted((a, b) -> b - a) .mapToInt(int1 -> int1) .toArray(); int [] bucket = new int [4 ]; return backTracking(matchsticks, 0 , bucket, 4 , target); } public boolean backTracking (int [] nums, int index, int [] bucket, int k, int target) { if (index == nums.length){ return true ; } for (int i = 0 ; i < k; i++){ if (i > 0 && index == 0 ){ break ; } if (bucket[i] + nums[index] > target){ continue ; } if (i > 0 && bucket[i] == bucket[i - 1 ]){ continue ; } bucket[i] += nums[index]; if (backTracking(nums, index + 1 , bucket, k, target)){ return true ; } bucket[i] -= nums[index]; } return false ; } }
八、贪心算法 455.分发饼干 假设你是一位很棒的家长,想要给你的孩子们一些小饼干。但是,每个孩子最多只能给一块饼干。对每个孩子 i,都有一个胃口值 g[i],这是能让孩子们满足胃口的饼干的最小尺寸;并且每块饼干 j,都有一个尺寸 s[j] 。如果 s[j] >= g[i],我们可以将这个饼干 j 分配给孩子 i ,这个孩子会得到满足。你的目标是尽可能满足越多数量的孩子,并输出这个最大数值。
思路1:优先考虑饼干,小饼干先喂饱小胃口
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 class Solution { public int findContentChildren (int [] g, int [] s) { Arrays.sort(g); Arrays.sort(s); int start = 0 ; int count = 0 ; for (int i = 0 ; i < s.length && start < g.length; i++){ if (s[i] >= g[start]){ start++; count++; } } return count; } }
思路2:优先考虑胃口,先喂饱大胃口
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 class Solution { public int findContentChildren (int [] g, int [] s) { Arrays.sort(g); Arrays.sort(s); int count = 0 ; int start = s.length - 1 ; for (int i = g.length - 1 ; i >= 0 ; i--){ if (start >= 0 && g[i] <= s[start]){ start--; count++; } } return count; } }
376.摆动序列 如果连续数字之间的差严格地在正数和负数之间交替,则数字序列称为 摆动序列 。 第一个差(如果存在的话)可能是正数或负数。仅有一个元素或者含两个不等元素的序列也视作摆动序列。
例如, [1, 7, 4, 9, 2, 5] 是一个 摆动序列 ,因为差值 (6, -3, 5, -7, 3) 是正负交替出现的。
相反,[1, 4, 7, 2, 5] 和 [1, 7, 4, 5, 5] 不是摆动序列,第一个序列是因为它的前两个差值都是正数,第二个序列是因为它的最后一个差值为零。
子序列 可以通过从原始序列中删除一些(也可以不删除)元素来获得,剩下的元素保持其原始顺序。给你一个整数数组 nums ,返回 nums 中作为 摆动序列 的 最长子序列的长度 。
方法一:贪心算法
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 class Solution { public int wiggleMaxLength (int [] nums) { if (nums.length < 2 ){ return nums.length; } int curDiff = 0 ; int preDiff = 0 ; int count = 1 ; for (int i = 1 ; i < nums.length; i++){ curDiff = nums[i] - nums[i - 1 ]; if (curDiff > 0 && preDiff <= 0 || (curDiff < 0 && preDiff >= 0 )){ count++; preDiff = curDiff; } } return count; } }
方法二:动态规划
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 class Solution { public int wiggleMaxLength (int [] nums) { int [][] dp = new int [nums.length][2 ]; dp[0 ][0 ] = dp[0 ][1 ] = 1 ; for (int i = 1 ; i < nums.length; i++){ dp[i][0 ] = dp[i][1 ] = 1 ; for (int j = 0 ; j < i; j++){ if (nums[j] > nums[i]){ dp[i][1 ] = Math.max(dp[i][1 ], dp[j][0 ] + 1 ); } if (nums[j] < nums[i]){ dp[i][0 ] = Math.max(dp[i][0 ], dp[j][1 ] + 1 ); } } } return Math.max(dp[nums.length - 1 ][0 ], dp[nums.length - 1 ][1 ]); } }
53.最大子序和 给定一个整数数组 nums ,找到一个具有最大和的连续子数组(子数组最少包含一个元素),返回其最大和。
方法一:贪心算法
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 class Solution { public int maxSubArray (int [] nums) { if (nums.length == 1 ){ return nums[0 ]; } int sum = Integer.MIN_VALUE; int count = 0 ; for (int i = 0 ; i < nums.length; i++){ count += nums[i]; sum = Math.max(sum, count); if (count <= 0 ){ count = 0 ; } } return sum; } }
方法二:动态规划
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 class Solution { public int maxSubArray (int [] nums) { int ans = Integer.MIN_VALUE; int [] dp = new int [nums.length]; dp[0 ] = nums[0 ]; ans = dp[0 ]; for (int i = 1 ; i < nums.length; i++){ dp[i] = Math.max(dp[i - 1 ] + nums[i], nums[i]); ans = Math.max(ans, dp[i]); } return ans; } }
122.买卖股票的最佳时机-II 给你一个整数数组 prices ,其中 prices[i] 表示某支股票第 i 天的价格。在每一天,你可以决定是否购买和/或出售股票。你在任何时候 最多 只能持有 一股 股票。你也可以先购买,然后在 同一天 出售。
返回 你能获得的 最大 利润
方法一:贪心算法
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 class Solution { public int maxProfit (int [] prices) { int result = 0 ; for (int i = 1 ; i < prices.length; i++){ result += Math.max(prices[i] - prices[i - 1 ], 0 ); } return result; } }
方法二:动态规划
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 class Solution { public int maxProfit (int [] prices) { int [][] dp = new int [prices.length][2 ]; dp[0 ][0 ] = 0 ; dp[0 ][1 ] = -prices[0 ]; for (int i = 1 ; i < prices.length; i++){ dp[i][0 ] = Math.max(dp[i - 1 ][0 ], dp[i - 1 ][1 ] + prices[i]); dp[i][1 ] = Math.max(dp[i - 1 ][1 ], dp[i - 1 ][0 ] - prices[i]); } return dp[prices.length - 1 ][0 ]; } }
55.跳跃游戏 给定一个非负整数数组 nums ,你最初位于数组的 第一个下标 。数组中的每个元素代表你在该位置可以跳跃的最大长度。判断你是否能够到达最后一个下标。
方法一:贪心算法
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 class Solution { public boolean canJump (int [] nums) { if (nums == null || nums.length == 0 ){ return false ; } int coverRange = 0 ; for (int i = 0 ; i <= coverRange; i++){ coverRange = Math.max(coverRange, i + nums[i]); if (coverRange >= nums.length - 1 ){ return true ; } } return false ; } }
方法二:动态规划
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 class Solution { public boolean canJump (int [] nums) { boolean [] dp = new boolean [nums.length]; dp[0 ] = true ; for (int i=1 ;i< nums.length;i++){ for (int j=0 ;j<i;j++){ if (dp[j] && nums[j]>= i-j){ dp[i] = true ; break ; } } } return dp[nums.length-1 ]; } }
45.跳跃游戏-II 给你一个非负整数数组 nums ,你最初位于数组的第一个位置。数组中的每个元素代表你在该位置可以跳跃的最大长度。你的目标是使用最少的跳跃次数到达数组的最后一个位置。假设你总是可以到达数组的最后一个位置。
方法一:贪心算法
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 class Solution { public int jump (int [] nums) { if (nums == null || nums.length <= 1 ){ return 0 ; } int jumpCount = 0 ; int curDistance = 0 ; int maxDistance = 0 ; for (int i = 0 ; i < nums.length; i++){ maxDistance = Math.max(maxDistance, i + nums[i]); if (maxDistance >= nums.length - 1 ){ jumpCount++; break ; } if (i == curDistance){ curDistance = maxDistance; jumpCount++; } } return jumpCount; } }
方法二:算法优化
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 class Solution { public int jump (int [] nums) { int result = 0 ; int end = 0 ; int tmp = 0 ; for (int i = 0 ; i <= end && end < nums.length - 1 ; ++i){ tmp = Math.max(tmp, i + nums[i]); if (i == end){ end = tmp; result++; } } return result; } }
1005.k次取反后最大化的数组和 给你一个整数数组 nums 和一个整数 k ,按以下方法修改该数组:选择某个下标 i 并将 nums[i] 替换为 -nums[i] 。
重复这个过程恰好 k 次。可以多次选择同一个下标 i 。以这种方式修改数组后,返回数组 可能的最大和 。
算法一:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 class Solution { public int largestSumAfterKNegations (int [] nums, int k) { if (nums.length == 1 ){ return k % 2 == 0 ? nums[0 ] : -nums[0 ]; } Arrays.sort(nums); int sum = 0 ; int index = 0 ; for (int i = 0 ; i < k; i++){ if (i < nums.length - 1 && nums[index] < 0 ){ nums[index] = -nums[index]; if (nums[index] >= Math.abs(nums[index + 1 ])){ index++; } continue ; } nums[index] = -nums[index]; } for (int i = 0 ; i < nums.length; i++){ sum += nums[i]; } return sum; } }
算法二:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 class Solution { public int largestSumAfterKNegations (int [] nums, int k) { nums = IntStream.of(nums) .boxed() .sorted((o1, o2) -> Math.abs(o2) - Math.abs(o1)) .mapToInt(Integer :: intValue).toArray(); int len = nums.length; for (int i = 0 ; i < len; i++){ if (nums[i] < 0 && k > 0 ){ nums[i] = -nums[i]; k--; } } if (k % 2 == 1 ){ nums[len - 1 ] = -nums[len - 1 ]; } return Arrays.stream(nums).sum(); } }
134.加油站 在一条环路上有 n 个加油站,其中第 i 个加油站有汽油 gas[i] 升。你有一辆油箱容量无限的的汽车,从第 i 个加油站开往第 i+1 个加油站需要消耗汽油 cost[i] 升。你从其中的一个加油站出发,开始时油箱为空。
给定两个整数数组 gas 和 cost ,如果你可以绕环路行驶一周,则返回出发时加油站的编号,否则返回 -1 。如果存在解,则 保证 它是 唯一 的。
解法一:贪心算法
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 class Solution { public int canCompleteCircuit (int [] gas, int [] cost) { int sum = 0 ; int min = 0 ; for (int i = 0 ; i < gas.length; i++){ sum += (gas[i] - cost[i]); min = Math.min(min, sum); } if (sum < 0 ){ return -1 ; } if (min >= 0 ){ return 0 ; } for (int i = gas.length - 1 ; i > 0 ; i--){ min += (gas[i] - cost[i]); if (min >= 0 ){ return i; } } return -1 ; } }
解法二:贪心算法
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 class Solution { public int canCompleteCircuit (int [] gas, int [] cost) { int curSum = 0 ; int totalSum = 0 ; int index = 0 ; for (int i = 0 ; i < gas.length; i++){ curSum += (gas[i] - cost[i]); totalSum += (gas[i] - cost[i]); if (curSum < 0 ){ index = (i + 1 ) % gas.length; curSum = 0 ; } } if (totalSum < 0 ){ return -1 ; } return index; } }
135.分发糖果 n 个孩子站成一排。给你一个整数数组 ratings 表示每个孩子的评分。你需要按照以下要求,给这些孩子分发糖果:
每个孩子至少分配到 1 个糖果。
相邻两个孩子评分更高的孩子会获得更多的糖果。
请你给每个孩子分发糖果,计算并返回需要准备的 最少糖果数目 。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 class Solution { public int candy (int [] ratings) { int len = ratings.length; int [] candy = new int [len]; candy[0 ] = 1 ; for (int i = 1 ; i < len; i++){ candy[i] = (ratings[i] > ratings[i - 1 ]) ? candy[i - 1 ] + 1 : 1 ; } for (int i = len - 2 ; i >= 0 ; i--){ if (ratings[i] > ratings[i + 1 ]){ candy[i] = Math.max(candy[i], candy[i + 1 ] + 1 ); } } int ans = 0 ; for (int num : candy){ ans += num; } return ans; } }
860.柠檬水找零 在柠檬水摊上,每一杯柠檬水的售价为 5 美元。顾客排队购买你的产品,(按账单 bills 支付的顺序)一次购买一杯。每位顾客只买一杯柠檬水,然后向你付 5 美元、10 美元或 20 美元。你必须给每个顾客正确找零,也就是说净交易是每位顾客向你支付 5 美元。
注意 ,一开始你手头没有任何零钱。
给你一个整数数组 bills ,其中 bills[i] 是第 i 位顾客付的账。如果你能给每位顾客正确找零,返回 true ,否则返回 false 。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 class Solution { public boolean lemonadeChange (int [] bills) { int five = 0 ; int ten = 0 ; for (int i = 0 ; i < bills.length; i++){ if (bills[i] == 5 ){ five++; }else if (bills[i] == 10 ){ five--; ten++; }else if (bills[i] == 20 ){ if (ten > 0 ){ ten--; five--; }else { five -= 3 ; } } if (five < 0 || ten < 0 ){ return false ; } } return true ; } }
406.根据身高重建队列 假设有打乱顺序的一群人站成一个队列,数组 people 表示队列中一些人的属性(不一定按顺序)。每个 people[i] = [hi, ki] 表示第 i 个人的身高为 hi ,前面 正好 有 ki 个身高大于或等于 hi 的人。
请你重新构造并返回输入数组 people 所表示的队列。返回的队列应该格式化为数组 queue ,其中 queue[j] = [hj, kj] 是队列中第 j 个人的属性(queue[0] 是排在队列前面的人)。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 class Solution { public int [][] reconstructQueue(int [][] people) { Arrays.sort(people, (a, b) -> { if (a[0 ] == b[0 ]){ return a[1 ] - b[1 ]; } return b[0 ] - a[0 ]; }); LinkedList<int []> que = new LinkedList <>(); for (int [] p : people){ que.add(p[1 ], p); } return que.toArray(new int [people.length][]); } }
452.用最少的箭射爆气球 有一些球形气球贴在一堵用 XY 平面表示的墙面上。墙面上的气球记录在整数数组 points ,其中points[i] = [xstart, xend] 表示水平直径在 xstart 和 xend之间的气球。你不知道气球的确切 y 坐标。
一支弓箭可以沿着 x 轴从不同点 完全垂直 地射出。在坐标 x 处射出一支箭,若有一个气球的直径的开始和结束坐标为 x``start,x``end, 且满足 xstart ≤ x ≤ x``end,则该气球会被 引爆 。可以射出的弓箭的数量 没有限制 。 弓箭一旦被射出之后,可以无限地前进。
给你一个数组 points ,返回引爆所有气球所必须射出的 最小 弓箭数 。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 class Solution { public int findMinArrowShots (int [][] points) { Arrays.sort(points, (a, b) -> Integer.compare(a[0 ], b[0 ])); int count = 1 ; for (int i = 1 ; i < points.length; i++){ if (points[i][0 ] > points[i - 1 ][1 ]){ count++; }else { points[i][1 ] = Math.min(points[i][1 ], points[i - 1 ][1 ]); } } return count; } }
435.无重叠区域 给定一个区间的集合 intervals ,其中 intervals[i] = [starti, endi] 。返回 需要移除区间的最小数量,使剩余区间互不重叠 。
方法一:按右边排序
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 class Solution { public int eraseOverlapIntervals (int [][] intervals) { Arrays.sort(intervals, (a, b) ->{ return a[1 ] - b[1 ]; }); int count = 0 ; int edge = Integer.MIN_VALUE; for (int i = 0 ; i < intervals.length; i++){ if (edge <= intervals[i][0 ]){ edge = intervals[i][1 ]; }else { count++; } } return count; } }
方法二:按左边排序
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 class Solution { public int eraseOverlapIntervals (int [][] intervals) { Arrays.sort(intervals, (a, b) -> { return Integer.compare(a[0 ], b[0 ]); }); int remove = 0 ; int pre = intervals[0 ][1 ]; for (int i = 1 ; i < intervals.length; i++){ if (pre > intervals[i][0 ]){ remove++; pre = Math.min(pre, intervals[i][1 ]); }else { pre = intervals[i][1 ]; } } return remove; } }
763.划分字母区间 字符串 S 由小写字母组成。我们要把这个字符串划分为尽可能多的片段,同一字母最多出现在一个片段中。返回一个表示每个字符串片段的长度的列表。
方法一:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 class Solution { public List<Integer> partitionLabels (String s) { List<Integer> list = new ArrayList <>(); int [] edge = new int [26 ]; char [] cs = s.toCharArray(); for (int i = 0 ; i < s.length(); i++){ edge[cs[i] - 'a' ] = i; } int index = 0 ; int last = -1 ; for (int i = 0 ; i < cs.length; i++){ index = Math.max(index, edge[cs[i] - 'a' ]); if (i == index){ list.add(i - last); last = i; } } return list; } }
56.合并区间 以数组 intervals 表示若干个区间的集合,其中单个区间为 intervals[i] = [starti, endi] 。请你合并所有重叠的区间,并返回 一个不重叠的区间数组,该数组需恰好覆盖输入中的所有区间 。
方法一:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 class Solution { public int [][] merge(int [][] intervals) { List<int []> result = new LinkedList <>(); Arrays.sort(intervals, (a, b) -> Integer.compare(a[0 ], b[0 ])); int start = intervals[0 ][0 ]; int right = intervals[0 ][1 ]; for (int i = 1 ; i < intervals.length; i++){ if (intervals[i][0 ] > right){ result.add(new int []{start, right}); start = intervals[i][0 ]; right = intervals[i][1 ]; }else { right = Math.max(right, intervals[i][1 ]); } } result.add(new int []{start, right}); return result.toArray(new int [result.size()][]); } }
方法二:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 class Solution { public int [][] merge(int [][] intervals) { LinkedList<int []> result = new LinkedList <>(); Arrays.sort(intervals, (a, b) -> Integer.compare(a[0 ], b[0 ])); result.add(intervals[0 ]); for (int i = 1 ; i < intervals.length; i++){ if (intervals[i][0 ] <= result.getLast()[1 ]){ int start = result.getLast()[0 ]; int end = Math.max(result.getLast()[1 ], intervals[i][1 ]); result.removeLast(); result.add(new int []{start, end}); }else { result.add(intervals[i]); } } return result.toArray(new int [result.size()][]); } }
738.单调递增的数字 当且仅当每个相邻位数上的数字 x 和 y 满足 x <= y 时,我们称这个整数是单调递增 的。给定一个整数 n ,返回 小于或等于 n 的最大数字,且数字呈 单调递增 。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 class Solution { public int monotoneIncreasingDigits (int n) { String s = String.valueOf(n); char [] cs = s.toCharArray(); int start = s.length(); for (int i = s.length() - 2 ; i >= 0 ; i--){ if (cs[i] > cs[i + 1 ]){ cs[i]--; start = i + 1 ; } } for (int i = start; i < s.length(); i++){ cs[i] = '9' ; } return Integer.parseInt(String.valueOf(cs)); } }
714.买卖股票的最佳时机含手续费 给定一个整数数组 prices,其中 prices[i]表示第 i 天的股票价格 ;整数 fee 代表了交易股票的手续费用。你可以无限次地完成交易,但是你每笔交易都需要付手续费。如果你已经购买了一个股票,在卖出它之前你就不能再继续购买股票了。
返回获得利润的最大值。
注意: 这里的一笔交易指买入持有并卖出股票的整个过程,每笔交易你只需要为支付一次手续费。
方法一:贪心算法
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 class Solution { public int maxProfit (int [] prices, int fee) { int buy = prices[0 ] + fee; int sum = 0 ; for (int price : prices){ if (price + fee < buy){ buy = price + fee; }else if (price > buy){ sum += price - buy; buy = price; } } return sum; } }
方法二:动态规划
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 class Solution { public int maxProfit (int [] prices, int fee) { if (prices == null || prices.length < 2 ){ return 0 ; } int [][] dp = new int [prices.length][2 ]; dp[0 ][0 ] = 0 ; dp[0 ][1 ] = -prices[0 ]; for (int i = 1 ; i < prices.length; i++){ dp[i][0 ] = Math.max(dp[i - 1 ][0 ], dp[i - 1 ][1 ] + prices[i] - fee); dp[i][1 ] = Math.max(dp[i - 1 ][1 ], dp[i - 1 ][0 ] - prices[i]); } return dp[prices.length - 1 ][0 ]; } }
968.监控二叉树 给定一个二叉树,我们在树的节点上安装摄像头。节点上的每个摄影头都可以监视其父对象、自身及其直接子对象。
计算监控树的所有节点所需的最小摄像头数量。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 class Solution { int res = 0 ; public int minCameraCover (TreeNode root) { if (minCamera(root) == 0 ){ res++; } return res; } public int minCamera (TreeNode root) { if (root == null ){ return 2 ; } int left = minCamera(root.left); int right = minCamera(root.right); if (left == 2 && right == 2 ){ return 0 ; }else if (left == 0 || right == 0 ){ res++; return 1 ; }else { return 2 ; } } }
九、动态规划 动态规划五部曲
确定dp数组(dp table)以及下标的含义
确定递推公式
dp数组如何初始化
确定遍历顺序
举例推导dp数组
—动规基础— 509.斐波那契数 斐波那契数 (通常用 F(n) 表示)形成的序列称为 斐波那契数列 。该数列由 0 和 1 开始,后面的每一项数字都是前面两项数字的和。也就是:
1 2 3 F(0) = 0, F(1) = 1, F(n) = F(n - 1) + F(n - 2),其中 n > 1
给定 n ,请计算 F(n) 。
写法一:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 class Solution { public int fib (int n) { if (n < 2 ){ return n; } int a = 0 , b = 1 , c = 0 ; for (int i = 1 ; i < n; i++){ c = a + b; a = b; b = c; } return c; } }
写法二:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 class Solution { public int fib (int n) { if (n < 2 ){ return n; } int [] dp = new int [n + 1 ]; dp[0 ] = 0 ; dp[1 ] = 1 ; for (int i = 2 ; i <= n; i++){ dp[i] = dp[i - 1 ] + dp[i - 2 ]; } return dp[n]; } }
70.爬楼梯 假设你正在爬楼梯。需要 n 阶你才能到达楼顶。每次你可以爬 1 或 2 个台阶。你有多少种不同的方法可以爬到楼顶呢?
写法一:常规写法
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 class Solution { public int climbStairs (int n) { int [] dp = new int [n + 1 ]; dp[0 ] = 1 ; dp[1 ] = 1 ; for (int i = 2 ; i <= n; i++){ dp[i] = dp[i - 1 ] + dp[i - 2 ]; } return dp[n]; } }
写法二:用变量记录代替数组
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 class Solution { public int climbStairs (int n) { if (n < 2 ){ return n; } int a = 1 , b = 2 , sum = 0 ; for (int i = 3 ; i <= n; i++){ sum = a + b; a = b; b = sum; } return b; } }
写法三:完全背包问题解法
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 class Solution { public int climbStairs (int n) { int [] dp = new int [n + 1 ]; dp[0 ] = 1 ; int [] weight = {1 , 2 }; for (int i = 0 ; i <= n; i++){ for (int j = 0 ; j < weight.length; j++){ if (i >= weight[j]){ dp[i] += dp[i - weight[j]]; } } } return dp[n]; } }
746.使用最小花费爬楼梯 给你一个整数数组 cost ,其中 cost[i] 是从楼梯第 i 个台阶向上爬需要支付的费用。一旦你支付此费用,即可选择向上爬一个或者两个台阶。你可以选择从下标为 0 或下标为 1 的台阶开始爬楼梯。请你计算并返回达到楼梯顶部的最低花费。
方法一:第一步不支付费用
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 class Solution { public int minCostClimbingStairs (int [] cost) { int len = cost.length; int [] dp = new int [len + 1 ]; dp[0 ] = 0 ; dp[1 ] = 0 ; for (int i = 2 ; i <= len; i++){ dp[i] = Math.min(dp[i - 1 ] + cost[i - 1 ], dp[i - 2 ] + cost[i - 2 ]); } return dp[len]; } }
方法二:第一步支付费用
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 class Solution { public int minCostClimbingStairs (int [] cost) { int [] dp = new int [cost.length]; dp[0 ] = cost[0 ]; dp[1 ] = cost[1 ]; for (int i = 2 ; i < cost.length; i++) { dp[i] = Math.min(dp[i - 1 ], dp[i - 2 ]) + cost[i]; } return Math.min(dp[cost.length - 1 ], dp[cost.length - 2 ]); } }
62.不同路径 一个机器人位于一个 m x n 网格的左上角 (起始点在下图中标记为 “Start” )。机器人每次只能向下或者向右移动一步。机器人试图达到网格的右下角(在下图中标记为 “Finish” )。
问总共有多少条不同的路径?
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 class Solution { public int uniquePaths (int m, int n) { int [][] dp = new int [m][n]; for (int i = 0 ; i < m; i++){ dp[i][0 ] = 1 ; } for (int i = 0 ; i < n; i++){ dp[0 ][i] = 1 ; } for (int i = 1 ; i < m; i++){ for (int j = 1 ; j < n; j++){ dp[i][j] = dp[i - 1 ][j] + dp[i][j - 1 ]; } } return dp[m - 1 ][n - 1 ]; } }
63.不同路径-II 一个机器人位于一个 m x n 网格的左上角 (起始点在下图中标记为 “Start” )。机器人每次只能向下或者向右移动一步。机器人试图达到网格的右下角(在下图中标记为 “Finish”)。
现在考虑网格中有障碍物。那么从左上角到右下角将会有多少条不同的路径?网格中的障碍物和空位置分别用 1 和 0 来表示。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 class Solution { public int uniquePathsWithObstacles (int [][] obstacleGrid) { int x = obstacleGrid.length; int y = obstacleGrid[0 ].length; int [][] dp = new int [x][y]; if (obstacleGrid[x - 1 ][y - 1 ] == 1 || obstacleGrid[0 ][0 ] == 1 ){ return 0 ; } for (int i = 0 ; i < x && obstacleGrid[i][0 ] == 0 ; i++){ dp[i][0 ] = 1 ; } for (int i = 0 ; i < y && obstacleGrid[0 ][i] == 0 ; i++){ dp[0 ][i] = 1 ; } for (int i = 1 ; i < x; i++){ for (int j = 1 ; j < y; j++){ dp[i][j] = (obstacleGrid[i][j] == 0 ) ? dp[i - 1 ][j] + dp[i][j - 1 ] : 0 ; } } return dp[x - 1 ][y - 1 ]; } }
343.整数拆分 给定一个正整数 n ,将其拆分为 k 个 正整数 的和( k >= 2 ),并使这些整数的乘积最大化。返回 你可以获得的最大乘积 。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 class Solution { public int integerBreak (int n) { int [] dp = new int [n + 1 ]; dp[2 ] = 1 ; for (int i = 3 ; i <= n; i++){ for (int j = 1 ; j <= i - j; j++){ dp[i] = Math.max(dp[i], Math.max(j * (i - j), j * dp[i - 1 ])); } } return dp[n]; } }
96.不同的二叉搜索树 给你一个整数 n ,求恰由 n 个节点组成且节点值从 1 到 n 互不相同的 二叉搜索树 有多少种?返回满足题意的二叉搜索树的种数。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 class Solution { public int numTrees (int n) { int [] dp = new int [n + 1 ]; dp[0 ] = 1 ; dp[1 ] = 1 ; for (int i = 2 ; i <= n; i++){ for (int j = 1 ; j <= i; j++){ dp[i] += dp[j - 1 ] * dp[i - j]; } } return dp[n]; } }
—背包问题— 416.分割等和子集 给你一个 只包含正整数 的 非空 数组 nums 。请你判断是否可以将这个数组分割成两个子集,使得两个子集的元素和相等。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 class Solution { public boolean canPartition (int [] nums) { if (nums == null || nums.length == 0 ){ return false ; } int len = nums.length; int sum = 0 ; for (int num : nums){ sum += num; } if (sum % 2 != 0 ){ return false ; } int target = sum / 2 ; int [] dp = new int [target + 1 ]; for (int i = 0 ; i < len; i++){ for (int j = target; j >= nums[i]; j--){ dp[j] = Math.max(dp[j], dp[j - nums[i]] + nums[i]); } } return dp[target] == target; } }
1049.最后一块石头的重量-II 有一堆石头,用整数数组 stones 表示。其中 stones[i] 表示第 i 块石头的重量。每一回合,从中选出任意两块石头 ,然后将它们一起粉碎。假设石头的重量分别为 x 和 y,且 x <= y。那么粉碎的可能结果如下:
如果 x == y,那么两块石头都会被完全粉碎;
如果 x != y,那么重量为 x 的石头将会完全粉碎,而重量为 y 的石头新重量为 y-x。
最后,最多只会剩下一块 石头。返回此石头 最小的可能重量 。如果没有石头剩下,就返回 0。
方法一:二维dp数组
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 class Solution { public int lastStoneWeightII (int [] stones) { int sum = 0 ; for (int s : stones){ sum += s; } int target = sum / 2 ; int [][] dp = new int [stones.length][target + 1 ]; for (int j = stones[0 ]; j <= target; j++){ dp[0 ][j] = stones[0 ]; } for (int i = 1 ; i < stones.length; i++){ for (int j = 1 ; j <= target; j++){ if (j >= stones[i]){ dp[i][j] = Math.max(dp[i - 1 ][j], dp[i - 1 ][j - stones[i]] + stones[i]); }else { dp[i][j] = dp[i - 1 ][j]; } } } System.out.println(dp[stones.length - 1 ][target]); return (sum - dp[stones.length - 1 ][target]) - dp[stones.length - 1 ][target]; } }
方法二:一维dp数组
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 class Solution { public int lastStoneWeightII (int [] stones) { int sum = 0 ; for (int s : stones){ sum += s; } int target = sum / 2 ; int [] dp = new int [target + 1 ]; for (int i = 0 ; i < stones.length; i++){ for (int j = target; j >= stones[i]; j--){ dp[j] = Math.max(dp[j], dp[j - stones[i]] + stones[i]); } } return (sum - dp[target]) - dp[target]; } }
494.目标和 给你一个整数数组 nums 和一个整数 target 。向数组中的每个整数前添加 '+' 或 '-' ,然后串联起所有整数,可以构造一个 表达式 :
例如,nums = [2, 1] ,可以在 2 之前添加 '+' ,在 1 之前添加 '-' ,然后串联起来得到表达式 "+2-1" 。
返回可以通过上述方法构造的、运算结果等于 target 的不同 表达式 的数目。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 class Solution { public int findTargetSumWays (int [] nums, int target) { int sum = 0 ; for (int num : nums){ sum += num; } if ((target + sum) % 2 != 0 ){ return 0 ; } int size = (target + sum) / 2 ; if (size < 0 ){ size = -size; } int [] dp = new int [size + 1 ]; dp[0 ] = 1 ; for (int i = 0 ; i < nums.length; i++){ for (int j = size; j >= nums[i]; j--){ dp[j] += dp[j - nums[i]]; } } return dp[size]; } }
474.一和零 给你一个二进制字符串数组 strs 和两个整数 m 和 n 。请你找出并返回 strs 的最大子集的长度,该子集中 最多 有 m 个 0 和 n 个 1 。如果 x 的所有元素也是 y 的元素,集合 x 是集合 y 的 子集 。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 class Solution { public int findMaxForm (String[] strs, int m, int n) { int [][] dp = new int [m + 1 ][n + 1 ]; int oneNum, zeroNum; for (String str : strs){ oneNum = 0 ; zeroNum = 0 ; for (char cs : str.toCharArray()){ if (cs == '0' ){ zeroNum++; }else { oneNum++; } } for (int i = m; i >= zeroNum; i--){ for (int j = n; j >= oneNum; j--){ dp[i][j] = Math.max(dp[i][j], dp[i - zeroNum][j - oneNum] + 1 ); } } } return dp[m][n]; } }
518.零钱兑换-II 给你一个整数数组 coins 表示不同面额的硬币,另给一个整数 amount 表示总金额。请你计算并返回可以凑成总金额的硬币组合数。如果任何硬币组合都无法凑出总金额,返回 0 。假设每一种面额的硬币有无限个。
题目数据保证结果符合 32 位带符号整数。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 class Solution { public int change (int amount, int [] coins) { int [] dp = new int [amount + 1 ]; dp[0 ] = 1 ; for (int i = 0 ; i < coins.length; i++){ for (int j = coins[i]; j <= amount; j++){ dp[j] += dp[j - coins[i]]; } } return dp[amount]; } }
377.组合总和-IV 给你一个由 不同 整数组成的数组 nums ,和一个目标整数 target 。请你从 nums 中找出并返回总和为 target 的元素组合的个数。题目数据保证答案符合 32 位整数范围。(实际是求排列!)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 class Solution { public int combinationSum4 (int [] nums, int target) { int [] dp = new int [target + 1 ]; dp[0 ] = 1 ; for (int i = 0 ; i <= target; i++){ for (int j = 0 ; j < nums.length; j++){ if (i >= nums[j]){ dp[i] += dp[i - nums[j]]; } } } return dp[target]; } }
322.零钱兑换 给你一个整数数组 coins ,表示不同面额的硬币;以及一个整数 amount ,表示总金额。计算并返回可以凑成总金额所需的 最少的硬币个数 。如果没有任何一种硬币组合能组成总金额,返回 -1 。
你可以认为每种硬币的数量是无限 的。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 class Solution { public int coinChange (int [] coins, int amount) { int [] dp = new int [amount + 1 ]; int max = Integer.MAX_VALUE; for (int j = 0 ; j < dp.length; j++){ dp[j] = max; } dp[0 ] = 0 ; for (int i = 0 ; i < coins.length; i++){ for (int j = coins[i]; j <= amount; j++){ if (dp[j - coins[i]] != max){ dp[j] = Math.min(dp[j], dp[j - coins[i]] + 1 ); } } } return dp[amount] == max ? -1 : dp[amount]; } }
279.完全平方数 给你一个整数 n ,返回 和为 n 的完全平方数的最少数量 。完全平方数 是一个整数,其值等于另一个整数的平方;换句话说,其值等于一个整数自乘的积。例如,1、4、9 和 16 都是完全平方数,而 3 和 11 不是。
解法一:先遍历物品, 再遍历背包
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 class Solution { public int numSquares (int n) { int max = Integer.MAX_VALUE; int [] dp = new int [n + 1 ]; for (int j = 0 ; j <= n; j++){ dp[j] = max; } dp[0 ] = 0 ; for (int i = 1 ; i * i <= n; i++){ for (int j = i * i; j <= n; j++){ if (dp[j - i * i] != max){ dp[j] = Math.min(dp[j], dp[j - i * i] + 1 ); } } } return dp[n]; } }
解法二:先遍历背包, 再遍历物品
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 class Solution { public int numSquares (int n) { int max = Integer.MAX_VALUE; int [] dp = new int [n + 1 ]; for (int j = 0 ; j <= n; j++){ dp[j] = max; } dp[0 ] = 0 ; for (int j = 1 ; j <= n; j++){ for (int i = 1 ; i * i <= j; i++){ dp[j] = Math.min(dp[j], dp[j - i * i] + 1 ); } } return dp[n]; } }
139.单词拆分 给你一个字符串 s 和一个字符串列表 wordDict 作为字典。请你判断是否可以利用字典中出现的单词拼接 出 s 。
注意: 不要求字典中出现的单词全部都使用,并且字典中的单词可以重复使用。
方法一:动态规划完全背包
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 class Solution { public boolean wordBreak (String s, List<String> wordDict) { HashSet<String> set = new HashSet <>(wordDict); boolean [] vaild = new boolean [s.length() + 1 ]; vaild[0 ] = true ; for (int i = 1 ; i <= s.length(); i++){ for (int j = 0 ; j < i && !vaild[i]; j++){ if (set.contains(s.substring(j, i)) && vaild[j]){ vaild[i] = true ; } } } return vaild[s.length()]; } }
方法二:另一种思路的完全背包
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 class Solution { public boolean wordBreak (String s, List<String> wordDict) { boolean [] dp = new boolean [s.length() + 1 ]; dp[0 ] = true ; for (int i = 1 ; i <= s.length(); i++){ for (String word : wordDict){ int len = word.length(); if (i >= len && dp[i - len] && word.equals(s.substring(i - len, i))){ dp[i] = true ; break ; } } } return dp[s.length()]; } }
方法三:回溯+记忆化
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 class Solution { Set<String> set; int [] memo; public boolean wordBreak (String s, List<String> wordDict) { memo = new int [s.length()]; set = new HashSet <>(wordDict); return backTracking(s, 0 ); } public boolean backTracking (String s, int startIndex) { if (startIndex == s.length()){ return true ; } if (memo[startIndex] == -1 ){ return false ; } for (int i = startIndex; i < s.length(); i++){ String sub = s.substring(startIndex, i + 1 ); if (!set.contains(sub)){ continue ; } boolean res = backTracking(s, i + 1 ); if (res){ return true ; } } memo[startIndex] = -1 ; return false ; } }
—打家劫舍系列— 198.打家劫舍 你是一个专业的小偷,计划偷窃沿街的房屋。每间房内都藏有一定的现金,影响你偷窃的唯一制约因素就是相邻的房屋装有相互连通的防盗系统,如果两间相邻的房屋在同一晚上被小偷闯入,系统会自动报警 。给定一个代表每个房屋存放金额的非负整数数组,计算你 不触动警报装置的情况下 ,一夜之内能够偷窃到的最高金额。
解法:动态规划
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 class Solution { public int rob (int [] nums) { if (nums == null || nums.length == 0 ){ return 0 ; } if (nums.length == 1 ){ return nums[0 ]; } int len = nums.length; int [] dp = new int [len]; dp[0 ] = nums[0 ]; dp[1 ] = Math.max(dp[0 ], nums[1 ]); for (int i = 2 ; i < len; i++){ dp[i] = Math.max(dp[i - 1 ], dp[i - 2 ] + nums[i]); } return dp[len - 1 ]; } }
213.打家劫舍-II 你是一个专业的小偷,计划偷窃沿街的房屋,每间房内都藏有一定的现金。这个地方所有的房屋都 围成一圈 ,这意味着第一个房屋和最后一个房屋是紧挨着的。同时,相邻的房屋装有相互连通的防盗系统,如果两间相邻的房屋在同一晚上被小偷闯入,系统会自动报警 。给定一个代表每个房屋存放金额的非负整数数组,计算你 在不触动警报装置的情况下 ,今晚能够偷窃到的最高金额。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 class Solution { public int rob (int [] nums) { if (nums == null || nums.length == 0 ){ return 0 ; } if (nums.length == 1 ){ return nums[0 ]; } int len = nums.length; return Math.max(robAction(nums, 0 , len - 1 ), robAction(nums, 1 , len)); } public int robAction (int [] nums, int start, int end) { int a = 0 , b = 0 , c = 0 ; for (int i = start; i < end; i++){ b = c; c = Math.max(b, a + nums[i]); a = b; } return c; } }
337.打家劫舍-III 小偷又发现了一个新的可行窃的地区。这个地区只有一个入口,我们称之为 root 。除了 root 之外,每栋房子有且只有一个“父“房子与之相连。一番侦察之后,聪明的小偷意识到“这个地方的所有房屋的排列类似于一棵二叉树”。 如果 两个直接相连的房子在同一天晚上被打劫 ,房屋将自动报警。
给定二叉树的 root 。返回 在不触动警报的情况下 ,小偷能够盗取的最高金额
方法一:直接递归(超时)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 class Solution { public int rob (TreeNode root) { if (root == null ){ return 0 ; } int money = root.val; if (root.left != null ){ money += rob(root.left.left) + rob(root.left.right); } if (root.right != null ){ money += rob(root.right.left) + rob(root.right.right); } return Math.max(money, rob(root.left) + rob(root.right)); } }
方法二:记录状态递归
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 class Solution { public int rob (TreeNode root) { Map<TreeNode, Integer> map = new HashMap <>(); return robAction(root, map); } public int robAction (TreeNode root, Map<TreeNode, Integer> map) { if (root == null ){ return 0 ; } if (map.containsKey(root)){ return map.get(root); } int money = root.val; if (root.left != null ){ money += robAction(root.left.left, map) + robAction(root.left.right, map); } if (root.right != null ){ money += robAction(root.right.left, map) + robAction(root.right.right, map); } int res = Math.max(money, robAction(root.left, map) + robAction(root.right, map)); map.put(root, res); return res; } }
方法三:状态标记递归(推荐)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 class Solution { public int rob (TreeNode root) { int [] res = robAction(root); return Math.max(res[0 ], res[1 ]); } public int [] robAction(TreeNode root) { int [] res = new int [2 ]; if (root == null ){ return res; } int [] left = robAction(root.left); int [] right = robAction(root.right); res[0 ] = Math.max(left[0 ], left[1 ]) + Math.max(right[0 ], right[1 ]); res[1 ] = root.val + left[0 ] + right[0 ]; return res; } }
—股票买卖系列— 121.买卖股票的最佳时机 给定一个数组 prices ,它的第 i 个元素 prices[i] 表示一支给定股票第 i 天的价格。你只能选择 某一天 买入这只股票,并选择在 未来的某一个不同的日子 卖出该股票。设计一个算法来计算你所能获取的最大利润。
返回你可以从这笔交易中获取的最大利润。如果你不能获取任何利润,返回 0 。
解法一:贪心算法
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 class Solution { public int maxProfit (int [] prices) { int low = Integer.MAX_VALUE; int res = 0 ; for (int i = 0 ; i < prices.length; i++){ low = Math.min(low, prices[i]); res = Math.max(res, prices[i] - low); } return res; } }
解法二:动态规划版本一
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 class Solution { public int maxProfit (int [] prices) { if (prices == null || prices.length == 0 ){ return 0 ; } int len = prices.length; int [][] dp = new int [len][2 ]; dp[0 ][0 ] = -prices[0 ]; dp[0 ][1 ] = 0 ; for (int i = 1 ; i < len; i++){ dp[i][0 ] = Math.max(dp[i - 1 ][0 ], -prices[i]); dp[i][1 ] = Math.max(dp[i - 1 ][1 ], dp[i - 1 ][0 ] + prices[i]); } return dp[len - 1 ][1 ]; } }
解法三:动态规范版本二
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 class Solution { public int maxProfit (int [] prices) { int [] dp = new int [2 ]; dp[0 ] = -prices[0 ]; dp[1 ] = 0 ; for (int i = 1 ; i <= prices.length; i++){ dp[0 ] = Math.max(dp[0 ], -prices[i - 1 ]); dp[1 ] = Math.max(dp[1 ], dp[0 ] + prices[i - 1 ]); } return dp[1 ]; } }
122.买卖股票的最佳时机-II 给你一个整数数组 prices ,其中 prices[i] 表示某支股票第 i 天的价格。在每一天,你可以决定是否购买和/或出售股票。你在任何时候 最多 只能持有 一股 股票。你也可以先购买,然后在 同一天 出售。
返回 你能获得的 最大 利润 。
解法一:动态规划
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 class Solution { public int maxProfit (int [] prices) { int [][] dp = new int [prices.length][2 ]; dp[0 ][0 ] = 0 ; dp[0 ][1 ] = -prices[0 ]; for (int i = 1 ; i < prices.length; i++){ dp[i][0 ] = Math.max(dp[i - 1 ][0 ], dp[i - 1 ][1 ] + prices[i]); dp[i][1 ] = Math.max(dp[i - 1 ][1 ], dp[i - 1 ][0 ] - prices[i]); } return dp[prices.length - 1 ][0 ]; } }
解法二:空间优化解法一
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 class Solution { public int maxProfit (int [] prices) { int [] dp = new int [2 ]; dp[0 ] = -prices[0 ]; dp[1 ] = 0 ; for (int i = 1 ; i <= prices.length; i++){ dp[0 ] = Math.max(dp[0 ], dp[1 ] - prices[i - 1 ]); dp[1 ] = Math.max(dp[1 ], dp[0 ] + prices[i - 1 ]); } return dp[1 ]; } }
123.买卖股票的最佳时机-III 给定一个数组,它的第 i 个元素是一支给定的股票在第 i 天的价格。设计一个算法来计算你所能获取的最大利润。你最多可以完成 两笔 交易。
注意: 你不能同时参与多笔交易(你必须在再次购买前出售掉之前的股票)。
版本一:动态规划
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 class Solution { public int maxProfit (int [] prices) { if (prices.length == 0 ){ return 0 ; } int len = prices.length; int [][] dp = new int [len][5 ]; dp[0 ][1 ] = -prices[0 ]; dp[0 ][3 ] = -prices[0 ]; for (int i = 1 ; i < len; i++){ dp[i][1 ] = Math.max(dp[i - 1 ][1 ], -prices[i]); dp[i][2 ] = Math.max(dp[i - 1 ][2 ], dp[i][1 ] + prices[i]); dp[i][3 ] = Math.max(dp[i - 1 ][3 ], dp[i][2 ] - prices[i]); dp[i][4 ] = Math.max(dp[i - 1 ][4 ], dp[i][3 ] + prices[i]); } return dp[len - 1 ][4 ]; } }
版本二:空间优化
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 class Solution { public int maxProfit (int [] prices) { int [] dp = new int [4 ]; dp[0 ] = -prices[0 ]; dp[1 ] = 0 ; dp[2 ] = -prices[0 ]; dp[3 ] = 0 ; for (int i = 1 ; i <= prices.length; i++){ dp[0 ] = Math.max(dp[0 ], -prices[i - 1 ]); dp[1 ] = Math.max(dp[1 ], dp[0 ] + prices[i - 1 ]); dp[2 ] = Math.max(dp[2 ], dp[1 ] - prices[i - 1 ]); dp[3 ] = Math.max(dp[3 ], dp[2 ] + prices[i - 1 ]); } return dp[3 ]; } }
188.买卖股票的最佳时机-IV 给定一个整数数组 prices ,它的第 i 个元素 prices[i] 是一支给定的股票在第 i 天的价格。设计一个算法来计算你所能获取的最大利润。你最多可以完成 k 笔交易。
注意: 你不能同时参与多笔交易(你必须在再次购买前出售掉之前的股票)。
版本一:三维dp数组
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 class Solution { public int maxProfit (int k, int [] prices) { if (prices.length == 0 ){ return 0 ; } int len = prices.length; int [][][] dp = new int [len][k + 1 ][2 ]; for (int i = 0 ; i <= k; i++){ dp[0 ][i][1 ] = -prices[0 ]; } for (int i = 1 ; i < len; i++){ for (int j = 1 ; j <= k; j++){ dp[i][j][0 ] = Math.max(dp[i - 1 ][j][0 ], dp[i - 1 ][j][1 ] + prices[i]); dp[i][j][1 ] = Math.max(dp[i - 1 ][j][1 ], dp[i - 1 ][j - 1 ][0 ] - prices[i]); } } return dp[len - 1 ][k][0 ]; } }
版本二:二维dp数组
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 class Solution { public int maxProfit (int k, int [] prices) { if (prices.length == 0 ){ return 0 ; } int len = prices.length; int [][] dp = new int [len][2 * k + 1 ]; for (int i = 1 ; i < k * 2 ; i+=2 ){ dp[0 ][i] = -prices[0 ]; } for (int i = 1 ; i < len; i++){ for (int j = 0 ; j < k * 2 - 1 ; j+=2 ){ dp[i][j + 1 ] = Math.max(dp[i - 1 ][j + 1 ], dp[i - 1 ][j] - prices[i]); dp[i][j + 2 ] = Math.max(dp[i - 1 ][j + 2 ], dp[i - 1 ][j + 1 ] + prices[i]); } } return dp[len - 1 ][k * 2 ]; } }
版本三:一维dp数组
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 class Solution { public int maxProfit (int k, int [] prices) { if (prices.length == 0 || k == 0 ){ return 0 ; } int [] dp = new int [2 * k]; for (int i = 0 ; i < dp.length / 2 ; i++){ dp[i * 2 ] = -prices[0 ]; } for (int i = 1 ; i <= prices.length; i++){ dp[0 ] = Math.max(dp[0 ], -prices[i - 1 ]); dp[1 ] = Math.max(dp[1 ], dp[0 ] + prices[i - 1 ]); for (int j = 2 ; j < dp.length; j+=2 ){ dp[j] = Math.max(dp[j], dp[j - 1 ] - prices[i - 1 ]); dp[j + 1 ] = Math.max(dp[j + 1 ], dp[j] + prices[i - 1 ]); } } return dp[dp.length - 1 ]; } }
309.买卖股票的最佳时机含冷冻期 给定一个整数数组 prices,其中第 prices[i] 表示第 *i* 天的股票价格 。设计一个算法计算出最大利润。在满足以下约束条件下,你可以尽可能地完成更多的交易(多次买卖一支股票): 卖出股票后,你无法在第二天买入股票 (即冷冻期为 1 天)。
注意: 你不能同时参与多笔交易(你必须在再次购买前出售掉之前的股票)。
版本一:动态规划
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 class Solution { public int maxProfit (int [] prices) { if (prices == null || prices.length < 2 ){ return 0 ; } int [][] dp = new int [prices.length][2 ]; dp[0 ][0 ] = 0 ; dp[0 ][1 ] = -prices[0 ]; dp[1 ][0 ] = Math.max(dp[0 ][0 ], dp[0 ][1 ] + prices[1 ]); dp[1 ][1 ] = Math.max(dp[0 ][1 ], -prices[1 ]); for (int i = 2 ; i < prices.length; i++){ dp[i][0 ] = Math.max(dp[i - 1 ][0 ], dp[i - 1 ][1 ] + prices[i]); dp[i][1 ] = Math.max(dp[i - 1 ][1 ], dp[i - 2 ][0 ] - prices[i]); } return dp[prices.length - 1 ][0 ]; } }
版本二:一维dp数组优化
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 class Solution { public int maxProfit (int [] prices) { int [] dp = new int [4 ]; dp[0 ] = -prices[0 ]; dp[1 ] = 0 ; for (int i = 1 ; i <= prices.length; i++){ int tmp = dp[0 ]; int tmp1 = dp[2 ]; dp[0 ] = Math.max(dp[0 ], Math.max(dp[3 ], dp[1 ]) - prices[i - 1 ]); dp[1 ] = Math.max(dp[1 ], dp[3 ]); dp[2 ] = tmp + prices[i - 1 ]; dp[3 ] = tmp1; } return Math.max(dp[3 ], Math.max(dp[1 ], dp[2 ])); } }
714.买卖股票的最佳时机含手续费 给定一个整数数组 prices,其中 prices[i]表示第 i 天的股票价格 ;整数 fee 代表了交易股票的手续费用。你可以无限次地完成交易,但是你每笔交易都需要付手续费。如果你已经购买了一个股票,在卖出它之前你就不能再继续购买股票了。返回获得利润的最大值。
注意: 这里的一笔交易指买入持有并卖出股票的整个过程,每笔交易你只需要为支付一次手续费。
解法一:贪心算法
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 class Solution { public int maxProfit (int [] prices, int fee) { int buy = prices[0 ] + fee; int sum = 0 ; for (int price : prices){ if (price + fee < buy){ buy = price + fee; }else if (price > buy){ sum += price - buy; buy = price; } } return sum; } }
解法二:动态规划-卖出时 支付手续费
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 class Solution { public int maxProfit (int [] prices, int fee) { int len = prices.length; int [][] dp = new int [len][2 ]; dp[0 ][0 ] = -prices[0 ]; for (int i = 1 ; i < len; i++){ dp[i][0 ] = Math.max(dp[i - 1 ][0 ], dp[i - 1 ][1 ] - prices[i]); dp[i][1 ] = Math.max(dp[i - 1 ][1 ], dp[i - 1 ][0 ] + prices[i] - fee); } return Math.max(dp[len - 1 ][0 ], dp[len - 1 ][1 ]); } }
解法三:动态规划-买入时 支付手续费
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 class Solution { public int maxProfit (int [] prices, int fee) { int len = prices.length; int [][] dp = new int [len][2 ]; dp[0 ][0 ] = -prices[0 ] - fee; for (int i = 1 ; i < len; i++){ dp[i][0 ] = Math.max(dp[i - 1 ][0 ], dp[i - 1 ][1 ] - prices[i] - fee); dp[i][1 ] = Math.max(dp[i - 1 ][1 ], dp[i - 1 ][0 ] + prices[i]); } return Math.max(dp[len - 1 ][0 ], dp[len - 1 ][1 ]); } }
解法四:动态规划
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 class Solution { public int maxProfit (int [] prices, int fee) { if (prices == null || prices.length < 2 ){ return 0 ; } int [][] dp = new int [prices.length][2 ]; dp[0 ][0 ] = 0 ; dp[0 ][1 ] = -prices[0 ]; for (int i = 1 ; i < prices.length; i++){ dp[i][0 ] = Math.max(dp[i - 1 ][0 ], dp[i - 1 ][1 ] + prices[i] - fee); dp[i][1 ] = Math.max(dp[i - 1 ][1 ], dp[i - 1 ][0 ] - prices[i]); } return dp[prices.length - 1 ][0 ]; } }
解法五:一维dp数组优化
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 class Solution { public int maxProfit (int [] prices, int fee) { int [] dp = new int [2 ]; dp[0 ] = -prices[0 ]; dp[1 ] = 0 ; for (int i = 1 ; i <= prices.length; i++){ dp[0 ] = Math.max(dp[0 ], dp[1 ] - prices[i - 1 ]); dp[1 ] = Math.max(dp[1 ], dp[0 ] + prices[i - 1 ] - fee); } return dp[1 ]; } }
—子序列系列— 300.最长上升子序列 给你一个整数数组 nums ,找到其中最长严格递增子序列的长度。子序列 是由数组派生而来的序列,删除(或不删除)数组中的元素而不改变其余元素的顺序。例如,[3,6,2,7] 是数组 [0,3,1,6,2,2,7] 的子序列。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 class Solution { public int lengthOfLIS (int [] nums) { int [] dp = new int [nums.length]; Arrays.fill(dp, 1 ); for (int i = 1 ; i < dp.length; i++){ for (int j = 0 ; j < i; j++){ if (nums[i] > nums[j]){ dp[i] = Math.max(dp[i], dp[j] + 1 ); } } } int res = 0 ; for (int i = 0 ; i < dp.length; i++){ res = Math.max(res, dp[i]); } return res; } }
674.最长连续递增序列 给定一个未经排序的整数数组,找到最长且 连续递增的子序列 ,并返回该序列的长度。连续递增的子序列 可以由两个下标 l 和 r(l < r)确定,如果对于每个 l <= i < r,都有 nums[i] < nums[i + 1] ,那么子序列 [nums[l], nums[l + 1], ..., nums[r - 1], nums[r]] 就是连续递增子序列。
解法一:动态规划
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 class Solution { public int findLengthOfLCIS (int [] nums) { int [] dp = new int [nums.length]; for (int i = 0 ; i < dp.length; i++){ dp[i] = 1 ; } int res = 1 ; for (int i = 0 ; i < nums.length - 1 ; i++){ if (nums[i + 1 ] > nums[i]){ dp[i + 1 ] = dp[i] + 1 ; } res = res > dp[i + 1 ] ? res : dp[i + 1 ]; } return res; } }
解法二:贪心法
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 class Solution { public int findLengthOfLCIS (int [] nums) { if (nums.length == 0 ){ return 0 ; } int res = 1 ; int count = 1 ; for (int i = 0 ; i < nums.length - 1 ; i++){ if (nums[i + 1 ] > nums[i]){ count++; }else { count = 1 ; } if (count > res){ res = count; } } return res; } }
718.最长重复子数组 给两个整数数组 nums1 和 nums2 ,返回 两个数组中 公共的 、长度最长的子数组的长度 。
版本一:动态规划
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 class Solution { public int findLength (int [] nums1, int [] nums2) { int result = 0 ; int [][] dp = new int [nums1.length + 1 ][nums2.length + 1 ]; for (int i = 1 ; i < nums1.length + 1 ; i++){ for (int j = 1 ; j < nums2.length + 1 ; j++){ if (nums1[i - 1 ] == nums2[j - 1 ]){ dp[i][j] = dp[i - 1 ][j - 1 ] + 1 ; result = Math.max(result, dp[i][j]); } } } return result; } }
版本二:滚动数组
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 class Solution { public int findLength (int [] nums1, int [] nums2) { int [] dp = new int [nums2.length + 1 ]; int result = 0 ; for (int i = 1 ; i <= nums1.length; i++){ for (int j = nums2.length; j > 0 ; j--){ if (nums1[i - 1 ] == nums2[j - 1 ]){ dp[j] = dp[j - 1 ] + 1 ; }else { dp[j] = 0 ; } result = Math.max(result, dp[j]); } } return result; } }
1143.最长公共子序列 给定两个字符串 text1 和 text2,返回这两个字符串的最长 公共子序列 的长度。如果不存在 公共子序列 ,返回 0 。一个字符串的 子序列 是指这样一个新的字符串:它是由原字符串在不改变字符的相对顺序的情况下删除某些字符(也可以不删除任何字符)后组成的新字符串。
例如,"ace" 是 "abcde" 的子序列,但 "aec" 不是 "abcde" 的子序列。两个字符串的 公共子序列 是这两个字符串所共同拥有的子序列。
版本一:二维dp数组
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 class Solution { public int longestCommonSubsequence (String text1, String text2) { int m = text1.length(); int n = text2.length(); int [][] dp = new int [m+1 ][n+1 ]; for (int i = 1 ;i <= m; i++){ for (int j = 1 ;j <= n; j++){ if (text1.charAt(i - 1 ) == text2.charAt(j - 1 )){ dp[i][j] = dp[i - 1 ][j - 1 ] + 1 ; }else { dp[i][j] = Math.max(dp[i - 1 ][j],dp[i][j - 1 ]); } } } return dp[m][n]; } }
版本二:一维dp数组
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 class Solution { public int longestCommonSubsequence (String text1, String text2) { int m = text1.length(); int n = text2.length(); int [] dp = new int [n + 1 ]; for (int i = 1 ; i <= m; i++){ int pre = dp[0 ]; for (int j = 1 ; j <= n; j++){ int cur = dp[j]; if (text1.charAt(i - 1 ) == text2.charAt(j - 1 )){ dp[j] = pre + 1 ; }else { dp[j] = Math.max(dp[j], dp[j - 1 ]); } pre = cur; } } return dp[n]; } }
1035.不相交的线 在两条独立的水平线上按给定的顺序写下 nums1 和 nums2 中的整数。现在,可以绘制一些连接两个数字 nums1[i] 和 nums2[j] 的直线,这些直线需要同时满足满足:
nums1[i] == nums2[j]且绘制的直线不与任何其他连线(非水平线)相交。
请注意,连线即使在端点也不能相交:每个数字只能属于一条连线。以这种方法绘制线条,并返回可以绘制的最大连线数。
解法和1143.最长公共子序列相同
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 class Solution { public int maxUncrossedLines (int [] nums1, int [] nums2) { int m = nums1.length; int n = nums2.length; int [][] dp = new int [m + 1 ][n + 1 ]; for (int i = 1 ; i <= m; i++){ for (int j = 1 ; j <= n; j++){ if (nums1[i - 1 ] == nums2[j - 1 ]){ dp[i][j] = dp[i - 1 ][j - 1 ] + 1 ; }else { dp[i][j] = Math.max(dp[i - 1 ][j], dp[i][j - 1 ]); } } } return dp[m][n]; } }
53.最大子数组和 给你一个整数数组 nums ,请你找出一个具有最大和的连续子数组(子数组最少包含一个元素),返回其最大和。子数组 是数组中的一个连续部分。
解法一:动态规划
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 class Solution { public int maxSubArray (int [] nums) { if (nums.length == 0 ){ return 0 ; } int res = nums[0 ]; int [] dp = new int [nums.length]; dp[0 ] = nums[0 ]; for (int i = 1 ; i < nums.length; i++){ dp[i] = Math.max(dp[i - 1 ] + nums[i], nums[i]); res = Math.max(res, dp[i]); } return res; } }
解法二:因为dp[i]的递推公式只与前一个值有关,所以可以用一个变量代替dp数组,空间复杂度为O(1)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 class Solution { public int maxSubArray (int [] nums) { int res = nums[0 ]; int pre = nums[0 ]; for (int i = 1 ; i < nums.length; i++){ pre = Math.max(pre + nums[i], nums[i]); res = Math.max(res, pre); } return res; } }
392.判断子序列 给定字符串 s 和 t ,判断 s 是否为 t 的子序列。字符串的一个子序列是原始字符串删除一些(也可以不删除)字符而不改变剩余字符相对位置形成的新字符串。(例如,"ace"是"abcde"的一个子序列,而"aec"不是)。
解法一:动态规划
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 class Solution { public boolean isSubsequence (String s, String t) { int slen = s.length(); int tlen = t.length(); int [][] dp = new int [slen + 1 ][tlen + 1 ]; for (int i = 1 ; i <= slen; i++){ for (int j = 1 ; j <= tlen; j++){ if (s.charAt(i - 1 ) == t.charAt(j - 1 )){ dp[i][j] = dp[i - 1 ][j - 1 ] + 1 ; }else { dp[i][j] = dp[i][j - 1 ]; } } } if (dp[slen][tlen] == slen){ return true ; } return false ; } }
解法二:双指针法(未写)
115.不同的子序列 给定一个字符串 s 和一个字符串 t ,计算在 s 的子序列中 t 出现的个数。字符串的一个 子序列 是指,通过删除一些(也可以不删除)字符且不干扰剩余字符相对位置所组成的新字符串。(例如,"ACE" 是 "ABCDE" 的一个子序列,而 "AEC" 不是)
题目数据保证答案符合 32 位带符号整数范围。
版本一:二维dp数组
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 class Solution { public int numDistinct (String s, String t) { int m = s.length(); int n = t.length(); int [][] dp = new int [m + 1 ][n + 1 ]; for (int i = 0 ; i <= m; i++){ dp[i][0 ] = 1 ; } for (int i = 1 ; i <= m; i++){ for (int j = 1 ; j <= n; j++){ if (s.charAt(i - 1 ) == t.charAt(j - 1 )){ dp[i][j] = dp[i - 1 ][j - 1 ] + dp[i - 1 ][j]; }else { dp[i][j] = dp[i - 1 ][j]; } } } return dp[m][n]; } }
版本二:一维dp数组
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 class Solution { public int numDistinct (String s, String t) { int m = s.length(); int n = t.length(); if (m < n){ return 0 ; } int [] dp = new int [n + 1 ]; for (int i = 0 ; i <= m; i++){ dp[0 ] = 1 ; } for (int i = 1 ; i <= m; i++){ for (int j = n; j >= 1 ; j--){ if (s.charAt(i - 1 ) == t.charAt(j - 1 )){ dp[j] += dp[j - 1 ]; } } } return dp[n]; } }
583.两个字符串的删除操作 给定两个单词 word1 和 word2 ,返回使得 word1 和 word2 相同 所需的最小步数 。每步 可以删除任意一个字符串中的一个字符。
解法一:dp数组中存储word1和word2最长相同子序列的长度
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 class Solution { public int minDistance (String word1, String word2) { int m = word1.length(); int n = word2.length(); int [][] dp = new int [m + 1 ][n + 1 ]; for (int i = 1 ; i <= m; i++){ for (int j = 1 ; j <= n; j++){ if (word1.charAt(i - 1 ) == word2.charAt(j - 1 )){ dp[i][j] = dp[i - 1 ][j - 1 ] + 1 ; }else { dp[i][j] = Math.max(dp[i - 1 ][j], dp[i][j - 1 ]); } } } return m + n - 2 * dp[m][n]; } }
解法二:dp数组中存储需要删除的字符个数
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 class Solution { public int minDistance (String word1, String word2) { int m = word1.length(); int n = word2.length(); int [][] dp = new int [m + 1 ][n + 1 ]; for (int i = 0 ; i <= m; i++){ dp[i][0 ] = i; } for (int i = 0 ; i <= n; i++){ dp[0 ][i] = i; } for (int i = 1 ; i <= m; i++){ for (int j = 1 ; j <= n; j++){ if (word1.charAt(i - 1 ) == word2.charAt(j - 1 )){ dp[i][j] = dp[i - 1 ][j - 1 ]; }else { dp[i][j] = Math.min(dp[i - 1 ][j - 1 ] + 2 , Math.min(dp[i - 1 ][j] + 1 , dp[i][j - 1 ] + 1 )); } } } return dp[m][n]; } }
72.编辑距离 给你两个单词 word1 和 word2, 请返回将 word1 转换成 word2 所使用的最少操作数 。你可以对一个单词进行如下三种操作:
解法一:动态规划
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 class Solution { public int minDistance (String word1, String word2) { int m = word1.length(); int n = word2.length(); int [][] dp = new int [m + 1 ][n + 1 ]; for (int i = 1 ; i <= m; i++){ dp[i][0 ] = i; } for (int j = 1 ; j <= n; j++){ dp[0 ][j] = j; } for (int i = 1 ; i <= m; i++){ for (int j = 1 ; j <= n; j++){ if (word1.charAt(i - 1 ) == word2.charAt(j - 1 )){ dp[i][j] = dp[i - 1 ][j - 1 ]; }else { dp[i][j] = Math.min(dp[i - 1 ][j - 1 ] + 1 , Math.min(dp[i - 1 ][j] + 1 , dp[i][j - 1 ] + 1 )); } } } return dp[m][n]; } }
解法二:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 class Solution { public int minDistance (String word1, String word2) { int ic = 1 ; int dc = 1 ; int rc = 1 ; if (word1 == null || word2 == null ){ return 0 ; } char [] str1 = word1.toCharArray(); char [] str2 = word2.toCharArray(); int m = str1.length +1 ; int n = str2.length +1 ; int [][] dp = new int [m][n]; for (int i=1 ;i<=str1.length;i++){ dp[i][0 ] = i * dc; } for (int j=1 ;j<=str2.length;j++){ dp[0 ][j] = ic * j; } for (int i=1 ;i<m;i++){ for (int j=1 ;j<n;j++){ if (str1[i-1 ] == str2[j-1 ]){ dp[i][j] = dp[i-1 ][j-1 ]; }else { dp[i][j] = dp[i-1 ][j-1 ] + rc; } dp[i][j] = Math.min(dp[i][j],dp[i][j-1 ] + ic); dp[i][j] = Math.min(dp[i][j],dp[i-1 ][j] + dc); } } return dp[str1.length][str2.length]; } }
解法三:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 class Solution { public int minDistance (String word1, String word2) { int ic = 1 ; int dc = 1 ; int rc = 1 ; if (word1 == null || word2 == null ){ return 0 ; } char [] str1 = word1.toCharArray(); char [] str2 = word2.toCharArray(); char [] longs = str1.length >= str2.length ? str1 : str2; char [] shorts = str1.length < str2.length ? str1 : str2; int m = str1.length; int n = str2.length; if (m < n){ int tmp = ic; ic = dc; dc = tmp; } int [] dp = new int [shorts.length +1 ]; for (int i=1 ;i<=shorts.length;i++){ dp[i] = ic * i; } for (int i=1 ;i<= longs.length;i++){ int pre = dp[0 ]; dp[0 ] = dc * i; for (int j=1 ;j<=shorts.length;j++){ int tmp = dp[j]; if (longs[i-1 ] == shorts[j-1 ]){ dp[j] = pre; }else { dp[j] = pre + rc; } dp[j] = Math.min(dp[j],dp[j-1 ]+ic); dp[j] = Math.min(dp[j],tmp+dc); pre = tmp; } } return dp[shorts.length]; } }
647.回文子串 给你一个字符串 s ,请你统计并返回这个字符串中 回文子串 的数目。回文字符串 是正着读和倒过来读一样的字符串。子字符串 是字符串中的由连续字符组成的一个序列。
具有不同开始位置或结束位置的子串,即使是由相同的字符组成,也会被视作不同的子串。
解法一:动态规划
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 class Solution { public int countSubstrings (String s) { int len = s.length(); if (s == null || len < 1 ){ return 0 ; } int ans = 0 ; boolean [][] dp = new boolean [len][len]; for (int j = 0 ; j < len; j++){ for (int i = 0 ; i <= j; i++){ if (s.charAt(i) == s.charAt(j)){ if (j - i < 3 ){ dp[i][j] = true ; }else { dp[i][j] = dp[i + 1 ][j - 1 ]; } }else { dp[i][j] = false ; } } } for (int i = 0 ; i < len; i++){ for (int j = 0 ; j < len; j++){ if (dp[i][j]){ ans++; } } } return ans; } }
解法二:中心扩散法
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 class Solution { public int countSubstrings (String s) { int len = s.length(); int ans = 0 ; if (s == null || len < 1 ){ return 0 ; } for (int i = 0 ; i < 2 * len - 1 ; i++){ int left = i / 2 ; int right = left + i % 2 ; while (left >= 0 && right < len && s.charAt(left) == s.charAt(right)){ ans++; left--; right++; } } return ans; } }
516.最长回文子序列 给你一个字符串 s ,找出其中最长的回文子序列,并返回该序列的长度。子序列定义为:不改变剩余字符顺序的情况下,删除某些字符或者不删除任何字符形成的一个序列。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 class Solution { public int longestPalindromeSubseq (String s) { int len = s.length(); int [][] dp = new int [len + 1 ][len + 1 ]; for (int i = len - 1 ; i >= 0 ; i--){ dp[i][i] = 1 ; for (int j = i + 1 ; j < len; j++){ if (s.charAt(i) == s.charAt(j)){ dp[i][j] = dp[i + 1 ][j - 1 ] + 2 ; }else { dp[i][j] = Math.max(dp[i + 1 ][j], Math.max(dp[i][j], dp[i][j - 1 ])); } } } return dp[0 ][len - 1 ]; } }
5.最长回文子串 给你一个字符串 s,找到 s 中最长的回文子串。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 class Solution { public String longestPalindrome (String s) { boolean [][] is = new boolean [s.length()][s.length()]; for (int i = 0 ; i < s.length(); i++) { is[i][i] = true ; } int left = 0 ; int right = 0 ; for (int i = s.length() - 2 ; i >= 0 ; i--) { for (int j = i + 1 ; j < s.length(); j++) { is[i][j] = s.charAt(i) == s.charAt(j); if (j > i + 1 ) { is[i][j] = is[i][j] && is[i + 1 ][j - 1 ]; } if (is[i][j] && j - i > right - left) { left = i; right = j; } } } return s.substring(left, right + 1 ); } }
十、单调栈 739.每日温度 给定一个整数数组 temperatures ,表示每天的温度,返回一个数组 answer ,其中 answer[i] 是指对于第 i 天,下一个更高温度出现在几天后。如果气温在这之后都不会升高,请在该位置用 0 来代替。
版本一:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 class Solution { public int [] dailyTemperatures(int [] temperatures) { int len = temperatures.length; int [] res = new int [len]; Deque<Integer> stack = new LinkedList <>(); for (int i = 0 ; i < len; i++){ while (!stack.isEmpty() && temperatures[i] > temperatures[stack.peek()]){ res[stack.peek()] = i - stack.peek(); stack.pop(); } stack.push(i); } return res; } }
版本二:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 class Solution { public int [] dailyTemperatures(int [] temperatures) { int len = temperatures.length; int [] res = new int [len]; Deque<Integer> stack = new LinkedList <>(); stack.push(0 ); for (int i = 0 ; i < len; i++){ if (temperatures[i] <= temperatures[stack.peek()]){ stack.push(i); }else { while (!stack.isEmpty() && temperatures[i] > temperatures[stack.peek()]){ res[stack.peek()] = i - stack.peek(); stack.pop(); } stack.push(i); } } return res; } }
496.下一个更大元素-I nums1 中数字 x 的 下一个更大元素 是指 x 在 nums2 中对应位置 右侧 的 第一个 比 x 大的元素。给你两个 没有重复元素 的数组 nums1 和 nums2 ,下标从 0 开始计数,其中nums1 是 nums2 的子集。
对于每个 0 <= i < nums1.length ,找出满足 nums1[i] == nums2[j] 的下标 j ,并且在 nums2 确定 nums2[j] 的 下一个更大元素 。如果不存在下一个更大元素,那么本次查询的答案是 -1 。
返回一个长度为 nums1.length 的数组 ans 作为答案,满足 ans[i] 是如上所述的 下一个更大元素 。
版本一:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 class Solution { public int [] nextGreaterElement(int [] nums1, int [] nums2) { Stack<Integer> stack = new Stack <>(); int [] res = new int [nums1.length]; Arrays.fill(res, - 1 ); HashMap<Integer, Integer> map = new HashMap <>(); for (int i = 0 ; i < nums1.length; i++){ map.put(nums1[i], i); } stack.add(0 ); for (int i = 1 ; i < nums2.length; i++){ if (nums2[i] <= nums2[stack.peek()]){ stack.add(i); }else { while (!stack.isEmpty() && nums2[stack.peek()] < nums2[i]){ if (map.containsKey(nums2[stack.peek()])){ Integer index = map.get(nums2[stack.peek()]); res[index] = nums2[i]; } stack.pop(); } stack.add(i); } } return res; } }
版本二:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 class Solution { public int [] nextGreaterElement(int [] nums1, int [] nums2) { HashMap<Integer, Integer> map = new HashMap <>(); for (int i = 0 ; i < nums1.length; i++){ map.put(nums1[i], i); } int [] res = new int [nums1.length]; Stack<Integer> stack = new Stack <>(); Arrays.fill(res, -1 ); for (int i = 0 ; i < nums2.length; i++){ while (!stack.isEmpty() && nums2[i] > nums2[stack.peek()]){ int pre = nums2[stack.pop()]; if (map.containsKey(pre)){ res[map.get(pre)] = nums2[i]; } } stack.push(i); } return res; } }
503.下一个更大元素-II 给定一个循环数组 nums ( nums[nums.length - 1] 的下一个元素是 nums[0] ),返回 nums 中每个元素的 下一个更大元素 x 的 下一个更大的元素 是按数组遍历顺序,这个数字之后的第一个比它更大的数,这意味着你应该循环地搜索它的下一个更大的数。如果不存在,则输出 -1 。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 class Solution { public int [] nextGreaterElements(int [] nums) { if (nums == null || nums.length <= 1 ){ return new int []{-1 }; } int len = nums.length; int [] res = new int [len]; Arrays.fill(res, -1 ); Stack<Integer> stack = new Stack <>(); for (int i = 0 ; i < 2 * len; i++){ while (!stack.isEmpty() && nums[i % len] > nums[stack.peek()]){ res[stack.peek()] = nums[i % len]; stack.pop(); } stack.push(i % len); } return res; } }
42.接雨水 给定 n 个非负整数表示每个宽度为 1 的柱子的高度图,计算按此排列的柱子,下雨之后能接多少雨水。
解法一:双指针法
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 class Solution { public int trap (int [] height) { int sum = 0 ; int len = height.length; for (int i = 0 ; i < len; i++){ if (i == 0 || i == len - 1 ){ continue ; } int rightHeight = height[i]; int leftHeight = height[i]; for (int r = i + 1 ; r < len; r++){ if (height[r] > rightHeight){ rightHeight = height[r]; } } for (int l = i - 1 ; l >= 0 ; l--){ if (height[l] > leftHeight){ leftHeight = height[l]; } } int h = Math.min(leftHeight, rightHeight) - height[i]; if (h > 0 ){ sum += h; } } return sum; } }
解法二:动态规划
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 class Solution { public int trap (int [] height) { int len = height.length; if (len <= 2 ){ return 0 ; } int [] maxLeft = new int [len]; int [] maxRight = new int [len]; maxLeft[0 ] = height[0 ]; for (int i = 1 ; i < len; i++){ maxLeft[i] = Math.max(height[i], maxLeft[i - 1 ]); } maxRight[len - 1 ] = height[len - 1 ]; for (int i = len - 2 ; i >= 0 ; i--){ maxRight[i] = Math.max(maxRight[i + 1 ], height[i]); } int sum = 0 ; for (int i = 0 ; i < len; i++){ int count = Math.min(maxLeft[i], maxRight[i]) - height[i]; if (count > 0 ){ sum += count; } } return sum; } }
解法三:单调栈
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 class Solution { public int trap (int [] height) { int len = height.length; if (len < 2 ){ return 0 ; } Stack<Integer> stack = new Stack <>(); stack.push(0 ); int sum = 0 ; for (int i = 1 ; i < len; i++){ int stackTop = stack.peek(); if (height[i] < height[stackTop]){ stack.push(i); }else if (height[i] == height[stackTop]){ stack.pop(); stack.push(i); }else { int heightAtIndex = height[i]; while (!stack.isEmpty() && (heightAtIndex > height[stackTop])){ int mid = stack.pop(); if (!stack.isEmpty()){ int left = stack.peek(); int h = Math.min(height[left], height[i]) - height[mid]; int w = i - left - 1 ; int hold = h * w; if (hold > 0 ){ sum += hold; } stackTop = stack.peek(); } } stack.push(i); } } return sum; } }
84.柱状图中最大的矩形 给定 n 个非负整数,用来表示柱状图中各个柱子的高度。每个柱子彼此相邻,且宽度为 1 。求在该柱状图中,能够勾勒出来的矩形的最大面积。
解法一:双指针法
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 class Solution { public int largestRectangleArea (int [] heights) { int len = heights.length; int [] minLeftIndex = new int [len]; int [] maxRightIndex = new int [len]; minLeftIndex[0 ] = -1 ; for (int i = 1 ; i < len; i++){ int t = i - 1 ; while (t >= 0 && heights[t] >= heights[i]){ t = minLeftIndex[t]; } minLeftIndex[i] = t; } maxRightIndex[len - 1 ] = len; for (int i = len - 2 ; i >= 0 ; i--){ int t = i + 1 ; while (t < len && heights[t] >= heights[i]){ t = maxRightIndex[t]; } maxRightIndex[i] = t; } int result = 0 ; for (int i = 0 ; i < len; i++){ int sum = heights[i] * (maxRightIndex[i] - minLeftIndex[i] - 1 ); result = Math.max(result, sum); } return result; } }
解法二:单调栈
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 class Solution { public int largestRectangleArea (int [] heights) { Stack<Integer> stack = new Stack <>(); int [] newHeights = new int [heights.length + 2 ]; newHeights[0 ] = 0 ; newHeights[newHeights.length - 1 ] = 0 ; for (int i = 0 ; i < heights.length; i++){ newHeights[i + 1 ] = heights[i]; } heights = newHeights; stack.push(0 ); int result = 0 ; for (int i = 1 ; i < heights.length; i++){ if (heights[i] > heights[stack.peek()]){ stack.push(i); }else if (heights[i] == heights[stack.peek()]){ stack.pop(); stack.push(i); }else { while (heights[i] < heights[stack.peek()]){ int mid = stack.peek(); stack.pop(); int left = stack.peek(); int right = i; int w = right - left - 1 ; int h = heights[mid]; result = Math.max(result, w * h); } stack.push(i); } } return result; } }